Community acquired pneumonia (CAP) is an acute lung infection that develops outside of a hospital setting. It is caused by bacteria, viruses, fungi or protozoa. The most common bacteria that cause CAP include Streptococcus pneumoniae, Haemophilus influenzae, Staphylococcus aureus, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, and Moraxella catarrhalis. Risk factors for CAP include chronic health conditions, smoking, HIV, and medications that suppress the immune system. Symptoms typically include fever, cough, shortness of breath, and chest pain. Diagnosis involves chest x-ray and testing sputum or blood samples. Complications can include respiratory failure, organ damage,








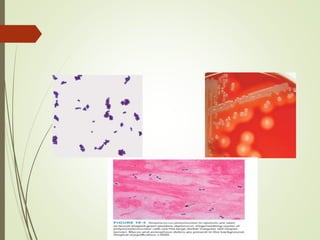
![Streptococus pneumonia
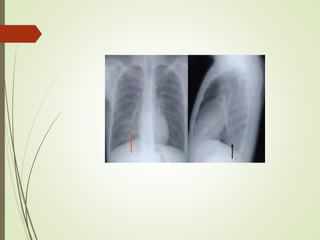
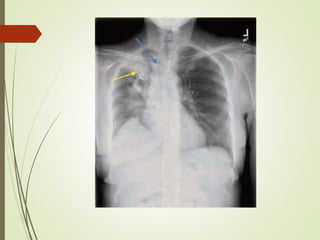
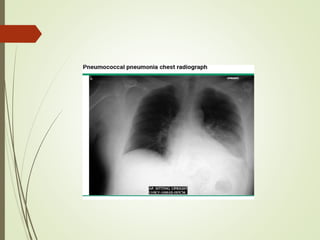
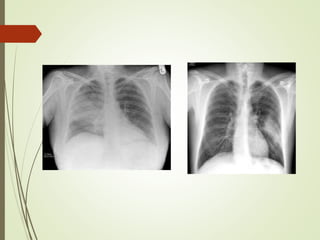
Streptococcus most common organisum causing CAP
increased frequency inthree subsets of patients: (1) those
with underlying chronicdiseases such as CHF, COPD, or
diabetes;
(2) those with either congenital or acquired immunoglobulin
defects (e.g.,with the acquired immune deficiency syndrome
[AIDS]);and
(3) those with decreased or absent splenic function(e.g.,
sickle cell disease or after splenectomy).](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/communityacquiredpneumonia-180113170030/85/Community-acquired-pneumonia-11-320.jpg)