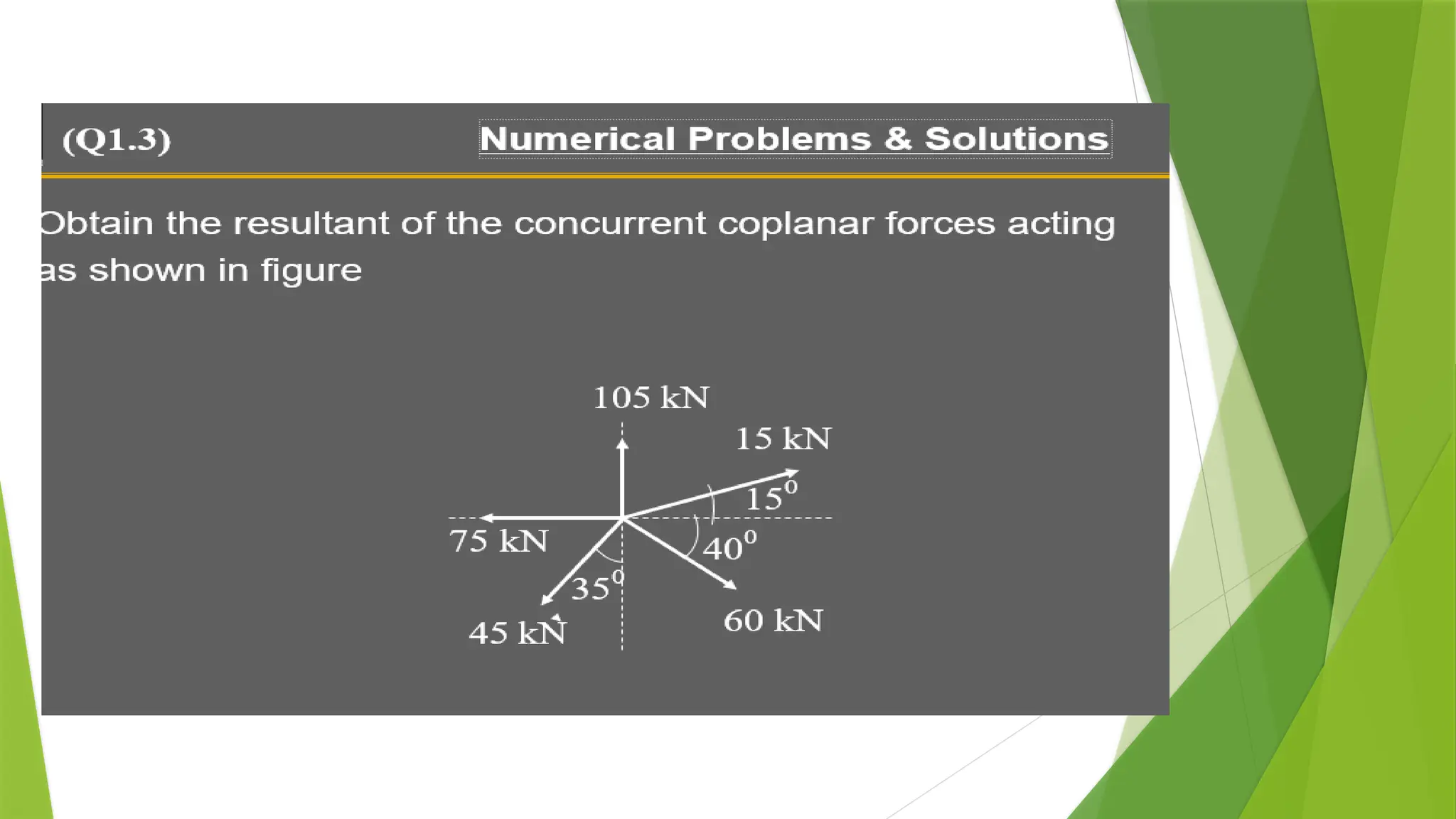
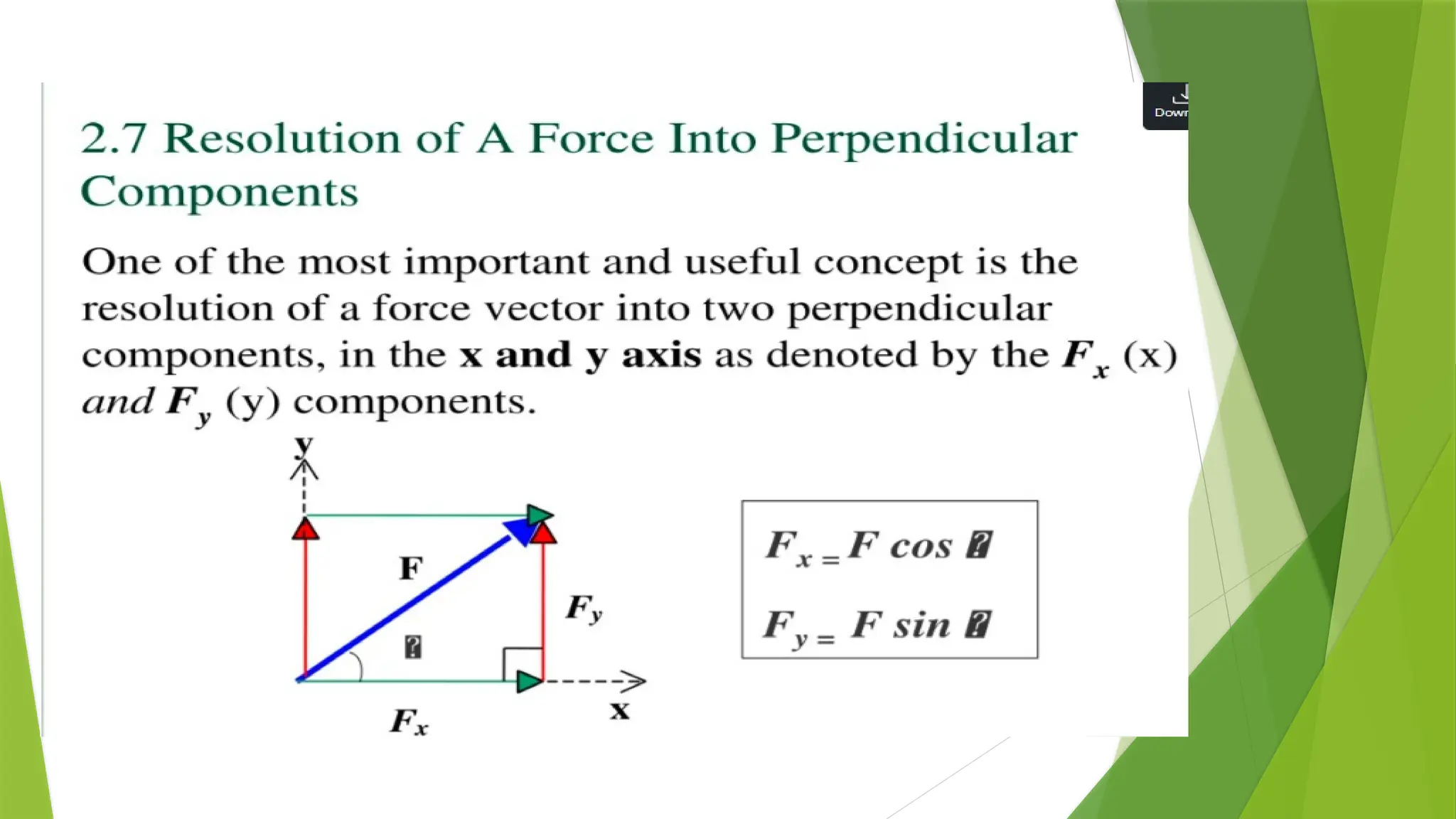
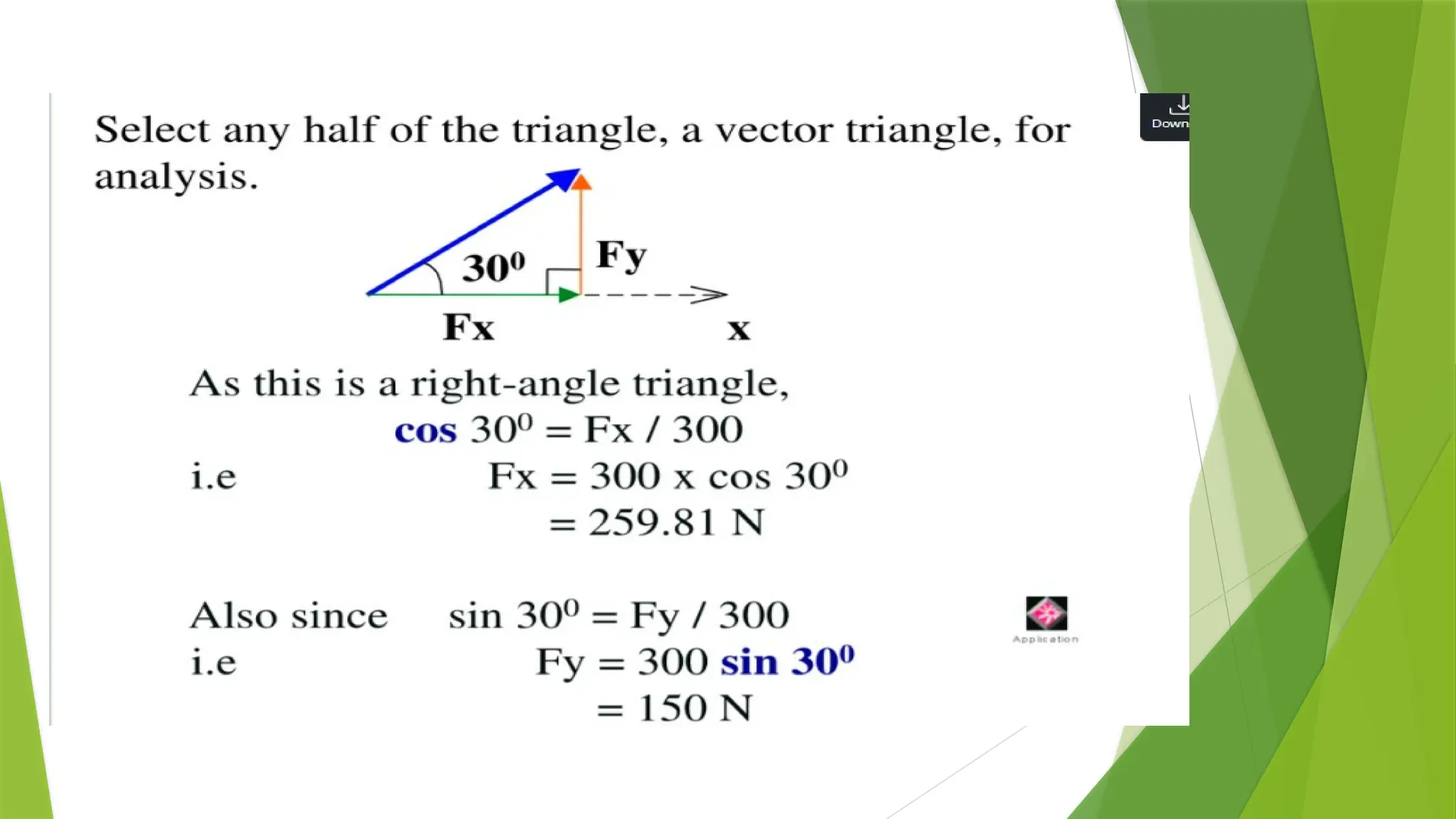
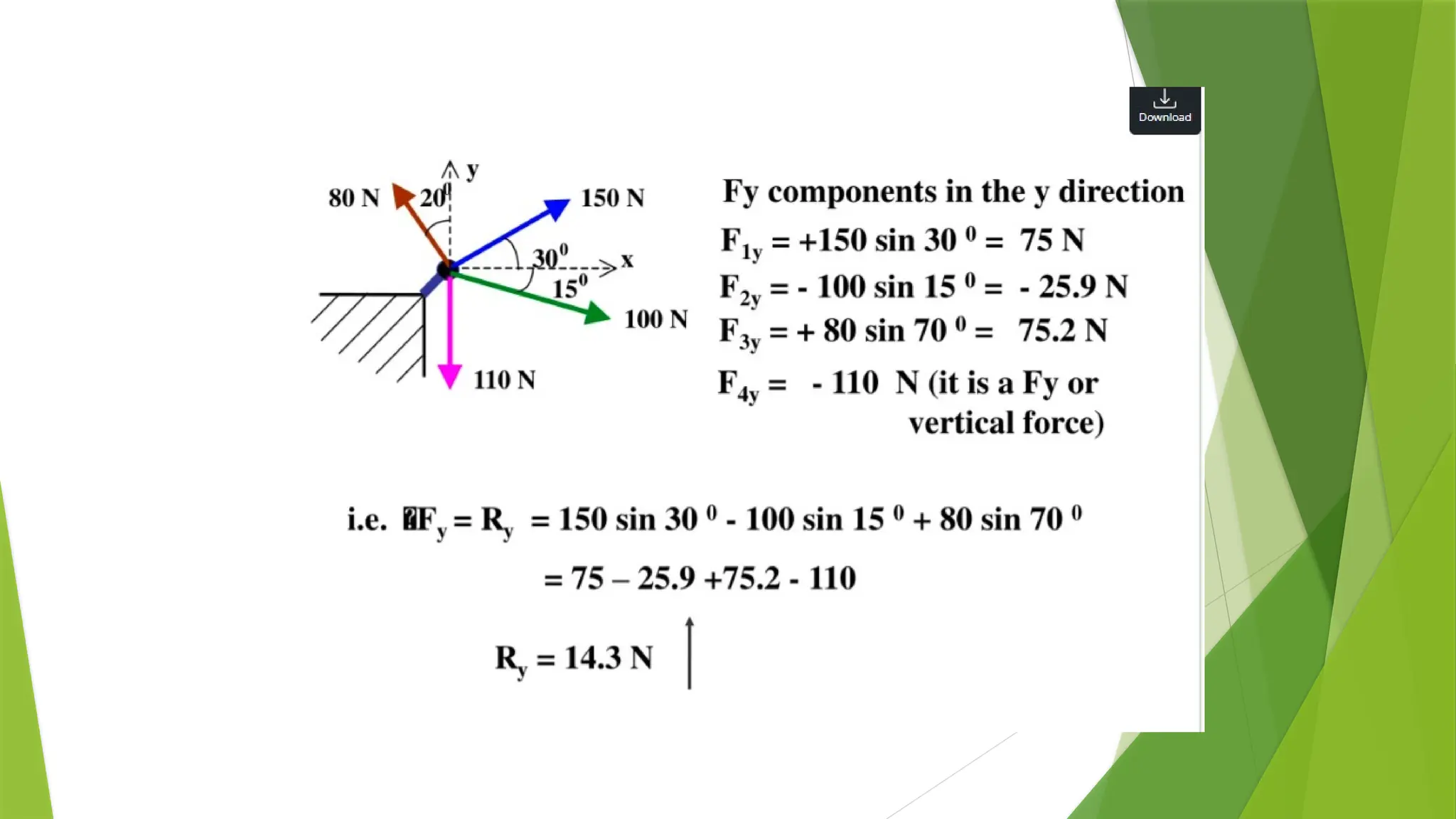
The document discusses the fundamentals of engineering mechanics, detailing the behavior of bodies under the action of forces and classifying mechanics into three categories: rigid bodies, deformable bodies, and fluids. It categorizes forces into systems such as coplanar, non-coplanar, concurrent, and non-concurrent forces based on their lines of action and interactions. Additionally, it explains various types of coplanar and non-coplanar forces, highlighting their characteristics and relationships.