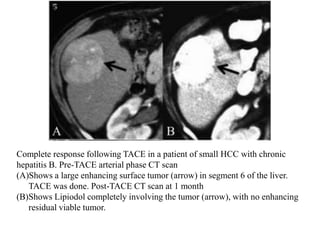
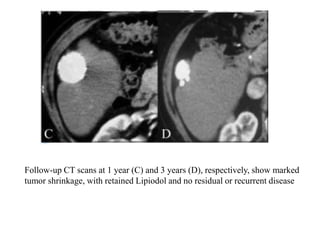
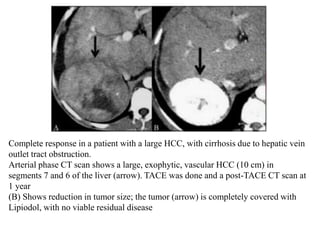
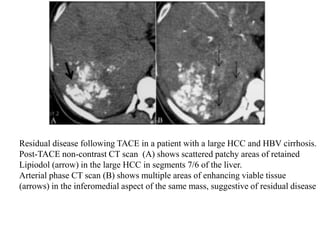
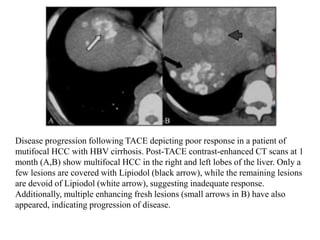
Transarterial chemoembolization (TACE) involves delivering chemotherapy drugs and embolic agents directly into liver cancers via catheters in the hepatic artery. TACE is generally used to treat hepatocellular carcinoma that cannot be surgically removed. During the procedure, a catheter is placed into the hepatic artery supplying the tumor and chemotherapy mixed with iodinated oil is injected, followed by embolization of the artery with gelatin sponges. TACE can reduce tumor size and symptoms but common side effects include abdominal pain and nausea. Response to treatment is evaluated after 3-4 weeks using imaging to assess the extent of tumor coverage by the oil and residual enhancement.