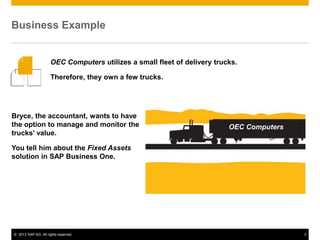
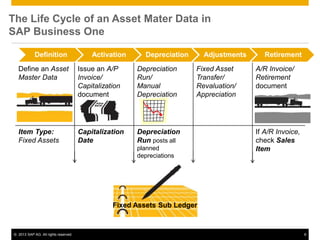
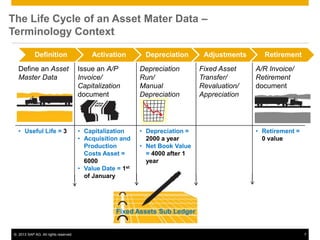
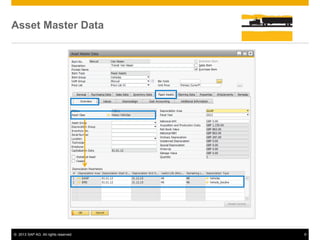
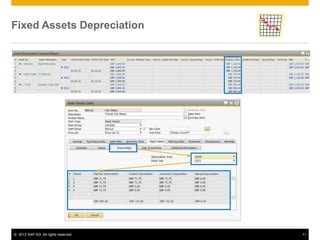
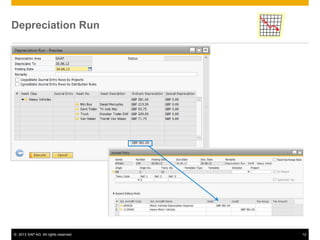
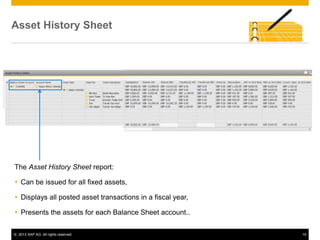
The document provides an overview of managing fixed assets in SAP Business One, including key processes such as asset master data definition, depreciation, capitalizing assets, and retirement procedures. It emphasizes the importance of asset classes, depreciation methods, and the lifecycle of fixed assets within the software. The document also outlines how to utilize the fixed assets solution to monitor and manage asset values effectively.