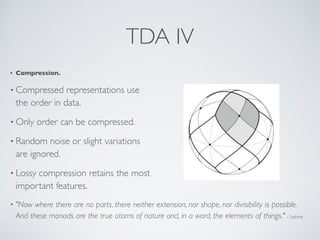
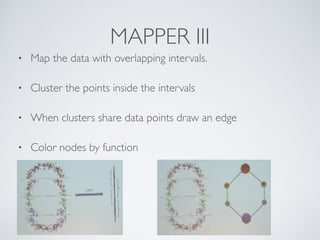
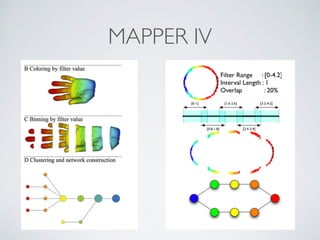
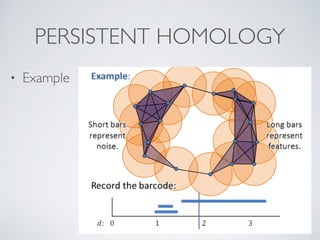
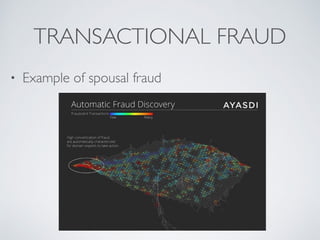
This document provides an overview of topological data analysis (TDA). It discusses how TDA marries 300-year old mathematics with modern data analysis to capture the shape of data. TDA techniques like Mapper are invariant to transformations of scale, position or pose, can compress large datasets while retaining important features, and function well with noisy or incomplete data. Mapper works by mapping data with overlapping intervals, clustering points within each interval, and connecting clusters that share data points to represent the topological structure. The document provides several examples of applying TDA and Mapper to problems in computer vision, healthcare, finance, and model interpretation.