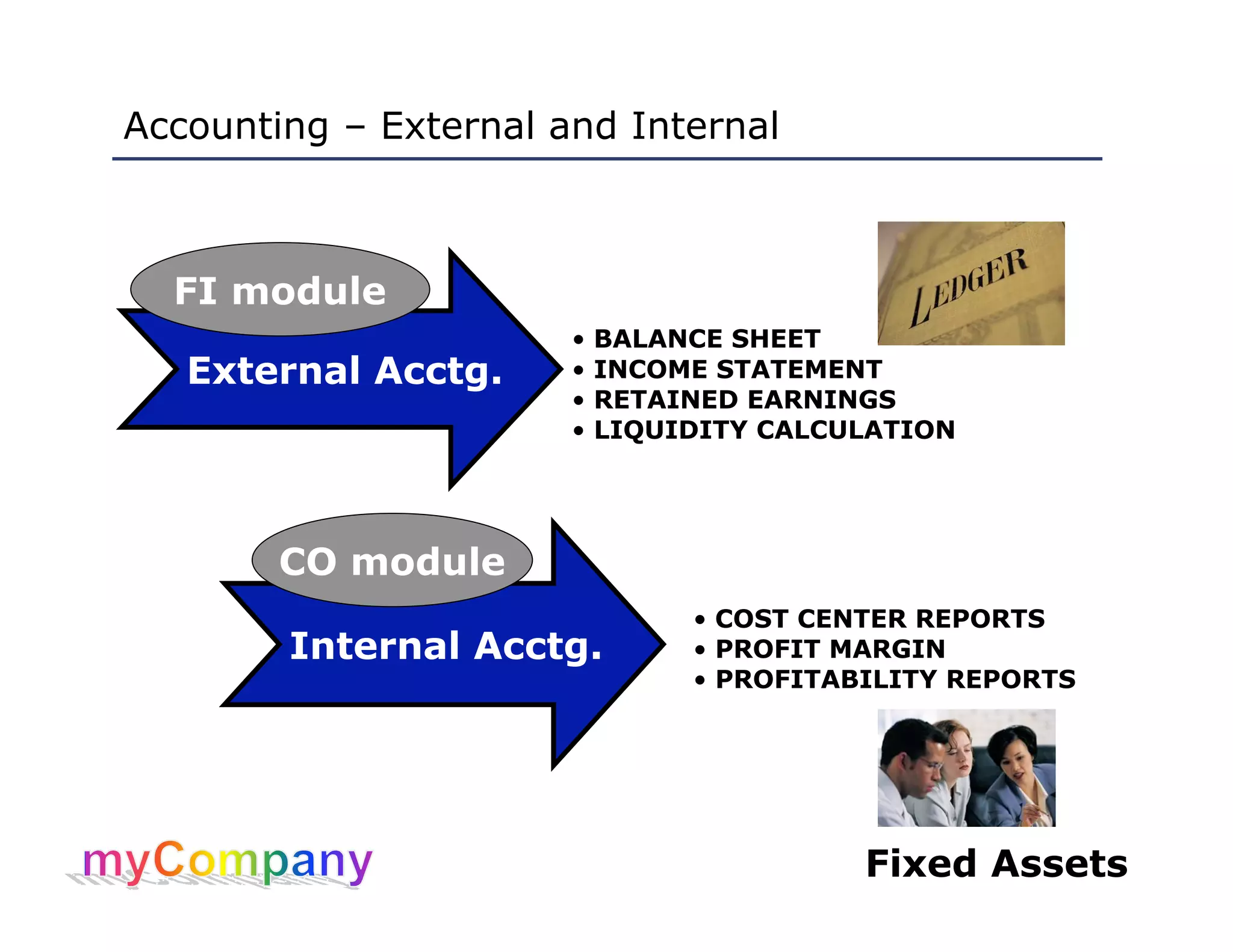
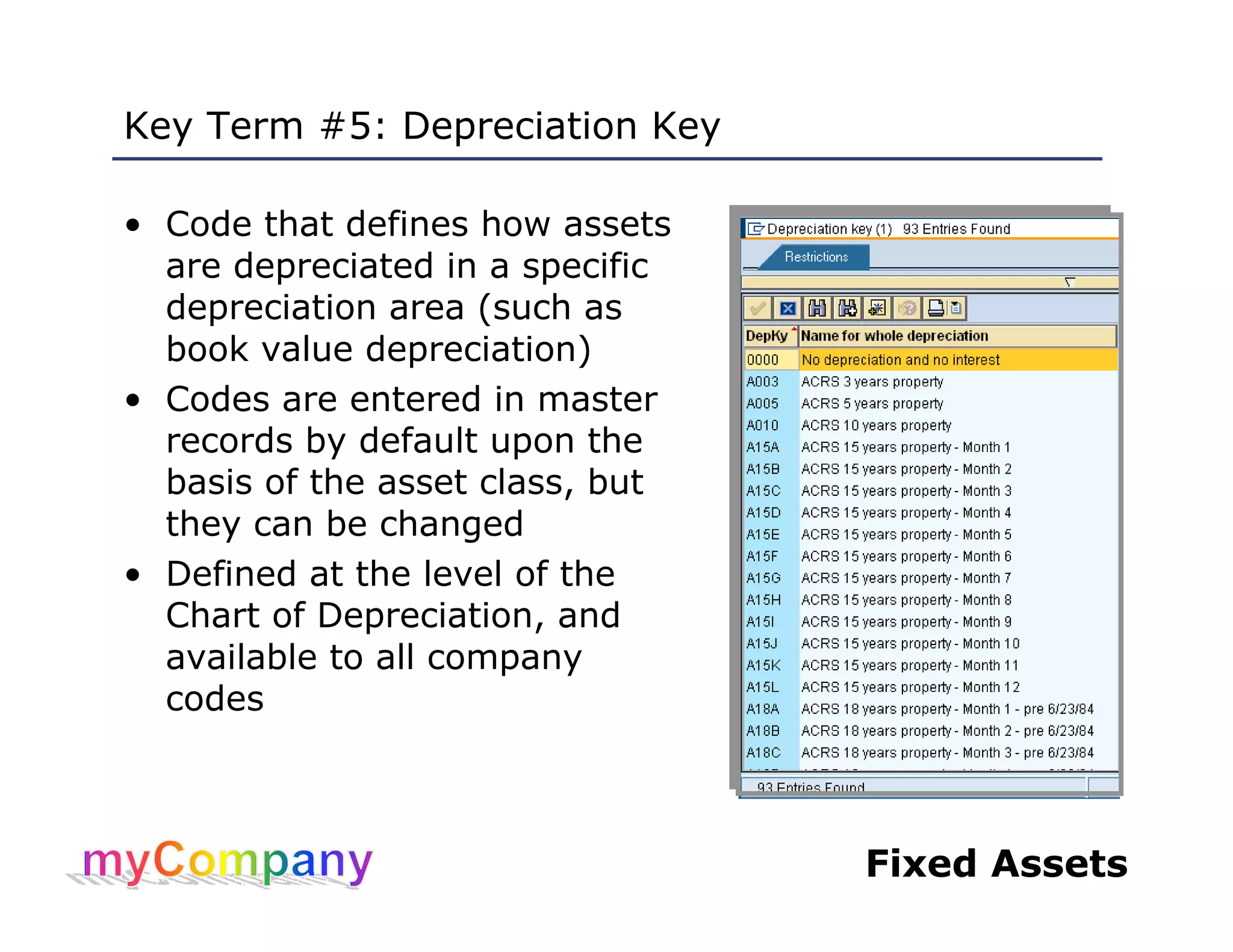
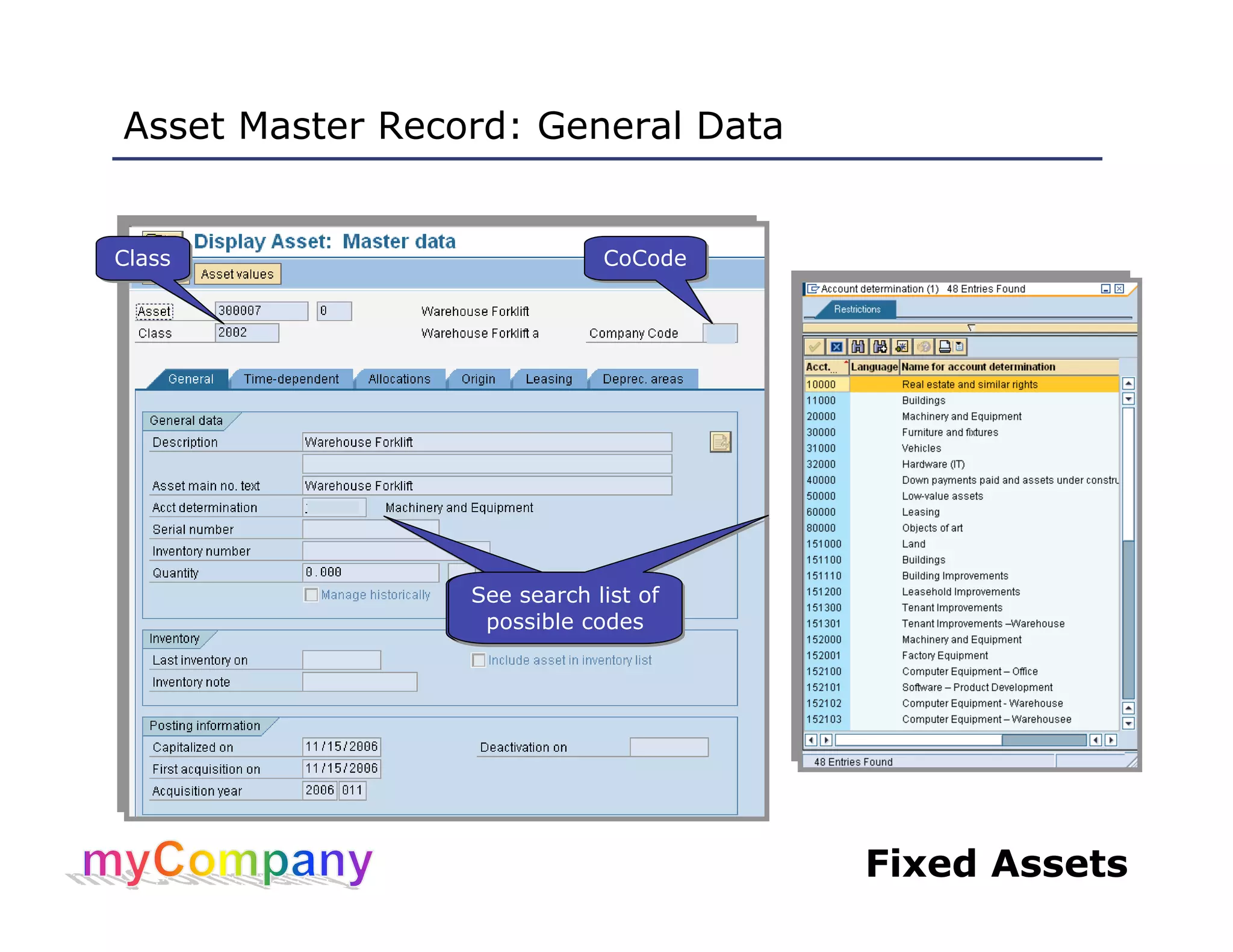
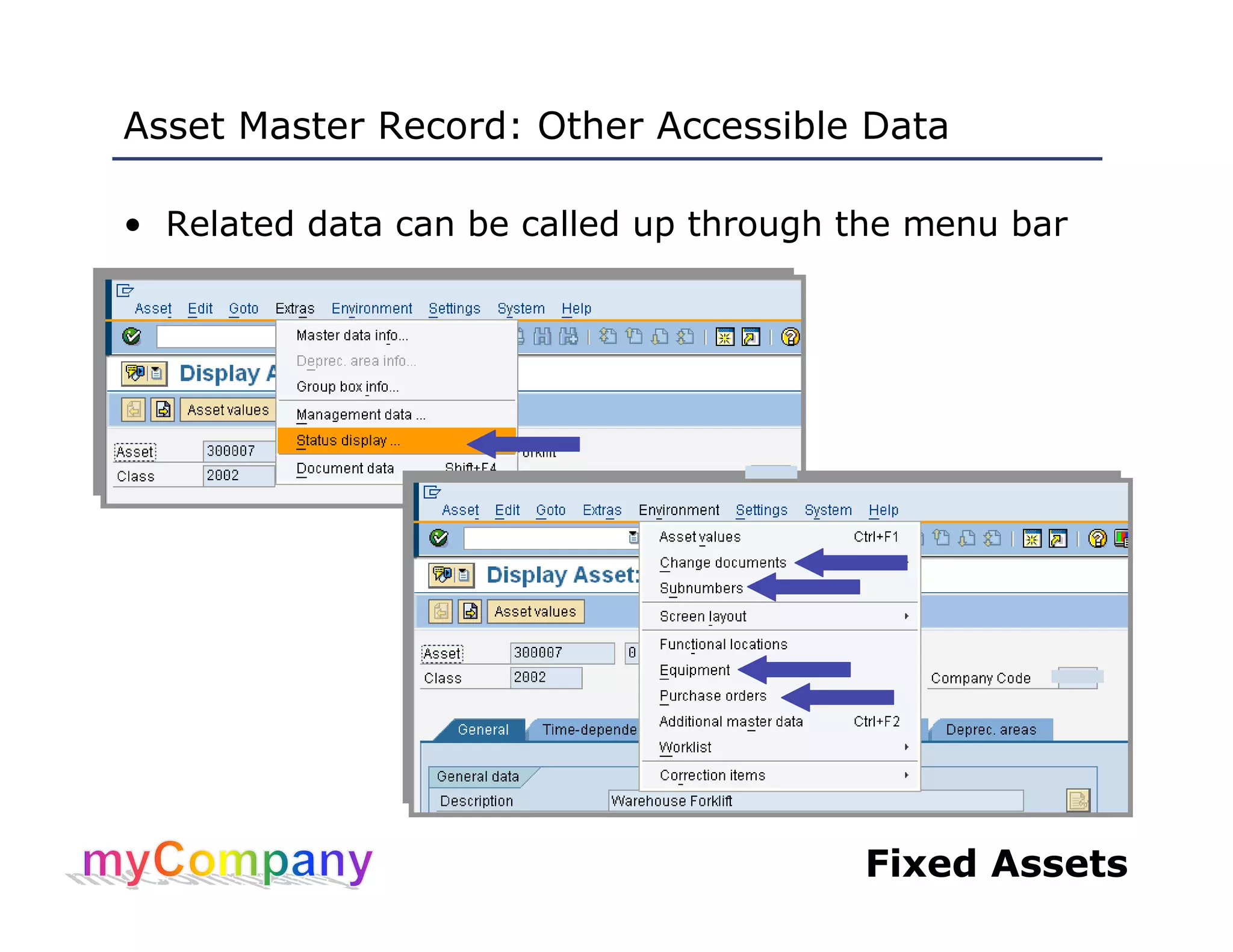
This document provides training materials for a course on SAP Fixed Assets. The course contains 5 units that cover: 1) Overview of asset management in SAP FI, 2) Working with asset master records, 3) Asset acquisition, cost and transfers, 4) Asset retirement, depreciation and valuation, and 5) Asset reporting. The training teaches students how to create, modify, and view asset master records, post acquisitions and costs, execute depreciation processes, and generate asset reports.