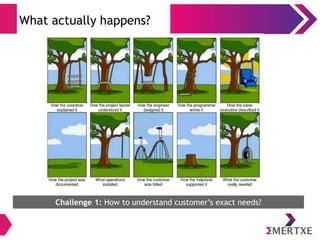
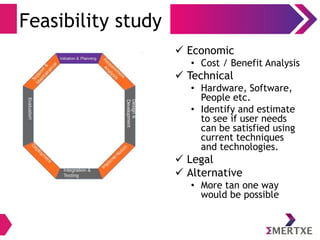
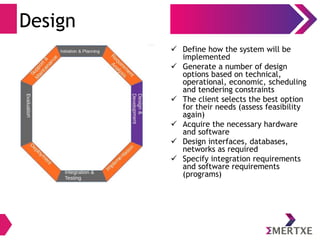
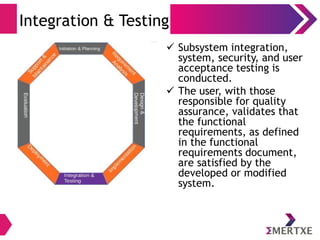
The document outlines the importance of the System Development Life Cycle (SDLC) for engineers, emphasizing the need to align technical success with business needs. It discusses challenges in understanding customer requirements, maintaining quality during product delivery, and emphasizes the significance of proper planning, estimation, and risk management. Case studies illustrate common pitfalls such as vendor issues, scalability failures, and the impact of excessive processes on team efficiency.