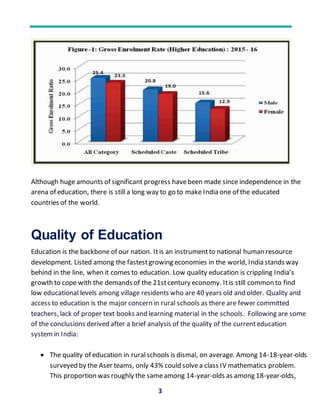
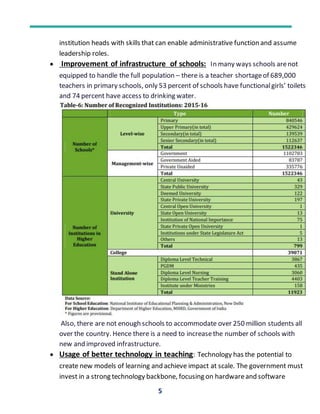
The document discusses the current state of education in India and ways to improve its quality. It notes that while access to education has increased, the quality remains low. Rural school education especially suffers from poor infrastructure, untrained teachers, and low learning outcomes. Several reforms are suggested such as improving teacher training, increasing vocational education, using technology in teaching, and rewarding creativity over rote learning. Overall, the education system needs widespread reforms to enhance quality and make students employable.