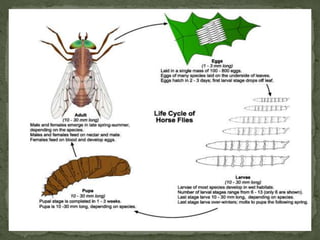
This document discusses the classification, life cycle, morphology, and medical importance of Tabanid flies. It begins by classifying Tabanids in the animal kingdom and notes there are over 4,300 species worldwide. It then describes the fly's life cycle from egg laying near water, to larvae feeding in water/mud, to pupae and finally adult flies. Key details about identifying species based on wing patterns and differentiating males and females are provided. The document concludes by explaining Tabanids can transmit diseases like loa loa filariasis and tularemia, and their bites cause blood loss in animals, which in severe cases of hundreds of ml per day.