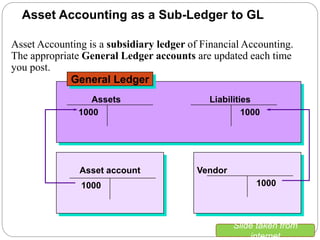
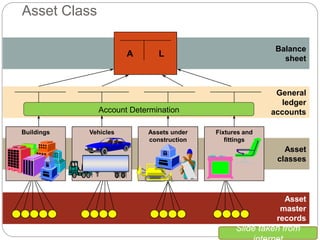
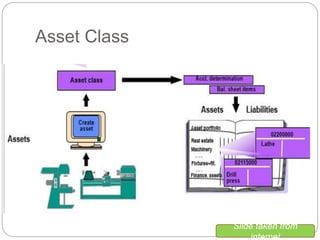
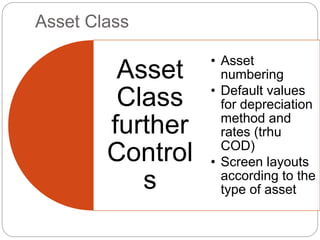
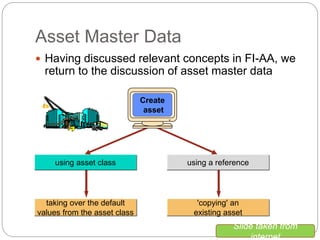
1) Fixed asset accounting in SAP involves setting up asset master records, which are linked to asset classes. Asset classes determine default values and account determinations.
2) Account determinations link assets to general ledger accounts for costs, depreciation, accumulated depreciation, and disposals.
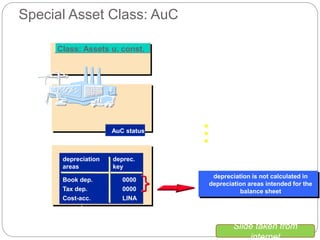
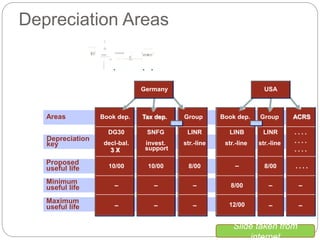
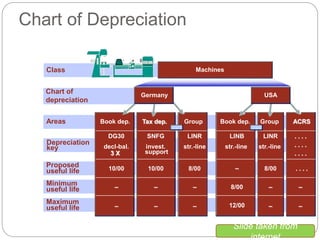
3) Depreciation keys define depreciation types and methods, while depreciation areas allow parallel valuation of assets for different purposes like book and tax.