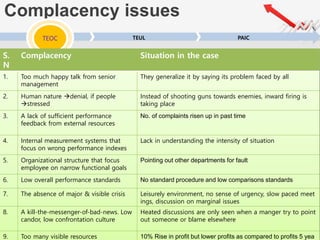
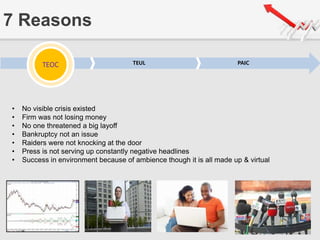
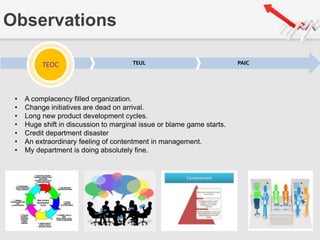
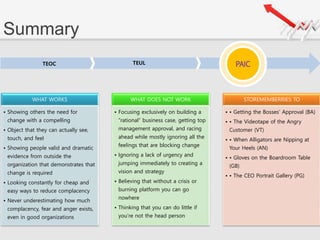
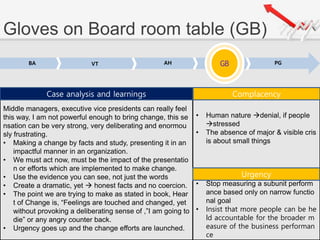
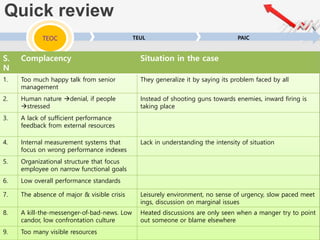
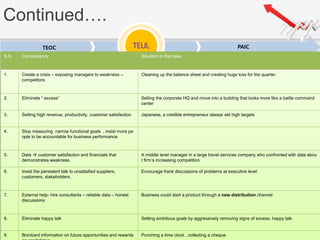
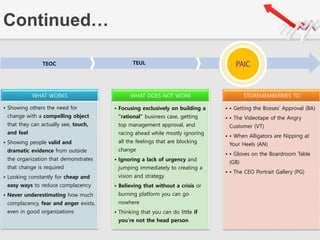
The document outlines a presentation by Team 4 on leadership and change management, focusing on the concepts of complacency and urgency in organizations. It emphasizes the importance of creating a sense of urgency for change, identifying complacency issues, and providing practical strategies for fostering organizational transformation. The presentation aims to address senior management's quick understanding, stakeholder needs, and summarization of key topics.