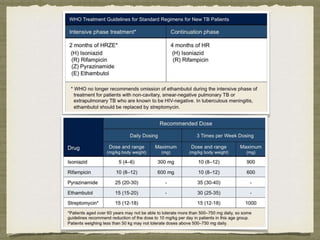
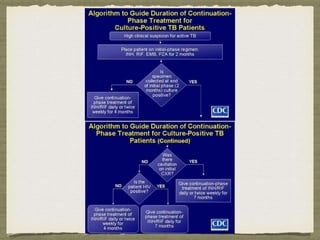
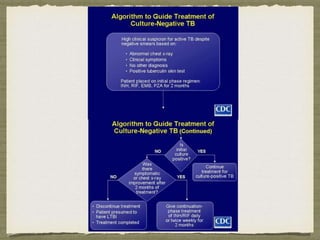
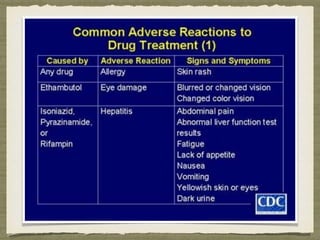
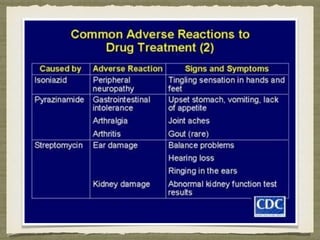
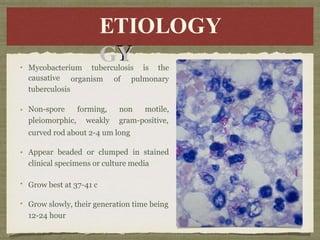
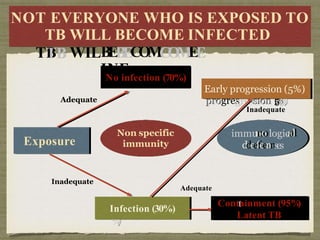
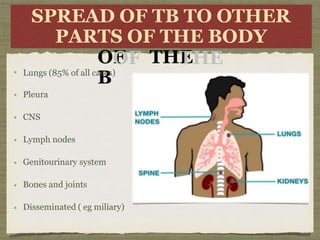
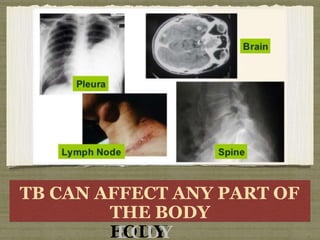
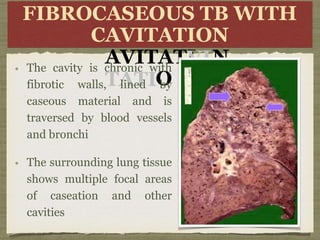
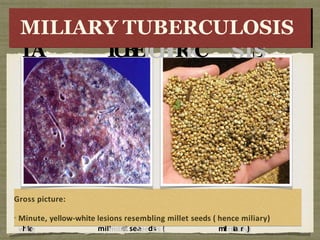
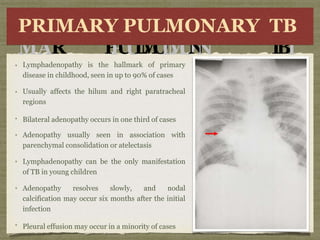
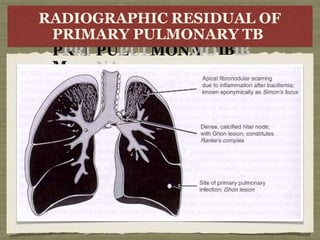
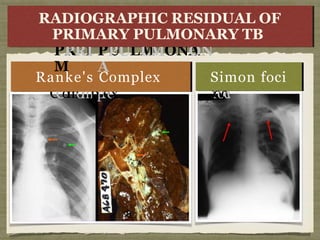
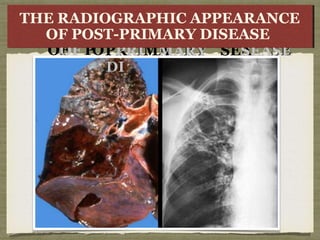
TB is an ancient disease that has infected humans for thousands of years. It is caused by the bacterium Mycobacterium tuberculosis, which is spread through airborne droplets when people with active pulmonary TB cough, sneeze or spit. Not everyone exposed to TB becomes infected, and only a small percentage of those infected will develop active disease, depending on factors like their immune status. Active TB most commonly affects the lungs but can spread to other organs. Diagnosis involves chest x-rays, sputum smears and cultures. Treatment requires multiple antibiotics taken for at least 6 months to cure the infection and prevent transmission.






















![MTB antigens in association with the class II major histocompatibility
complex are presented to naive CD4+ T cells, heralding the onset of
specific anti-TB cell-mediated immunity (T helper subset 1 [Th1] cell
immunity).
(a(a))seseccrerettiioonn ooff
IILL-2-2
t
th
he
ese
se ce
celllls
s t
to
o k
kiillll
o
o
(b(b))seseccrerettiioonn ooff
iinntteerr
a
allllo
ow
wiin
ng
g t
th
he
em
m t
to
o
kiki
susuppppoortrtss cytcytoottooxxiicc
T-l-lyympmphhooc
t
t
h
h
e
e
r
rcecellllss a
a
l
l
r
e
r
e
a
a
d
d
y
yi
i
n
n
f
f
e
e
c
c
t
t
e
e
d
d
w
w
i
i
t
t
h
ffeeroronn-γ-γ(I(IFN-γ)γ)
p
pr
ri
im
me
es
s u
un
niin
n llll t
th
he
e
iinnttraracecelllluullaarrp
p
a
a
t
t
h
h
o
o
g
g
e
e
n
n
eeff
ytee ffuunnctctiioonn,,a
a
l
l
l
l
o
o
w
w
i
i
n
n
g
h MT
MTB
B d
diire
rect
ctlly
y
f
f
e
e
c
c
t
t
e
e
d
d
m
m
a
a
c
r
o
c
r
o
p
p
h
h
a
a
g
g
e
e
s
,
s
ffiicicieennttlly.y.
Anti-TB CD4+ T cells coordinate the specific immune response by two
routes:
(a) secretion of IL-2 supports cytotoxic T-lymphocyte function, allowin g
these cells to kill other cells already infected with MTB directly
(b) secretion of interferon-γ (IFN-γ) primes uninfected macrophages,,
allowing them to kill the intracellular pathogen efficiently.
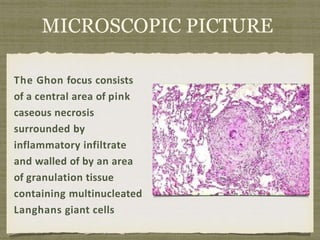
The onset of the cytotoxic T-lymphocyte response several weeks after
infection coincides with the development of caseous necrosis at the site of
primary infection and the development of delayed-type hypersensitivity](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/t-140513165753-phpapp02-230519073535-c66a1f9c/85/t-140513165753-phpapp02-pptx-34-320.jpg)


















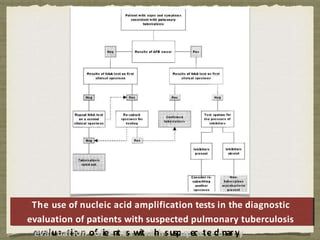
![Even with the use of broth-based culture systems, confirming the
presence of MTB from the time of specimen collection takes at least a
week and more often 2 to 3 weeks.
Methods to detect the presence of TB directly from clinical specimens
more rapidly have been a significant advance in the treatment of TB.
Current direct methods are based on nucleic acid amplification
techniques, and two different tests are commercially available: a
transcription-mediated amplification method (Amplified
Mycobacterium tuberculosis Direct [MTD] Test) and a polymerase
chain reaction–based assay (Amplicor; Roche Diagnostic Systems)
DIRECT AMPLIFICATION
TECHNIQUE](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/t-140513165753-phpapp02-230519073535-c66a1f9c/85/t-140513165753-phpapp02-pptx-69-320.jpg)