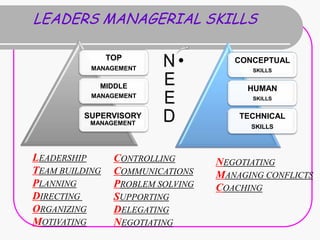
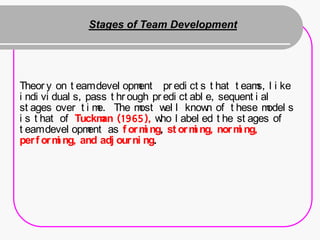
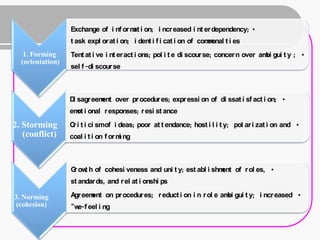
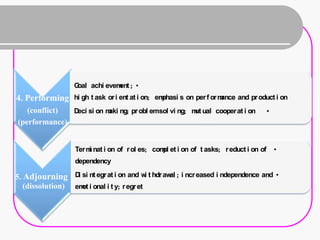
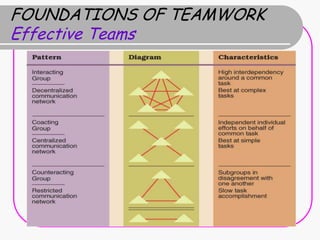
Teamwork is essential for success. A team is a small group of people with complementary skills focused on a common purpose. High performing teams have clear goals, effective structures, competent members, unified commitment, collaborative environments, and standards of excellence. Regular meetings are important but can become unproductive if people are late, topics stray, candor is lacking, or decisions are not implemented. Foundations of effective teamwork include communication networks and decision-making processes that allow for creativity and critical thinking without "groupthink."