This document provides an overview of topological data analysis and persistent homology. It discusses how topological data analysis uses techniques from fields like statistics, computer science, and algebraic topology to infer robust features about complex datasets. Persistent homology in particular analyzes the homology of filtrations to study topological features across different scales. The document also describes implementations of topological data analysis techniques and applications to areas such as brain networks, periodic systems, and cosmological data analysis.

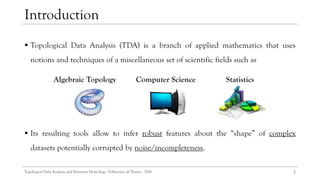
![TDA aims at inferring statistically significative information on the shape of the data.
3
The Shape of Data
[1]
Topological Data Analysis and Persistent Homology - Politecnico di Torino - 2018](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/thesispresentation-181228125022/85/Topological-Data-Analysis-and-Persistent-Homology-3-320.jpg)
![[15] [16]
4
Finding Loops and Voids in Universe
Topological Data Analysis and Persistent Homology - Politecnico di Torino - 2018](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/thesispresentation-181228125022/85/Topological-Data-Analysis-and-Persistent-Homology-4-320.jpg)
![Periodic behaviors Attractors
[7] [8]
5
Periodic Systems
Topological Data Analysis and Persistent Homology - Politecnico di Torino - 2018](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/thesispresentation-181228125022/85/Topological-Data-Analysis-and-Persistent-Homology-5-320.jpg)
![6
Effective Brain Networks Analysis
Topological Data Analysis and Persistent Homology - Politecnico di Torino - 2018
[17][5]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/thesispresentation-181228125022/85/Topological-Data-Analysis-and-Persistent-Homology-6-320.jpg)
![ This thesis focuses on Persistent Homology (PH) technique.
The purposes are:
7
Objectives 1/3
1) to provide a satisfying explanation of TDA and PH fundamentals
[2]
Topological Data Analysis and Persistent Homology - Politecnico di Torino - 2018](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/thesispresentation-181228125022/85/Topological-Data-Analysis-and-Persistent-Homology-7-320.jpg)
![8
Objectives 2/3
2) to analyze the robustness and the reliability of the inferred features
[3]
Topological Data Analysis and Persistent Homology - Politecnico di Torino - 2018](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/thesispresentation-181228125022/85/Topological-Data-Analysis-and-Persistent-Homology-8-320.jpg)
![ The input is a finite set of elements coming with a notion of distance
between them.
The elements are mapped into a point cloud (PCD).
PCD is completed by building "continuous" shape, a complex, on it.
10
From PCD to Complex
Topological Data Analysis and Persistent Homology - Politecnico di Torino - 2018
[13]
A
B
C
B
A
C
A
B
C](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/thesispresentation-181228125022/85/Topological-Data-Analysis-and-Persistent-Homology-10-320.jpg)
![ There are many ways to build simplicial complexes from a topological space.
To be a useful, a simplicial complex has to have an homology that approximates the
one of the space we want to study.
11
[18]
Simplicial Complexes
Topological Data Analysis and Persistent Homology - Politecnico di Torino - 2018](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/thesispresentation-181228125022/85/Topological-Data-Analysis-and-Persistent-Homology-11-320.jpg)
![12
Cech and Vietoris–Rips Complexes
Reconstruction Theorem
Nerve Theorem
𝐶 𝛼(X) ⊂ 𝑉2𝛼(X) ⊂ 𝐶2𝛼(X)
Cech complex is difficult to calculate, but it is quite small
and accurate.
[19]
𝐶 𝛼 𝑋 ≔ 𝑝1, … , 𝑝k : 𝑝1, … , 𝑝k ⊂ 𝑋,∩𝑖 𝐵 𝛼 𝑝i ≠ ∅
𝑉𝛼 𝑋 ≔ 𝑝1, … , 𝑝k : 𝑝1, … , 𝑝k ⊂ 𝑋, 𝑚𝑎𝑥 𝑝i,𝑝j∈𝜎
(𝑑(𝑝i, 𝑝j)) ≤ 𝛼
Vietoris–Rips complex is easy to calculate, but it is usually very
big and less accurate.
Topological Data Analysis and Persistent Homology - Politecnico di Torino - 2018](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/thesispresentation-181228125022/85/Topological-Data-Analysis-and-Persistent-Homology-12-320.jpg)
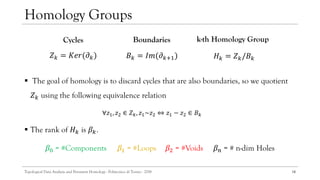
![ The homotopy equivalent items shares the same homology.
Homology groups are a more computable alternative to homotopy ones.
13
Homology
Boundary Operator
𝜎 = [𝑣0, … , 𝑣 𝑘] 𝜕 𝑘 𝜎 =
𝑖=0
𝑛
−1 𝑖
𝑣0,…, ො𝑣𝑖,…, 𝑣 𝑘
Simplex
𝜕 𝑣0, 𝑣1, 𝑣2, 𝑣3 = 𝑣1, 𝑣2, 𝑣3 - 𝑣0, 𝑣2, 𝑣3 + 𝑣0, 𝑣1, 𝑣3 - 𝑣0, 𝑣1, 𝑣2
[8]
Topological Data Analysis and Persistent Homology - Politecnico di Torino - 2018](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/thesispresentation-181228125022/85/Topological-Data-Analysis-and-Persistent-Homology-13-320.jpg)
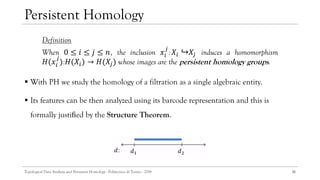
![The sequence of simplicial complexes with its inclusion maps is a filtration.
[20]
15
Filtrations
Which 𝑑 should we choose?
The most persistent features are detected using PH. They are supposed to represent
true characteristics of the underlying space.
Topological Data Analysis and Persistent Homology - Politecnico di Torino - 2018](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/thesispresentation-181228125022/85/Topological-Data-Analysis-and-Persistent-Homology-15-320.jpg)
![17
Persistence Barcode
[21]
Topological Data Analysis and Persistent Homology - Politecnico di Torino - 2018](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/thesispresentation-181228125022/85/Topological-Data-Analysis-and-Persistent-Homology-17-320.jpg)
![18
Persistence Diagram
Persistence Diagram
Given two persistent diagrams 𝐷1 and 𝐷2, the Bottleneck distance between them is
𝑑 𝐵 𝐷1, 𝐷2 = 𝑖𝑛𝑓𝛾 𝑠𝑢𝑝 𝑥∈𝐷1
| 𝑥 − 𝛾 𝑥 |∞ where 𝛾 ranges over all multi-bijections
𝐷1 → 𝐷2 .
[23]
Topological Data Analysis and Persistent Homology - Politecnico di Torino - 2018](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/thesispresentation-181228125022/85/Topological-Data-Analysis-and-Persistent-Homology-18-320.jpg)
![19
Stability Results
Theorem
Let 𝑋 and 𝑌 be two compact metric spaces and let 𝐹𝑖𝑙𝑡(𝑋)
and 𝐹𝑖𝑙𝑡(𝑌) be the Vietoris–Rips filtrations built on top them.
Then
𝑑 𝐵(𝐷(𝐹𝑖𝑙𝑡 𝑋 ), 𝐷(𝐹𝑖𝑙𝑡 𝑌 )) ≤ 2𝑑 𝐺𝐻(𝑋, 𝑌)
Moreover, if 𝑋 and 𝑌 are embedded in the same space then
𝑑 𝐵(𝐷(𝐹𝑖𝑙𝑡 𝑋 ), 𝐷(𝐹𝑖𝑙𝑡 𝑌 )) ≤ 2𝑑 𝐻(𝑋, 𝑌)
[24]
Topological Data Analysis and Persistent Homology - Politecnico di Torino - 2018](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/thesispresentation-181228125022/85/Topological-Data-Analysis-and-Persistent-Homology-19-320.jpg)
![20
Statistical Results
The most persistent features can be detected and separated from topological
noise using statistical methods as the Bootstrap.
Given a persistence diagram 𝑋 with an estimator 𝑋, with look for 𝛿 𝛼 such that
𝑃 𝑑 𝐵 𝑋, 𝑋 ≥ 𝛿 𝛼 ≤α, α∈(0,1)
The confidence set will be 𝑋: 𝑑 𝐵 𝑋, 𝑋 ≥ 𝛿 𝛼
[25]
Topological Data Analysis and Persistent Homology - Politecnico di Torino - 2018](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/thesispresentation-181228125022/85/Topological-Data-Analysis-and-Persistent-Homology-20-320.jpg)
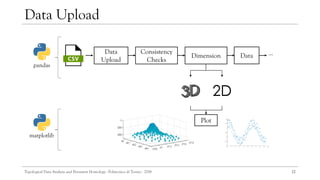
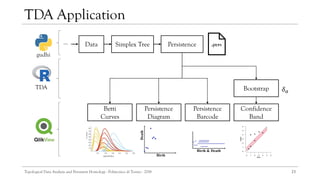
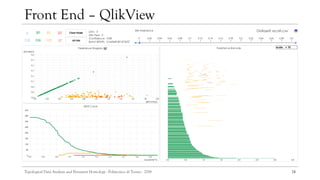
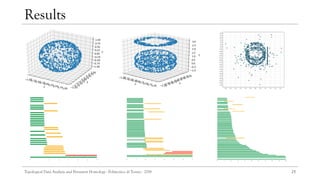
![21
Implementation
[27]
To analyze the topological information of different datasets, a console application
was implemented using GUDHI in Python, TDA in R and QlikView.
GUDHI proposed an efficient tree representation for simplicial complexes, the
simplex tree.
+ +
Topological Data Analysis and Persistent Homology - Politecnico di Torino - 2018](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/thesispresentation-181228125022/85/Topological-Data-Analysis-and-Persistent-Homology-21-320.jpg)

![BIBLIOGRAPHY
[1] G. Carlsson, The Shape of Data conference, Ayasdi Energy Summit, 2014.
[2] R. Ghrist, Three examples of applied and computational homology, 2008.
[3] P.Bubenik, Statistical Topological Data Analysis using Persistence Landscapes, Journal of Machine Learning Research 16, 2015.
[4] M. Alagappan, J. Carlsson, G. Carlsson, T. Ishkanov, A. Lehman, P. Y. Lum, G. Singh, and M. Vejdemo-Johansson, Extracting insights from the shape of complex data using topology,
Scientific Reports v. 3, Article number: 1236, 2013.
[5] R. Carhart-Harris, P. Expert, P. J. Hellyer, D. Nutt, G. Petri, F. Turkheimer and F. Vaccarino, Homological scaffolds of brain functional networks, Journal of The Royal Society Interface,
11(101):20140873, 2014.
[6] M. Lesnick, Studying the Shape of Data Using Topology, Institute for Advanced Study, School of Mathematics, 2013.
[7] P. Chardy, V. David and B. Sautour, Fitting a predator–prey model to zooplankton time-series data in the Gironde estuary (France): Ecological significance of the parameters, Estuarine,
Coastal and Shelf Science, Volume 67, Issue 4, Pages 605-617, 2006.
[8] S. Maletic, M. Rajkovic and Y. Zhao, Persistent topological features of dynamical systems, doi.org/10.1063/1.4949472, 2016.
[9] X. Feng, Y. Tong, G. W. Wei and K. Xia, Topological modeling of biomolecular data, Nanyang Technological University.
[10] B.Cottenceau, N.Delanoue ,L.Jaulin, Guaranteeing the homotopy type of a set defined by non-linear inequalities, DOI: 10.1007/s11155-007-9043-8, 2006.
[11] P. Lambrechts, The Poincaré conjecture and the shape of the universe slides, Wellesley College, 2009.
[12] E.A.Coutsias,S.Martin,A.ThompsonandJ.P.Watson,Topologyofcyclo-octaneenergylandscape, doi: 10.1063/1.3445267, 2010.
[13] G. Carlsson, T. Ishkhanov , D. L. Ringac, F. Memoli, G. Sapiro and G. Singh, Topological analysis of population activity in visual cortex, Journal of vision 8 8 (2008): 11.1-18.
[14] A. Hatcher, Algebraic Topology, Cambridge University Press, ISBN 0-521-79540-0, 2002.
[15] E.G.P. P. Bos, M. Caroli, R. van de Weygaert, H. Edelsbrunner, B. Eldering, M. van Engelen, J. Feldbrugge, E. ten Have, W. A. Hellwing, J. Hidding, B. J. T. Jones, N. Kruithof, C. Park,
P. Pranav, M.Teillaud and G.Vegter, Alpha,Betti and the Megaparsec Universe: on the Topology of the Cosmic Web, arXiv:1306.3640v1 [astro-ph.CO], 2013.
[16] J Cisewski-Kehea, S.B.Greenb, D.Nagai and X.Xu,Finding cosmic voids and filament loops using topological data analysis, arXiv:1811.08450v1 [astro-ph.CO], 2018.
[17] H. Liang and H. Wang, Structure-Function Network Mapping and Its Assessment via Persistent Homology, doi:10.1371/journal.pcbi.1005325, 2017.
[18] K. G. Wang, The Basic Theory of Presisten Homology, 2012.
[19] F. Chazal and B. Michel, An introduction to Topological Data Analysis: fundamental and practical aspects for data scientists, arXiv:1710.04019v1 [math.ST], 2017.
[20] M. Wright, Introduction to Persistent Homology video on M. Wright channel https : //www.youtube.com/watch?v = 2PSqWBIrn90 consulted on 10/10/2018, 2016.
[21] R. Ghrist, Barcodes: The Persistent Topology Of Data, Bull. Amer. Math. Soc. 45 (2008), 61-75 , Doi: https://doi.org/10.1090/S0273-0979-07-01191-3, 2007.
[22] G. W. Wei and K. Xia, Persistent homology analysis of protein structure, flexibility and folding, arXiv:1412.2779v1 [q-bio.BM], 2014.
[23] The NIPS 2012 workshop on Algebraic Topology and Machine Learning.
[24] K.Fukumizu,Y.HiraokaandG.Kusano,PersistenceweightedGaussiankernelfortopologicaldata analysis, 2016.
[25] J.Cisewski-Kehea,S.B.Greenb,D.NagaiandX.Xu,Findingcosmicvoidsandfilamentloopsusing topological data analysis, arXiv:1811.08450v1 [astro-ph.CO], 2018.
[26] H. A. Harrington, M. A. Porter and B. J. Stolz, Persistent homology of time-dependent functional networks constructed from coupled time series, DOI:10.1063/1.4978997, 2017.
[27] J. Boissonnat, C. Maria, The Simplex Tree: An Efficient Data Structure for General Simplicial Complexes, [Research Report] RR-7993, pp.20. <hal-00707901v1>, 2012.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/thesispresentation-181228125022/85/Topological-Data-Analysis-and-Persistent-Homology-28-320.jpg)