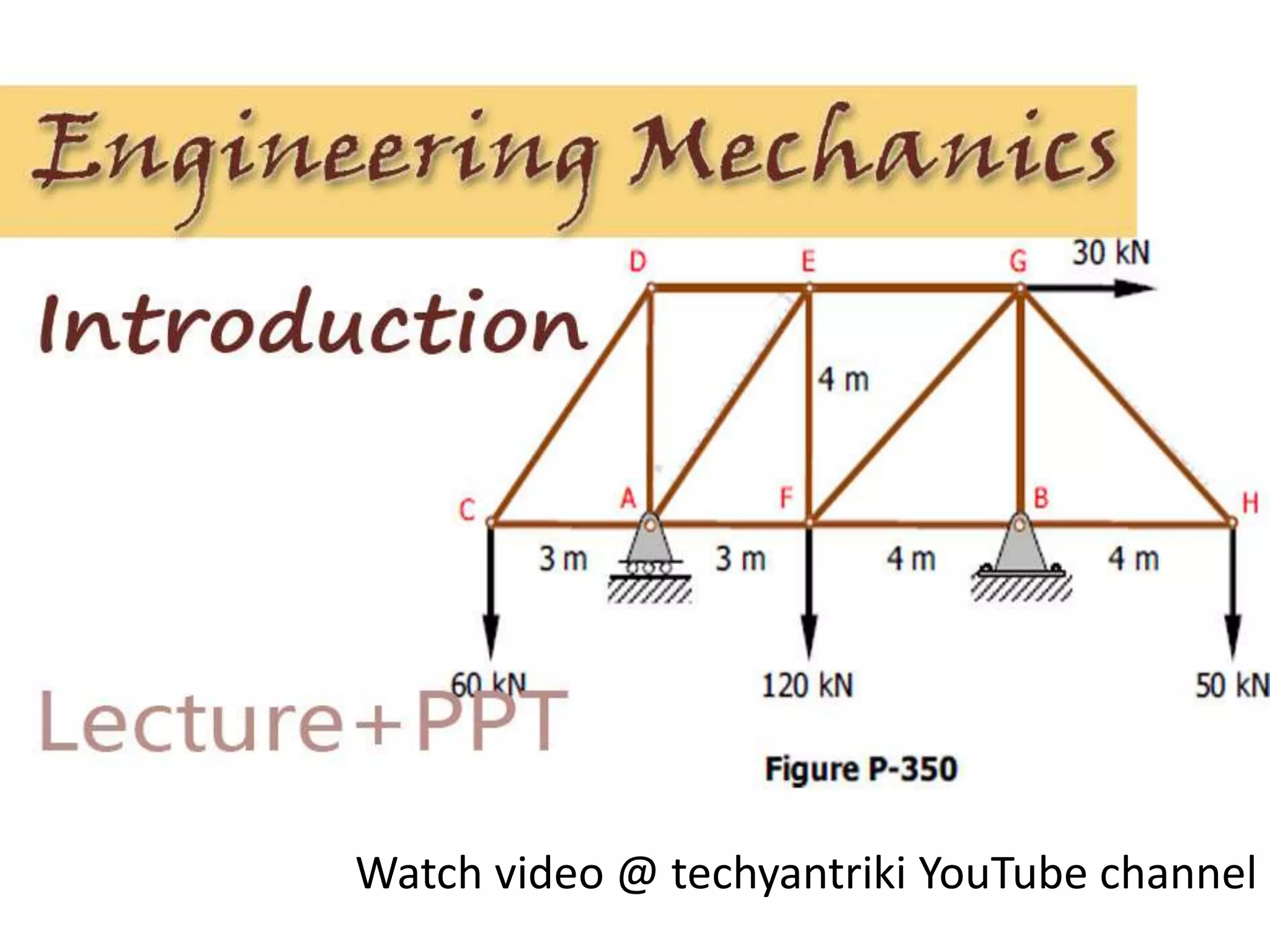
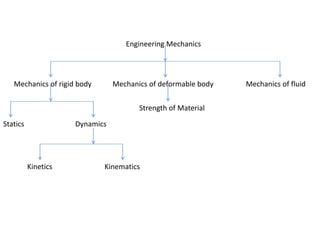
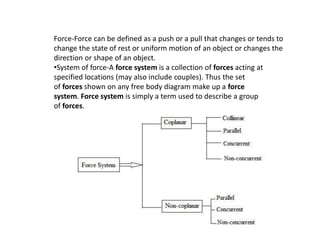
The document provides an overview of engineering mechanics, a branch of applied science focused on the behavior of bodies in motion or at rest and applying mechanical principles to solve engineering problems. Key terms such as mass, weight, velocity, speed, acceleration, momentum, rigid bodies, scalar and vector quantities, and forces are defined. The content includes explanations of how these concepts relate to the analysis of forces and motion in engineering contexts.