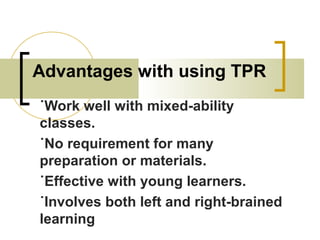
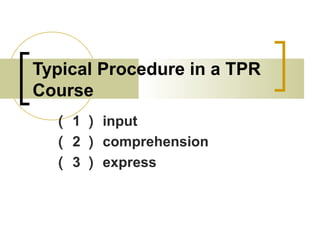
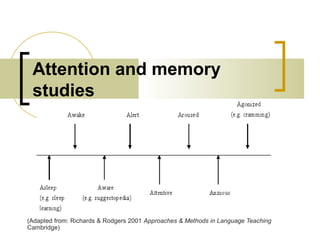
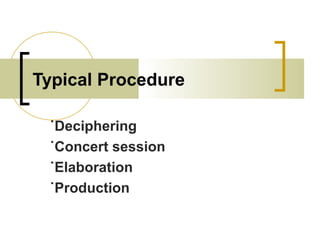
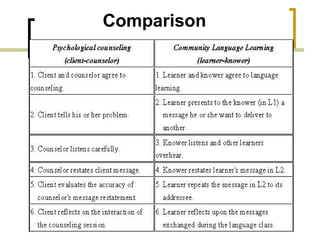
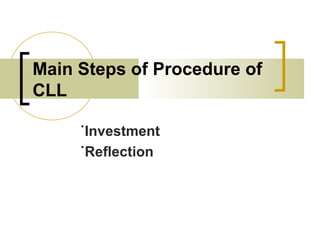
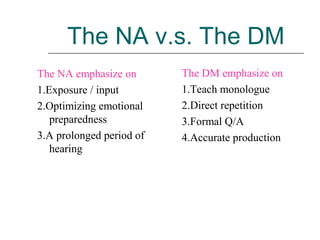
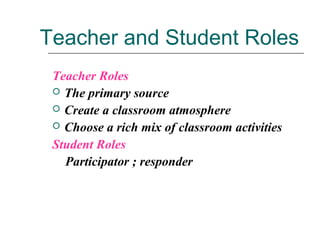
The document discusses several language teaching methods:
- The Grammar-Translation Method focuses on reading, writing, and translating skills. It emphasizes grammar rules and accuracy.
- The Direct Method aims to teach language directly without translation. It uses the target language and focuses on oral skills.
- The Audio-Lingual Method is based on behaviorism and drills patterns through repetition. It emphasizes form over meaning.
- The Cognitive Approach sees language learning as problem-solving. It provides systematic grammar instruction and production activities.