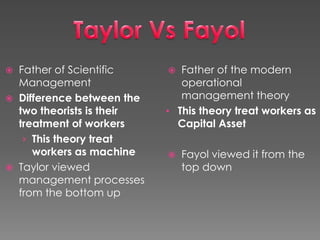
The document discusses the management theories of Taylorism and Fayolism. It provides examples of how Frederick Taylor's scientific management principles were applied through experiments and case studies. It also explains Henri Fayol's 14 principles of management. The key differences between Taylor and Fayol are discussed, with Taylor focusing on workers as machines and Fayol treating workers as capital assets. An example is given of how Tata Consultancy Services applied Fayol's principles to become a leading technology company.