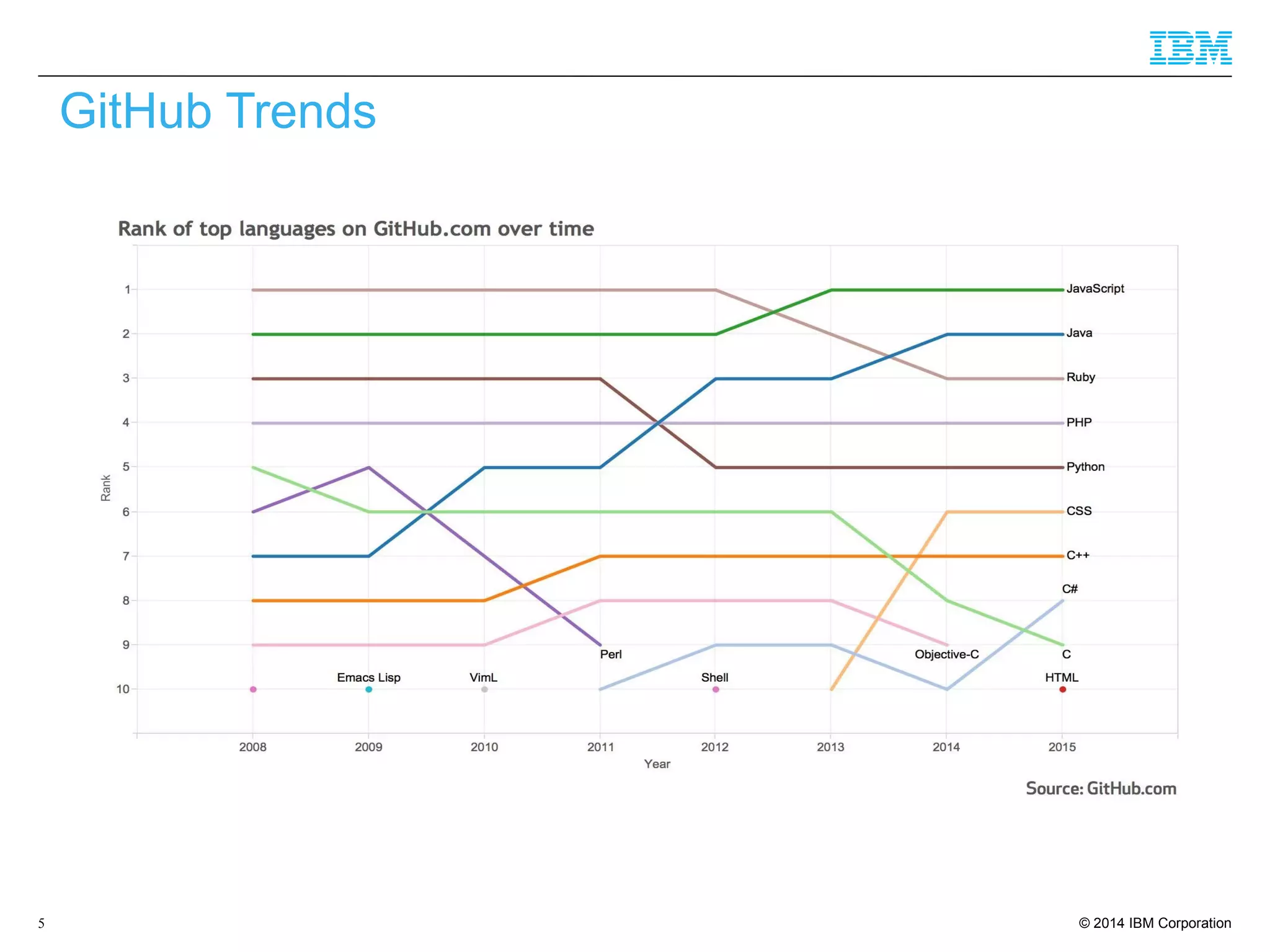
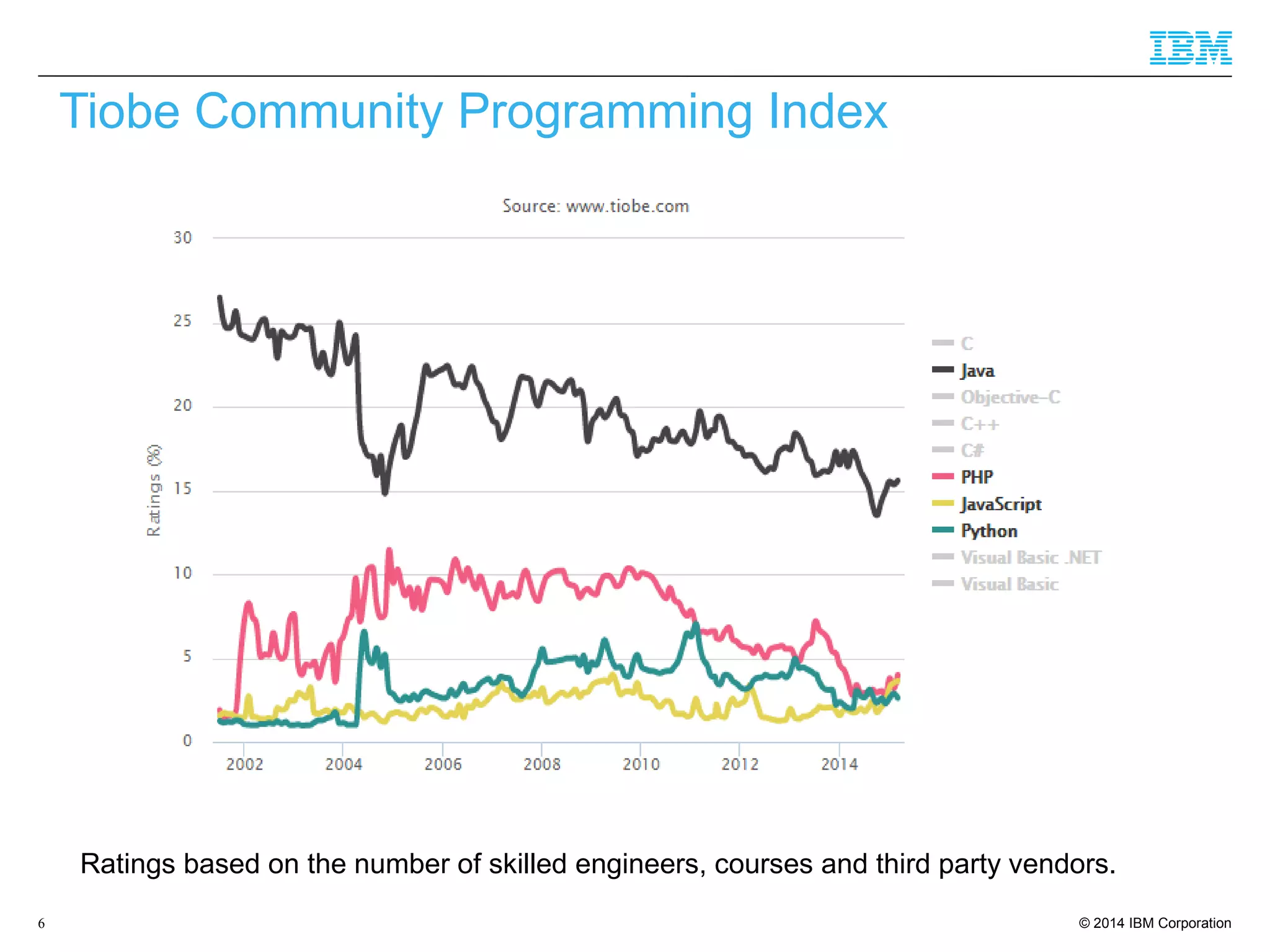
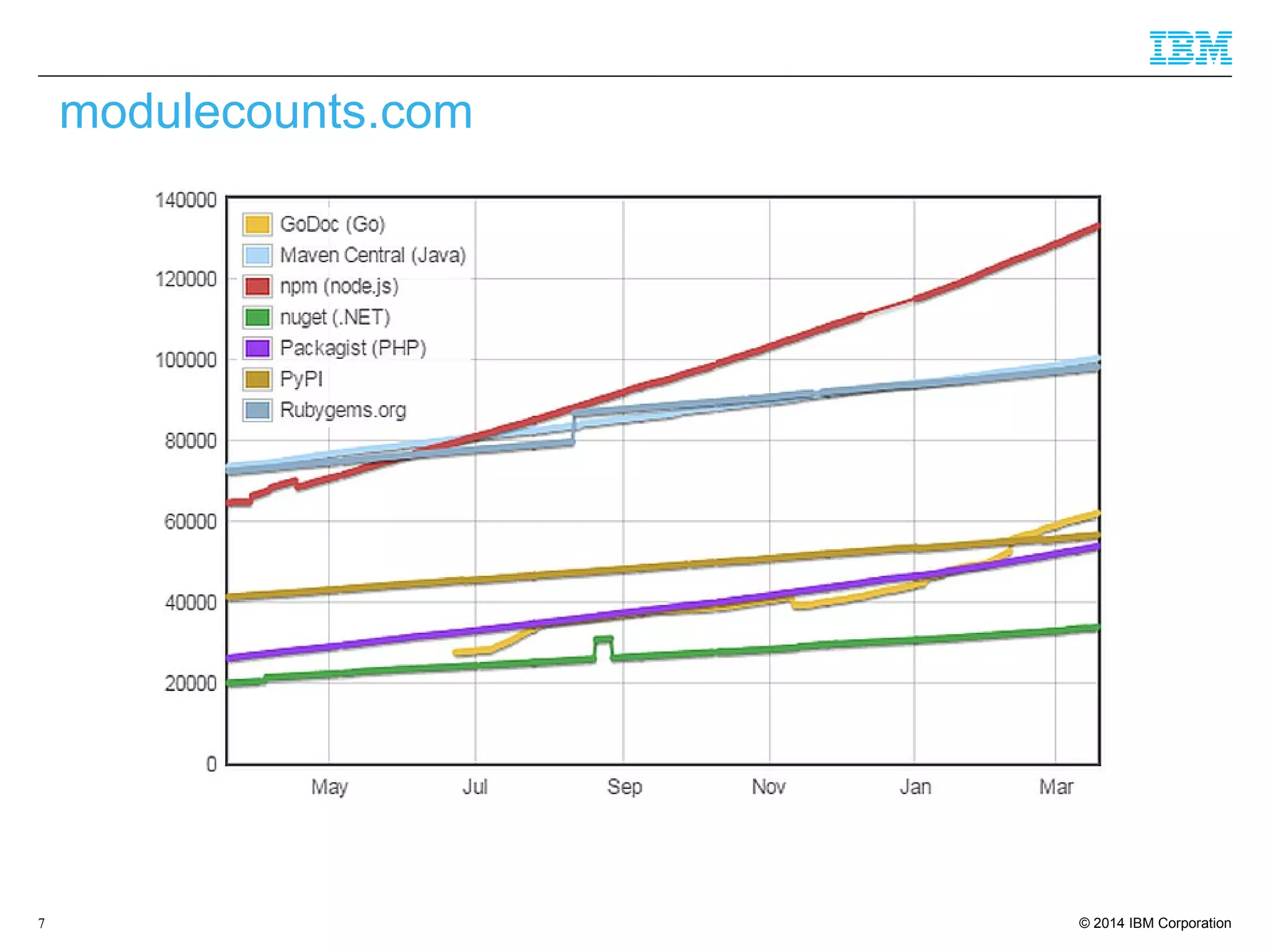
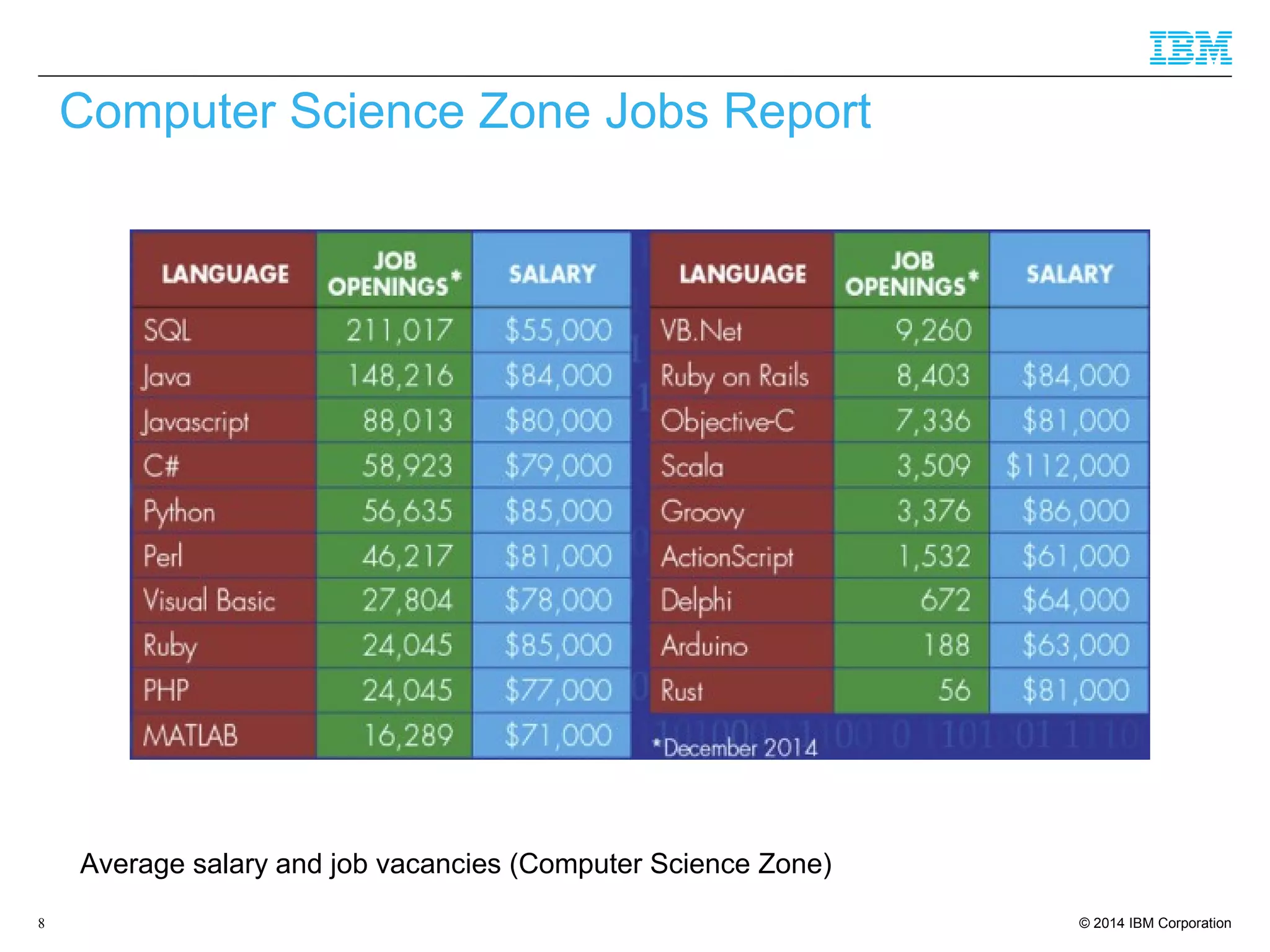
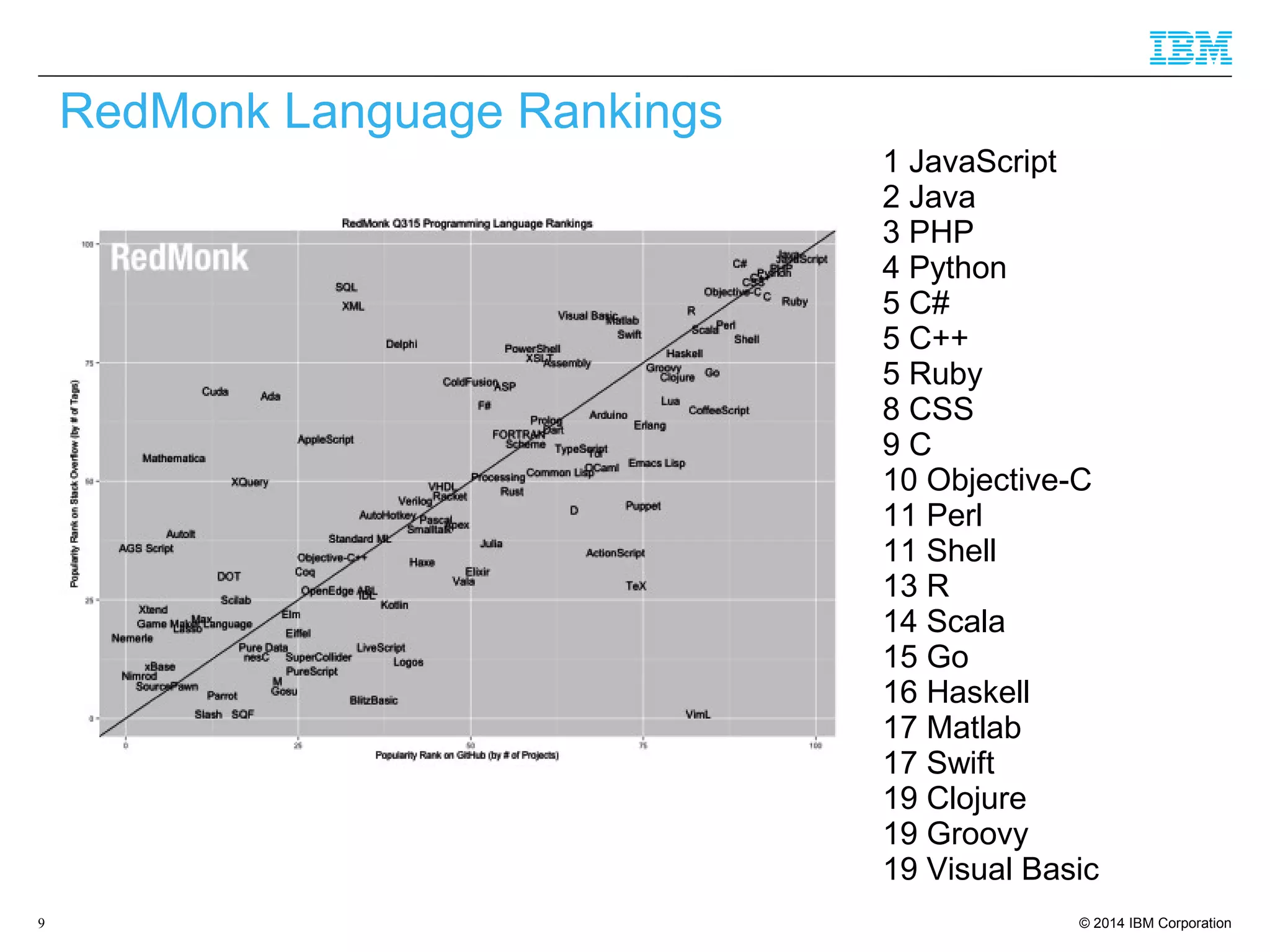
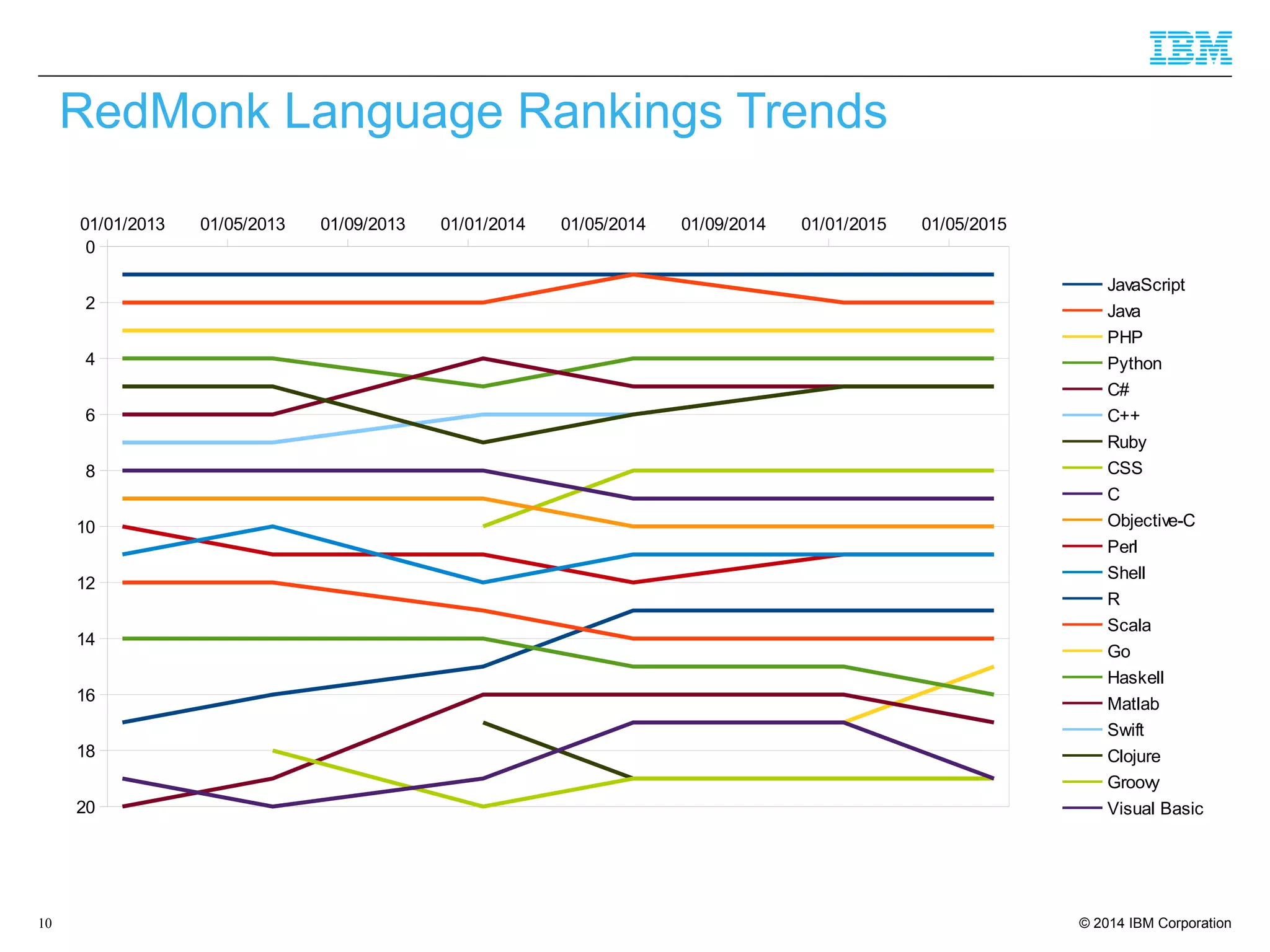
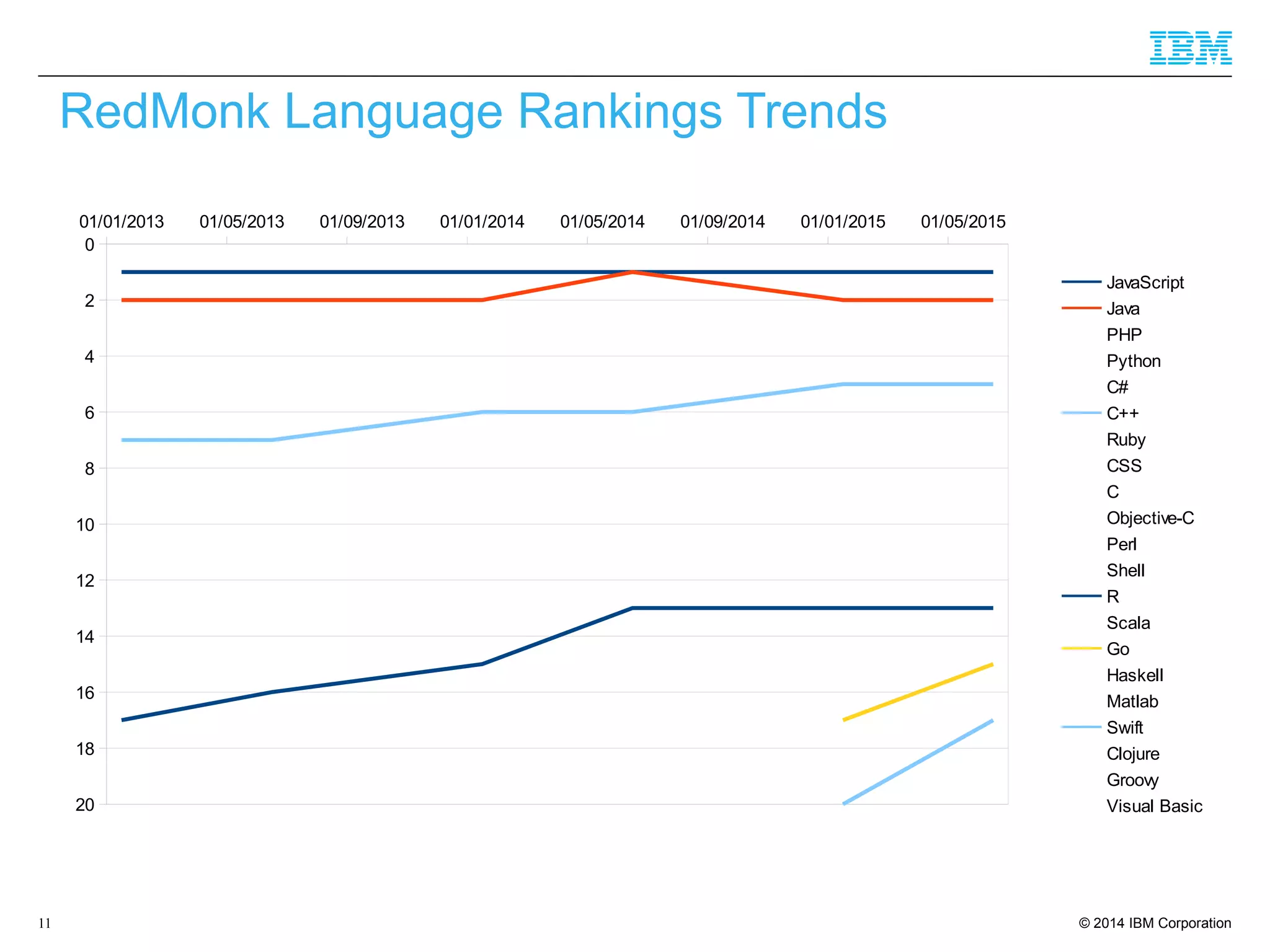
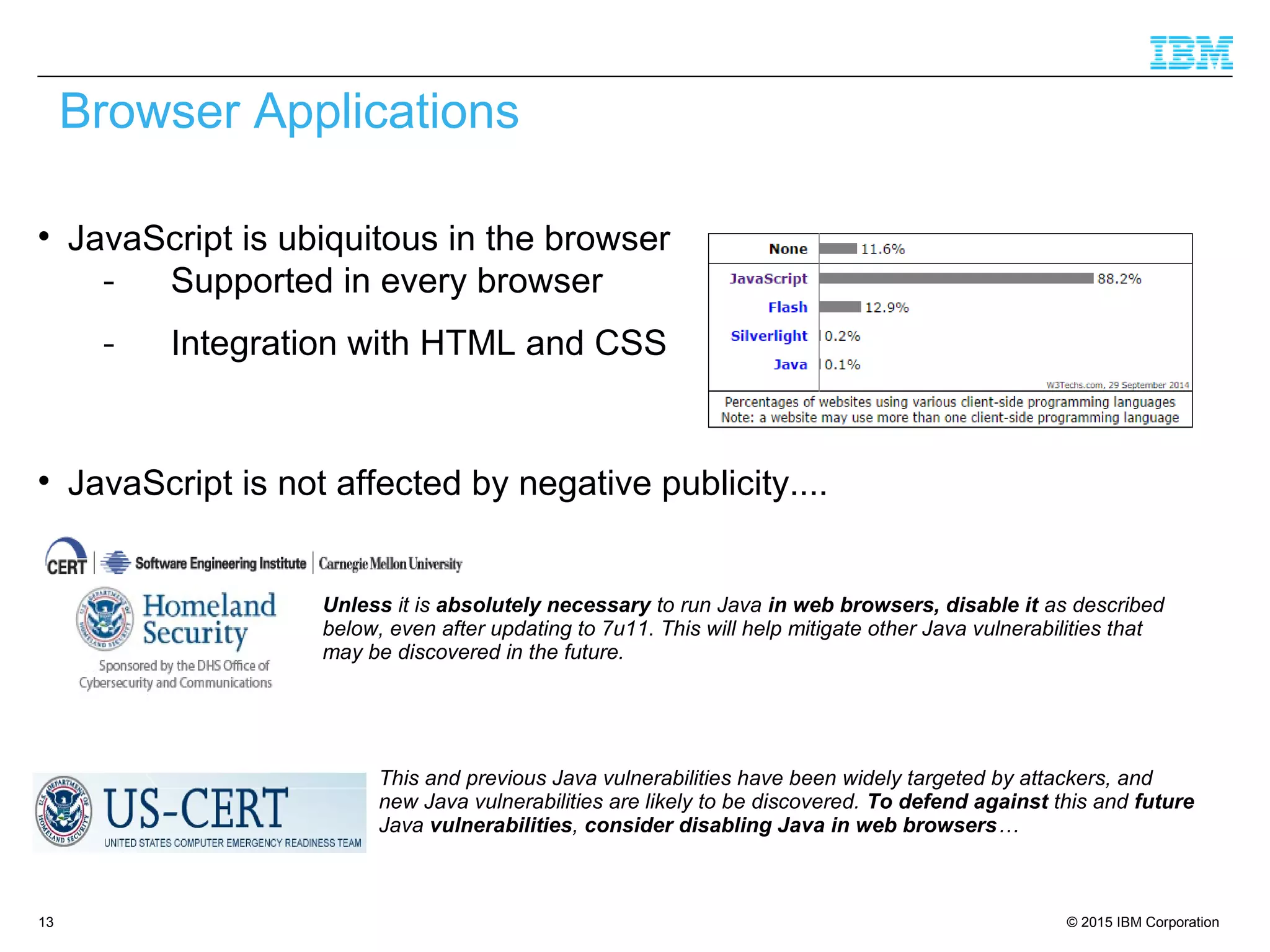
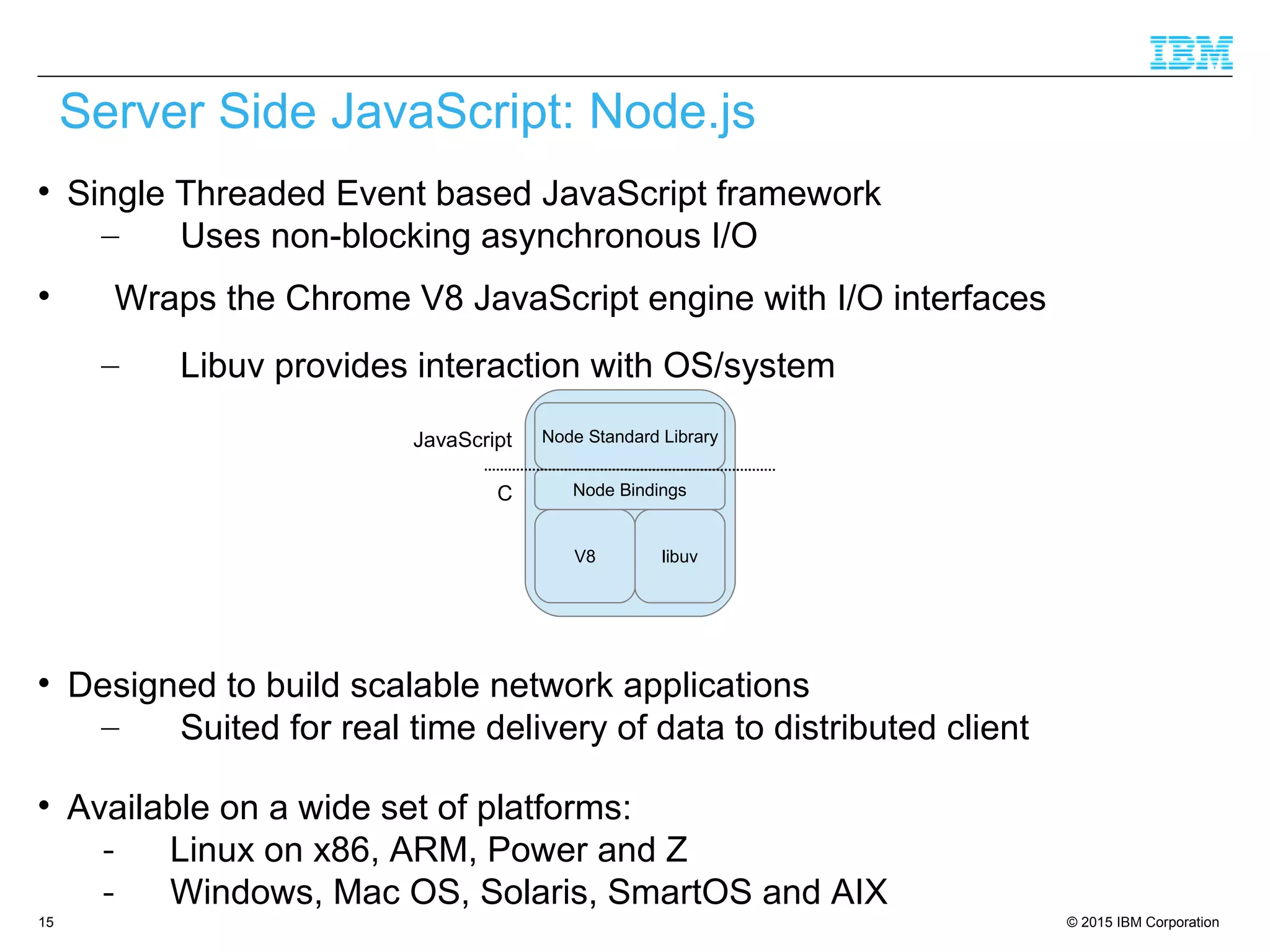
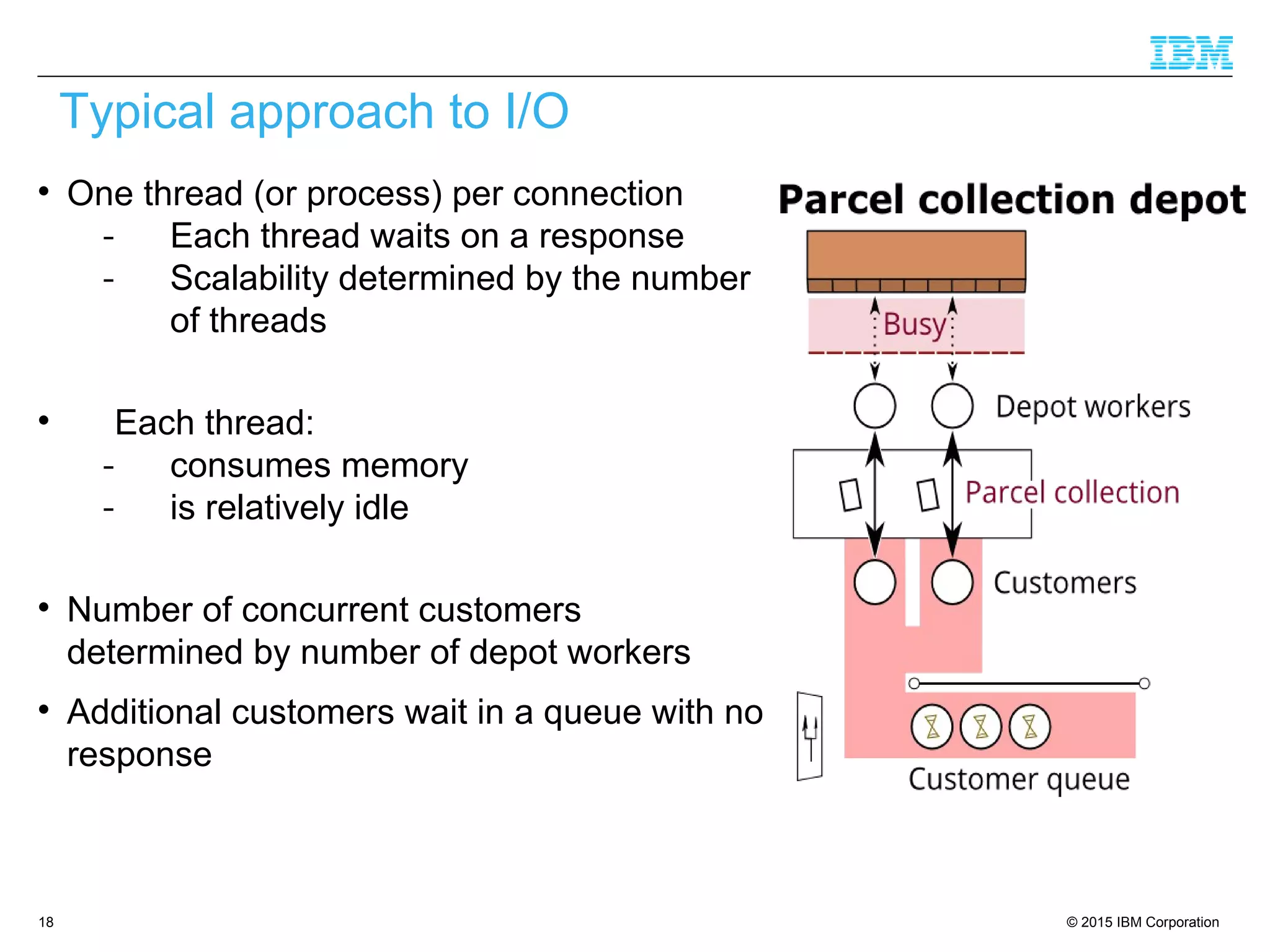
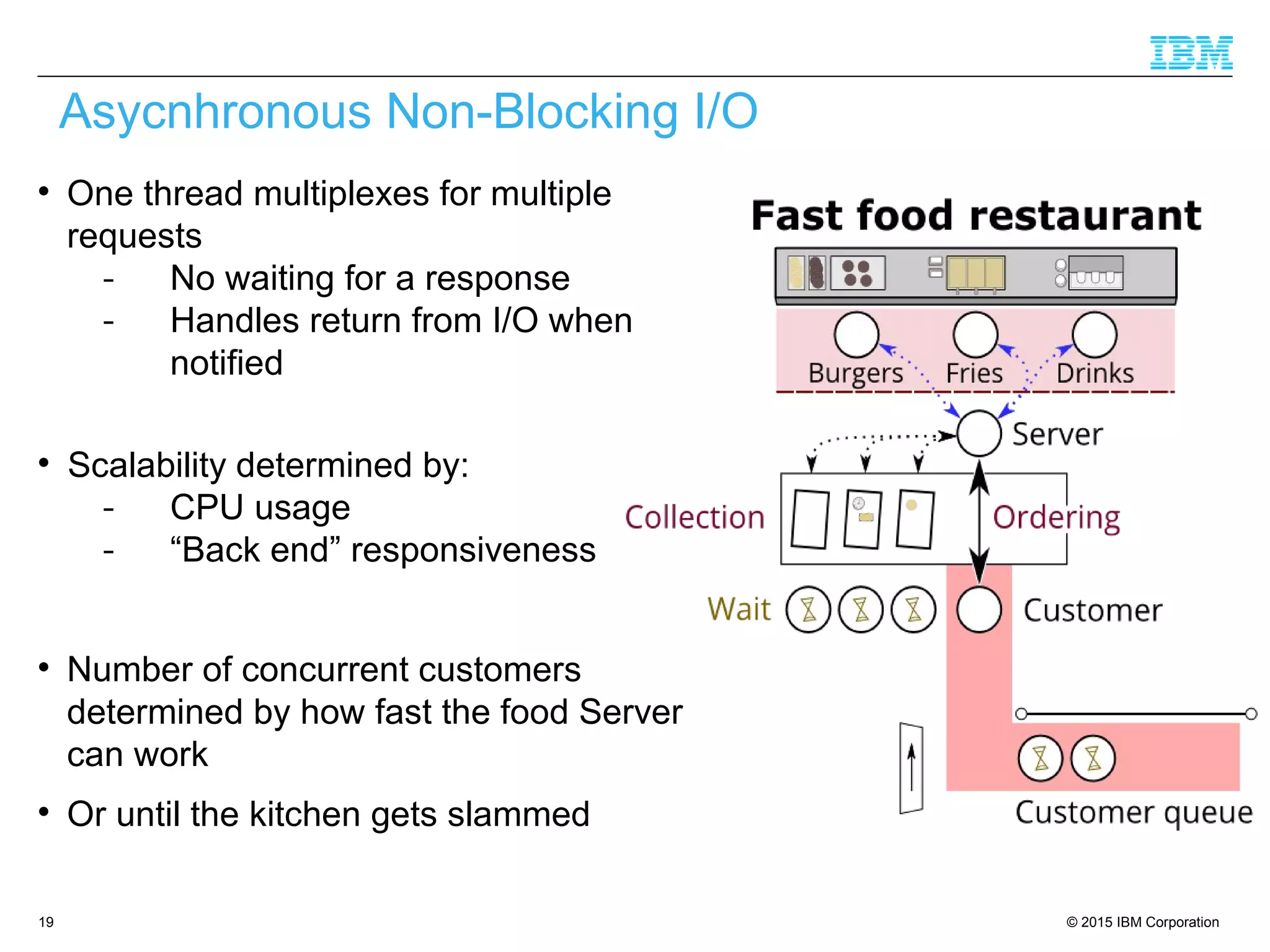
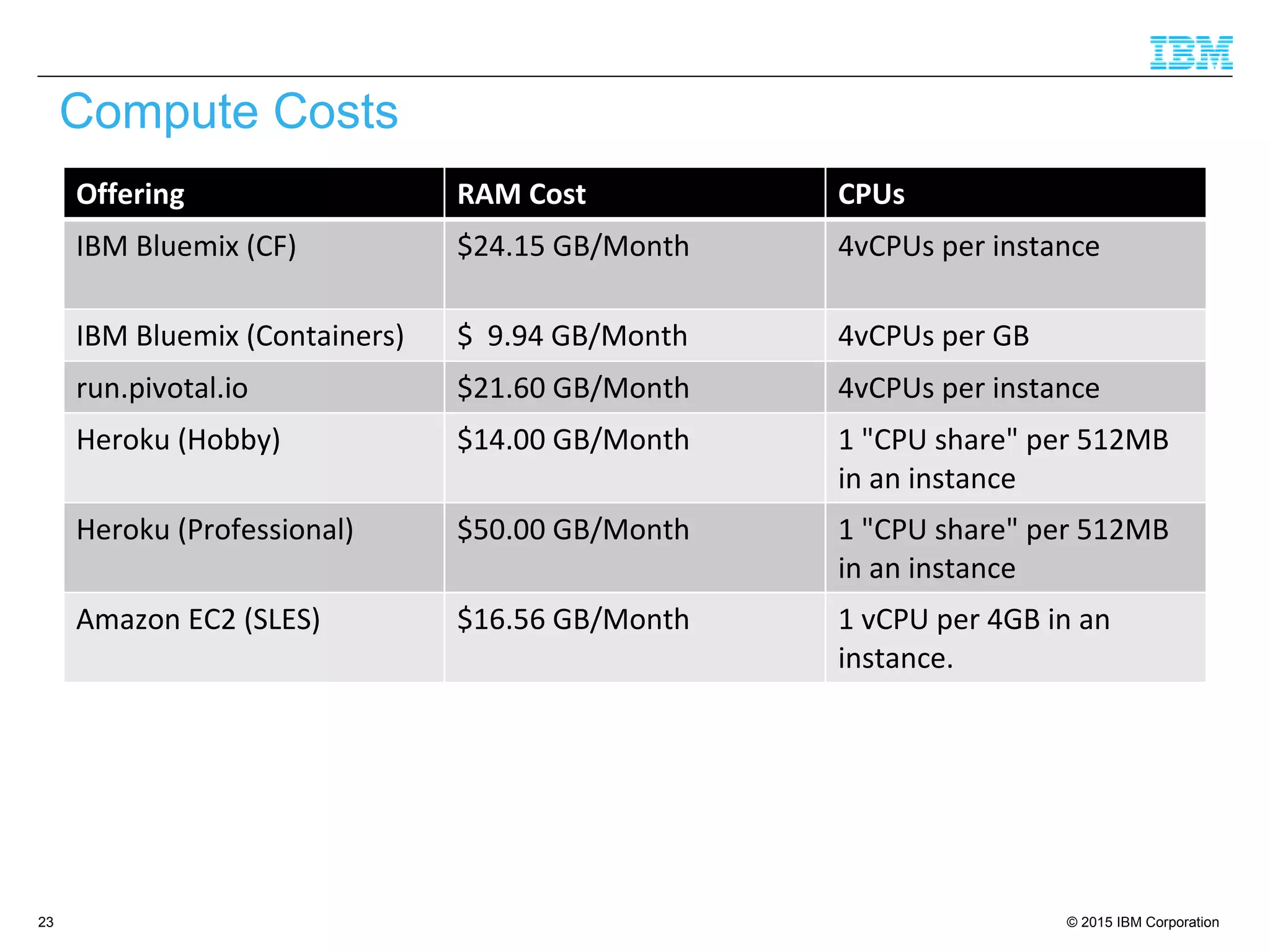
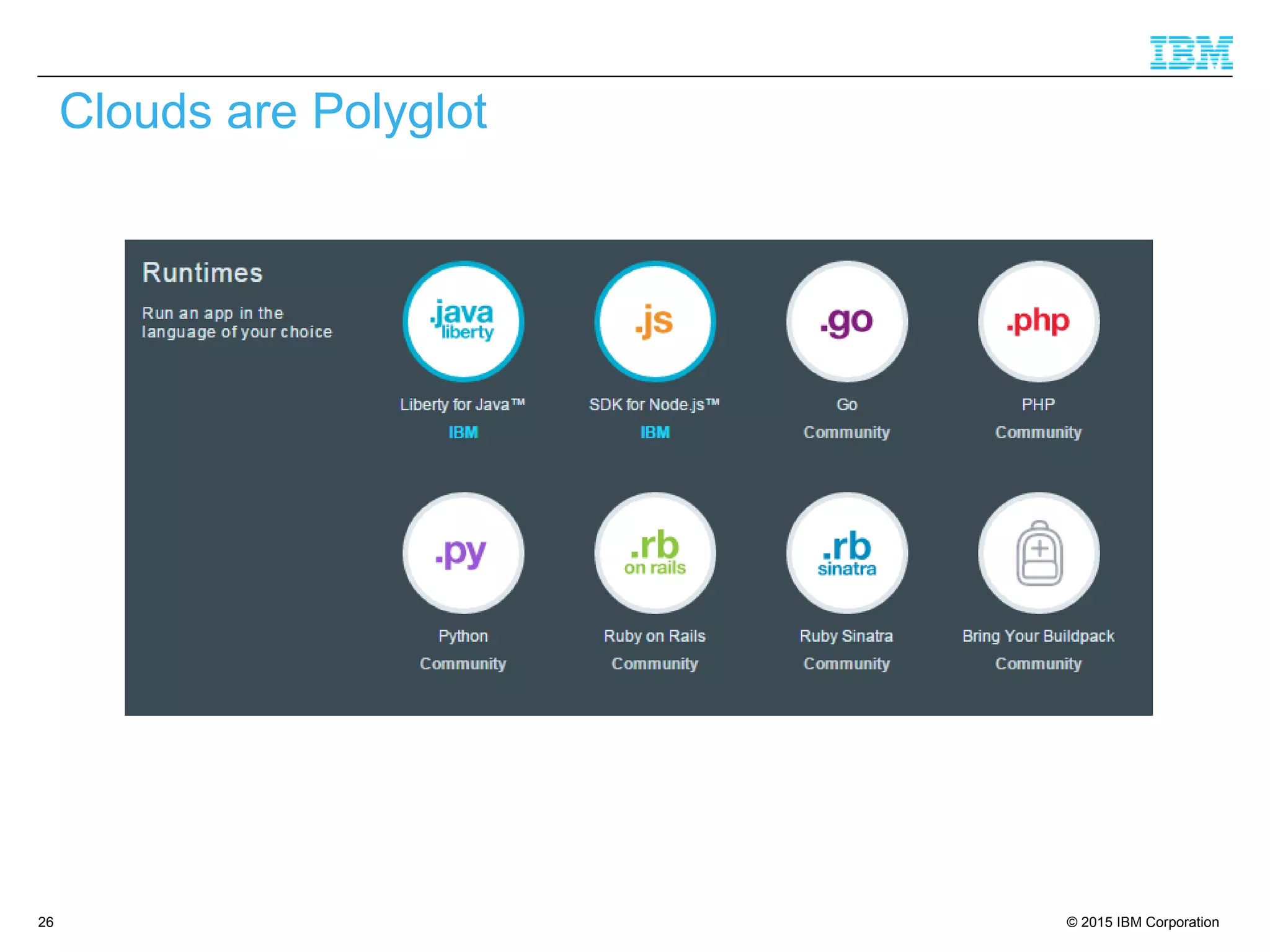
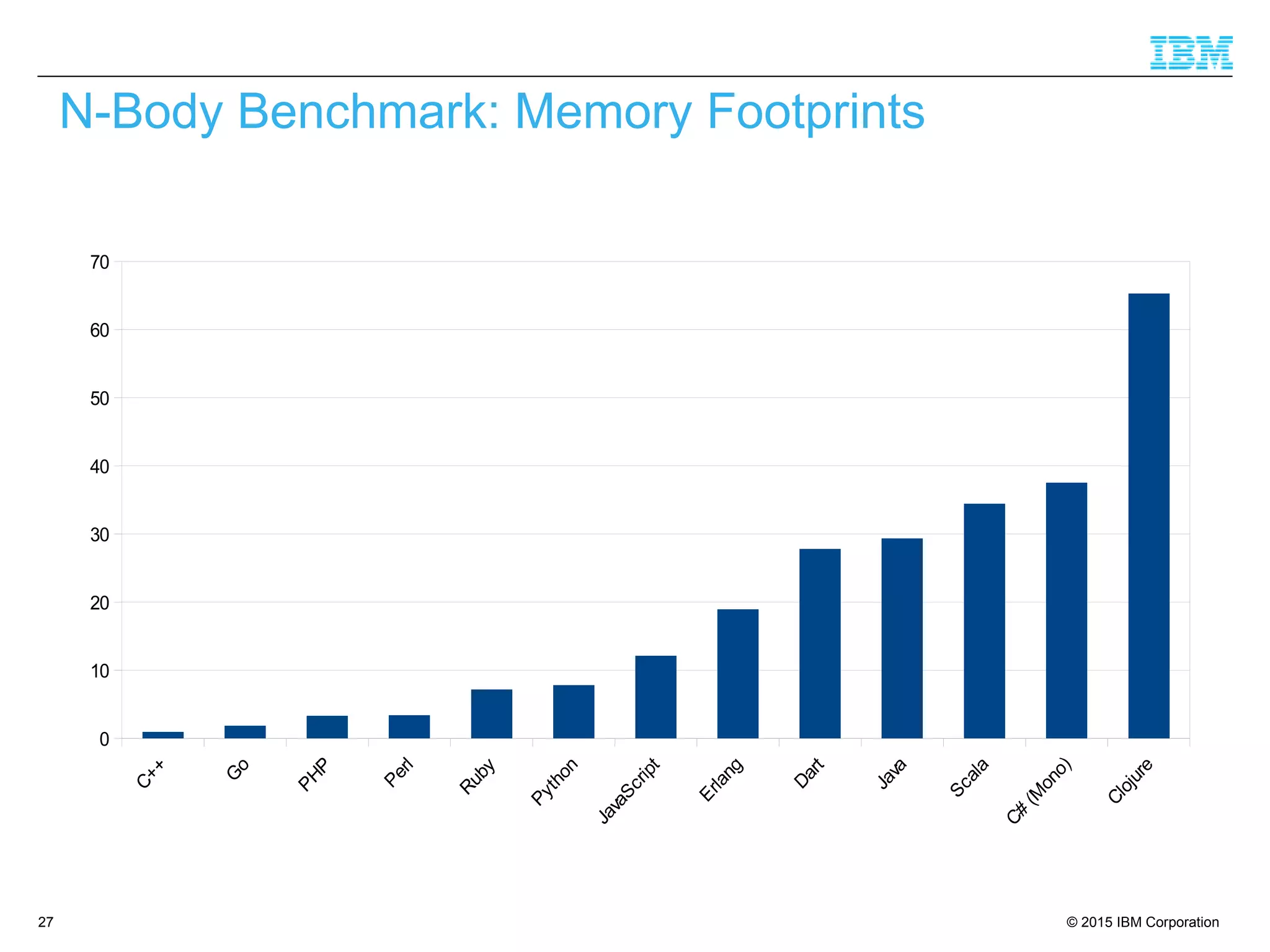
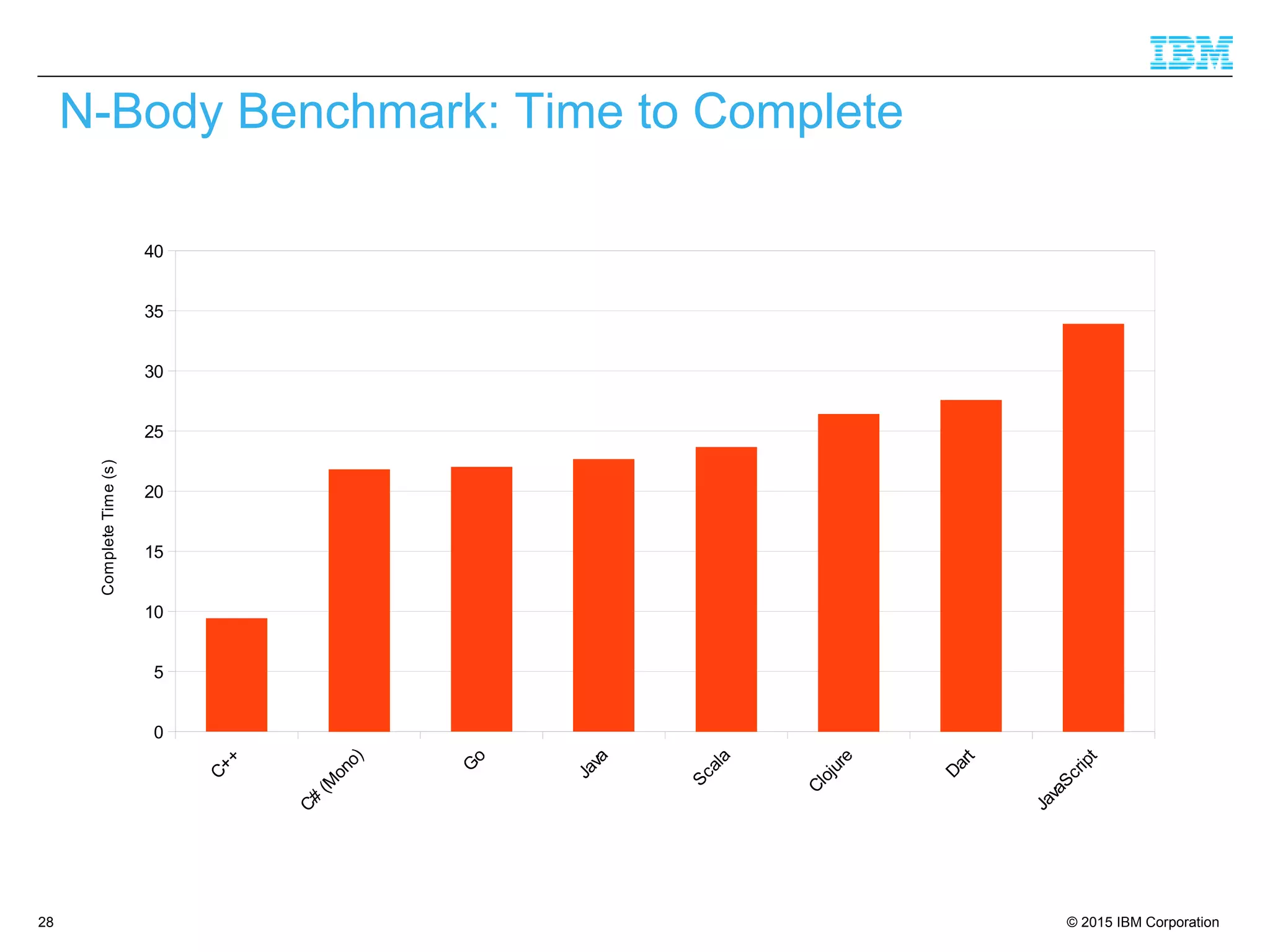
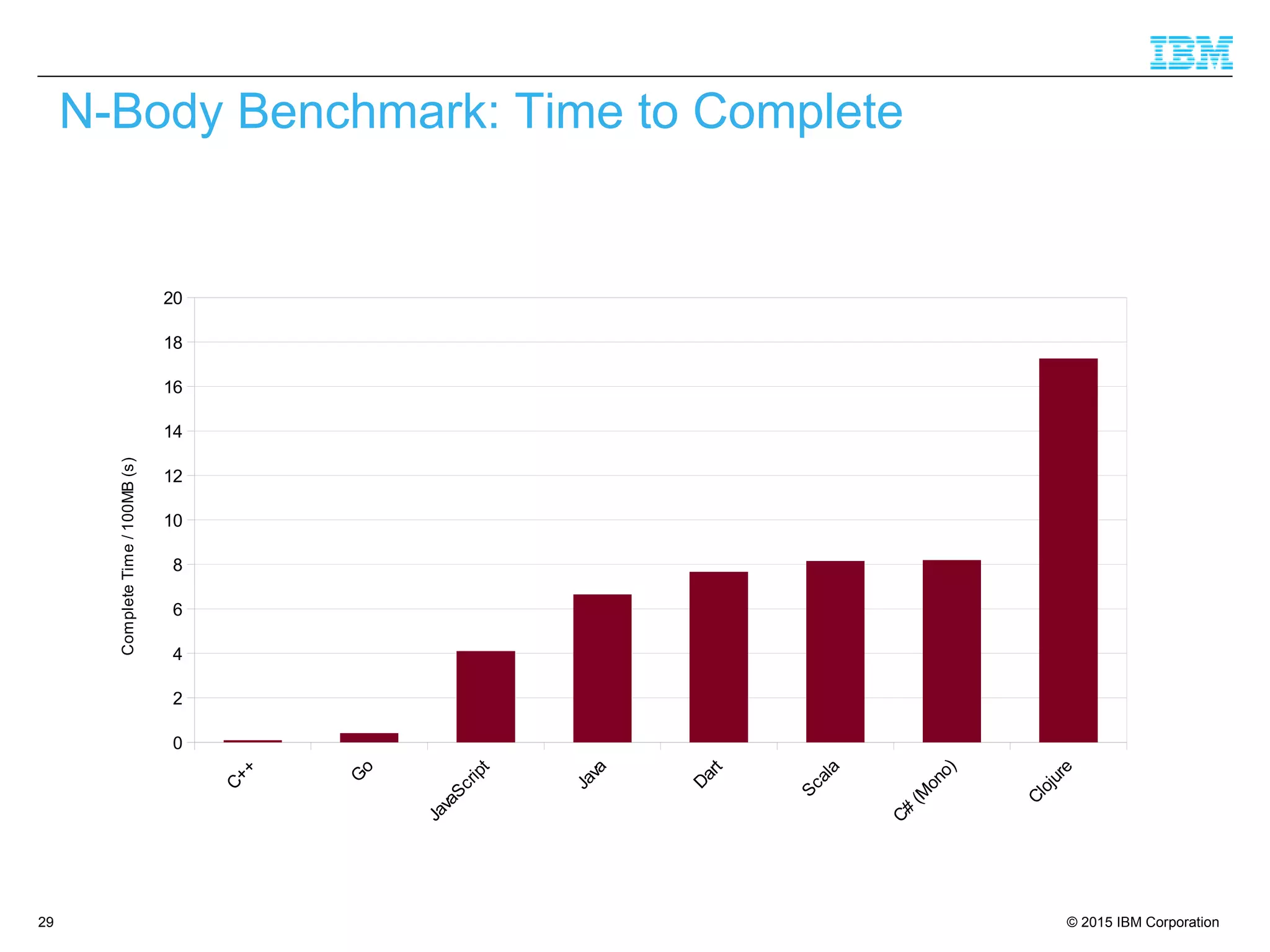
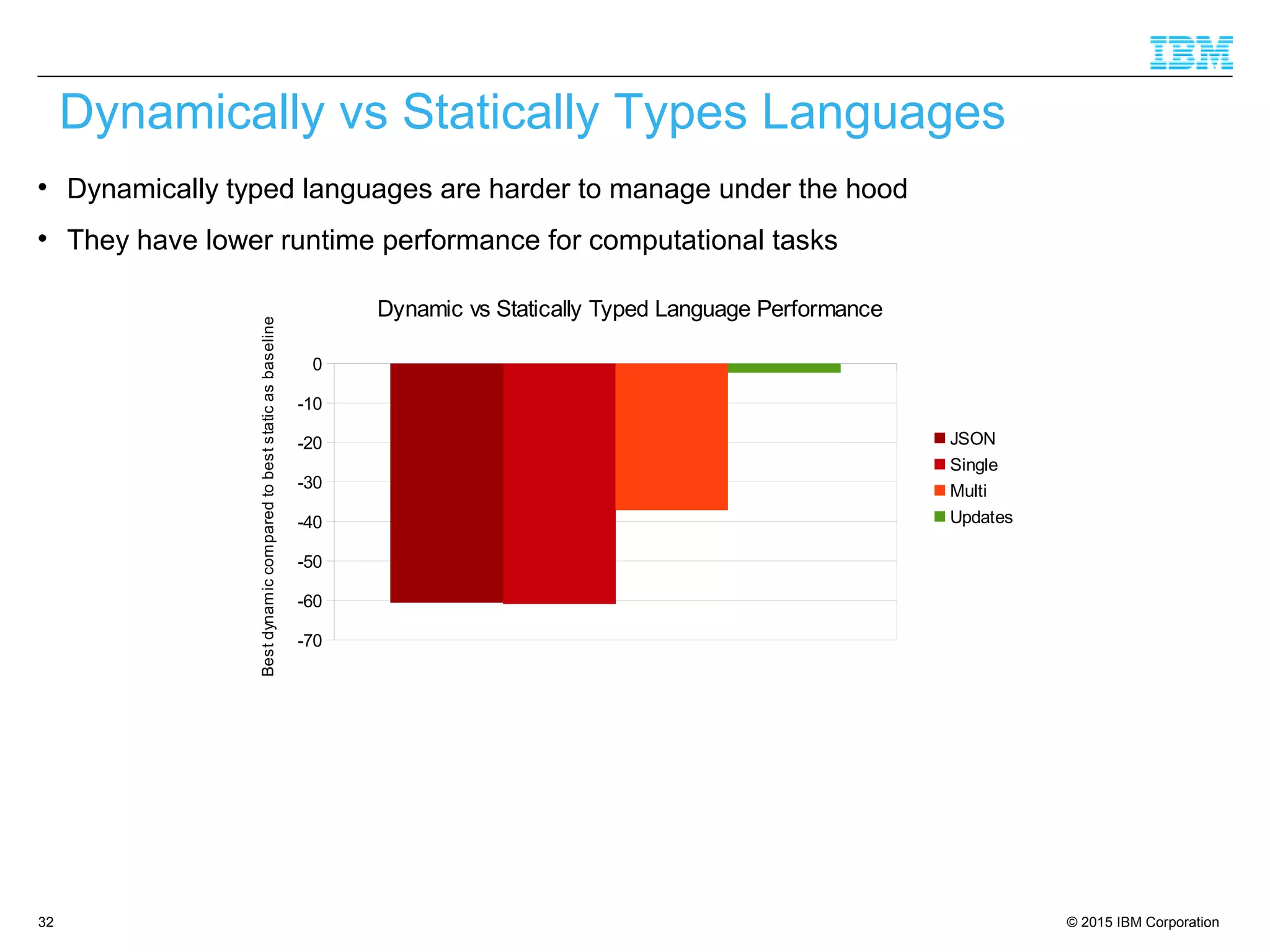
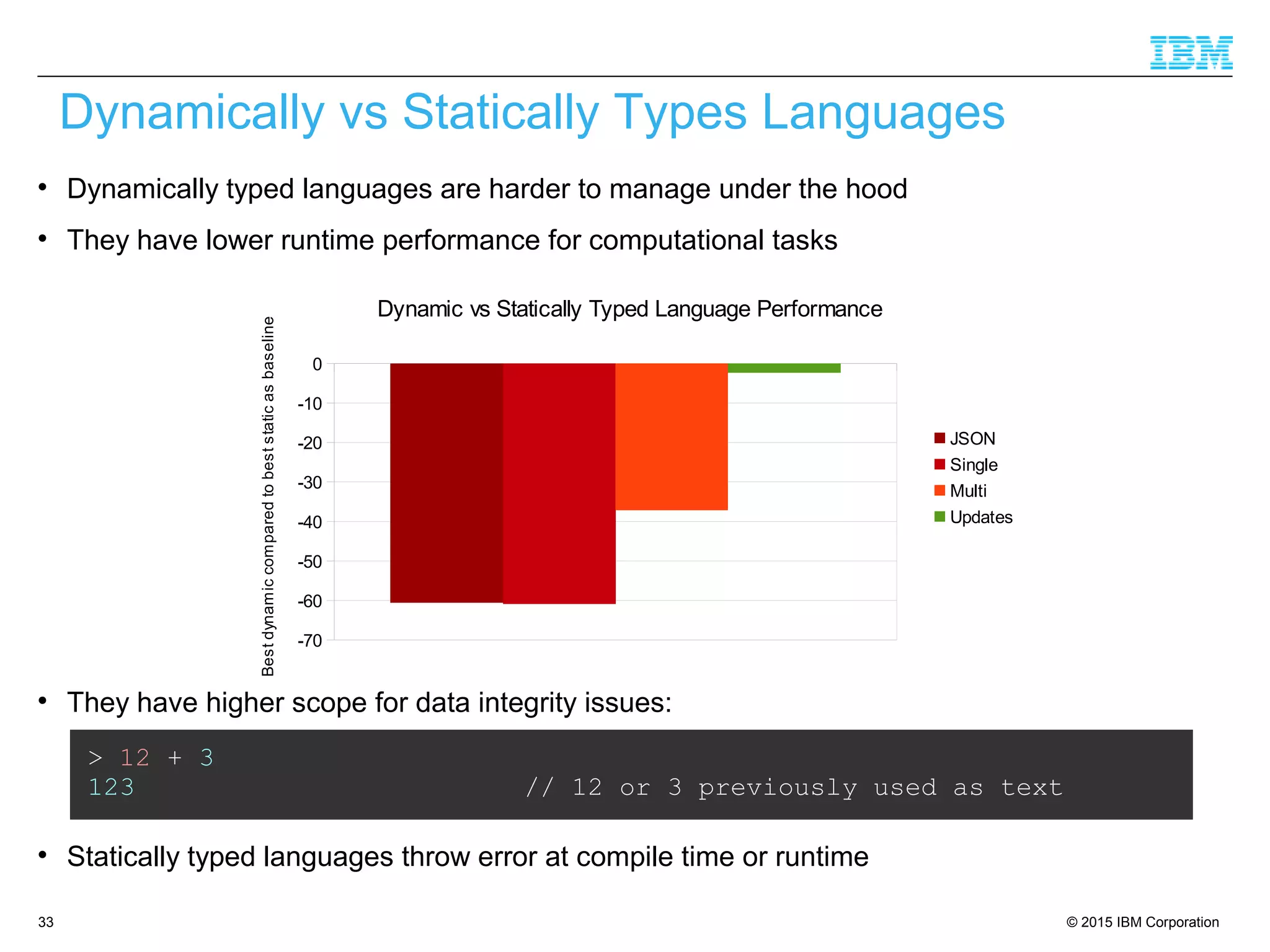
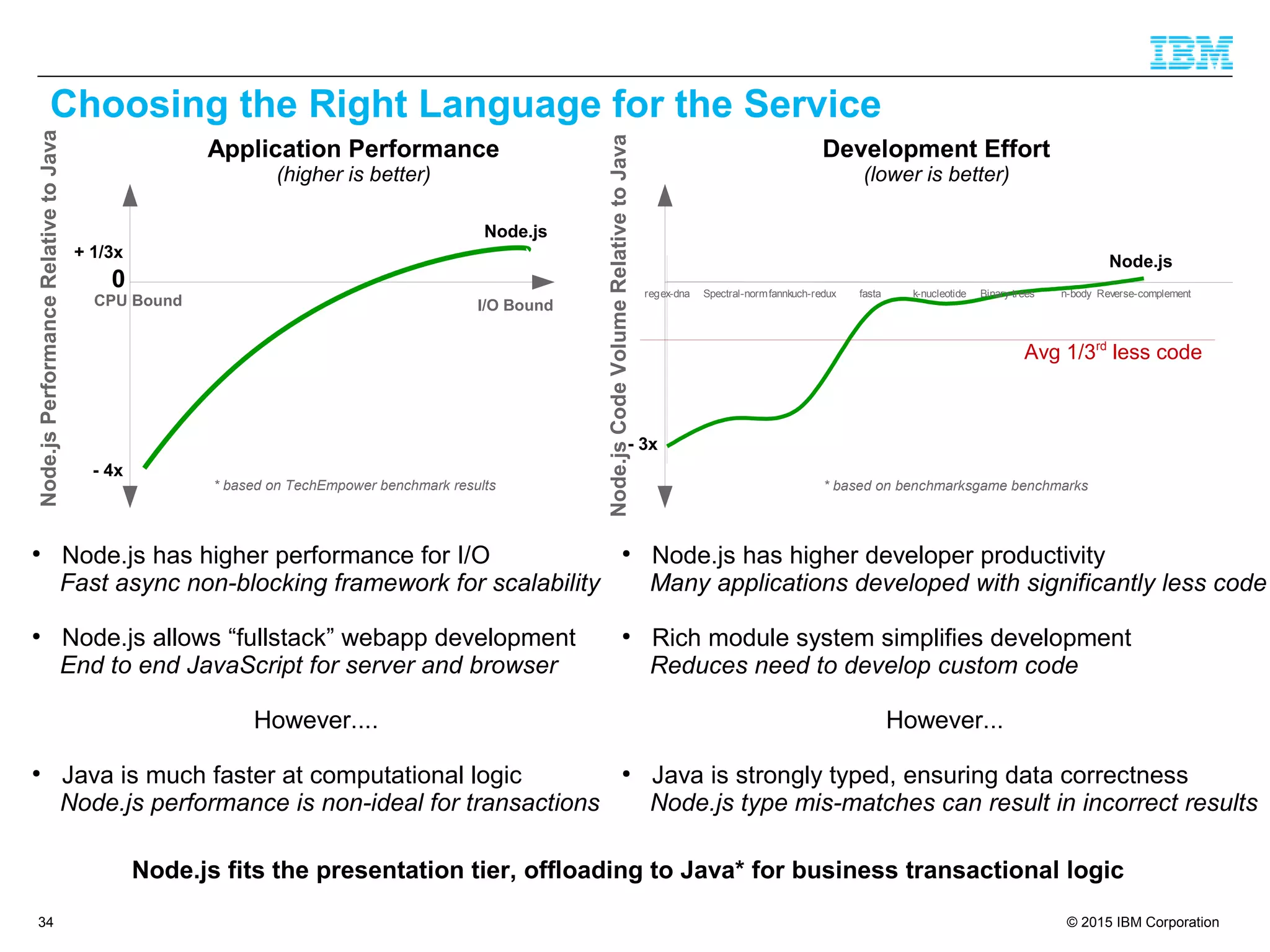
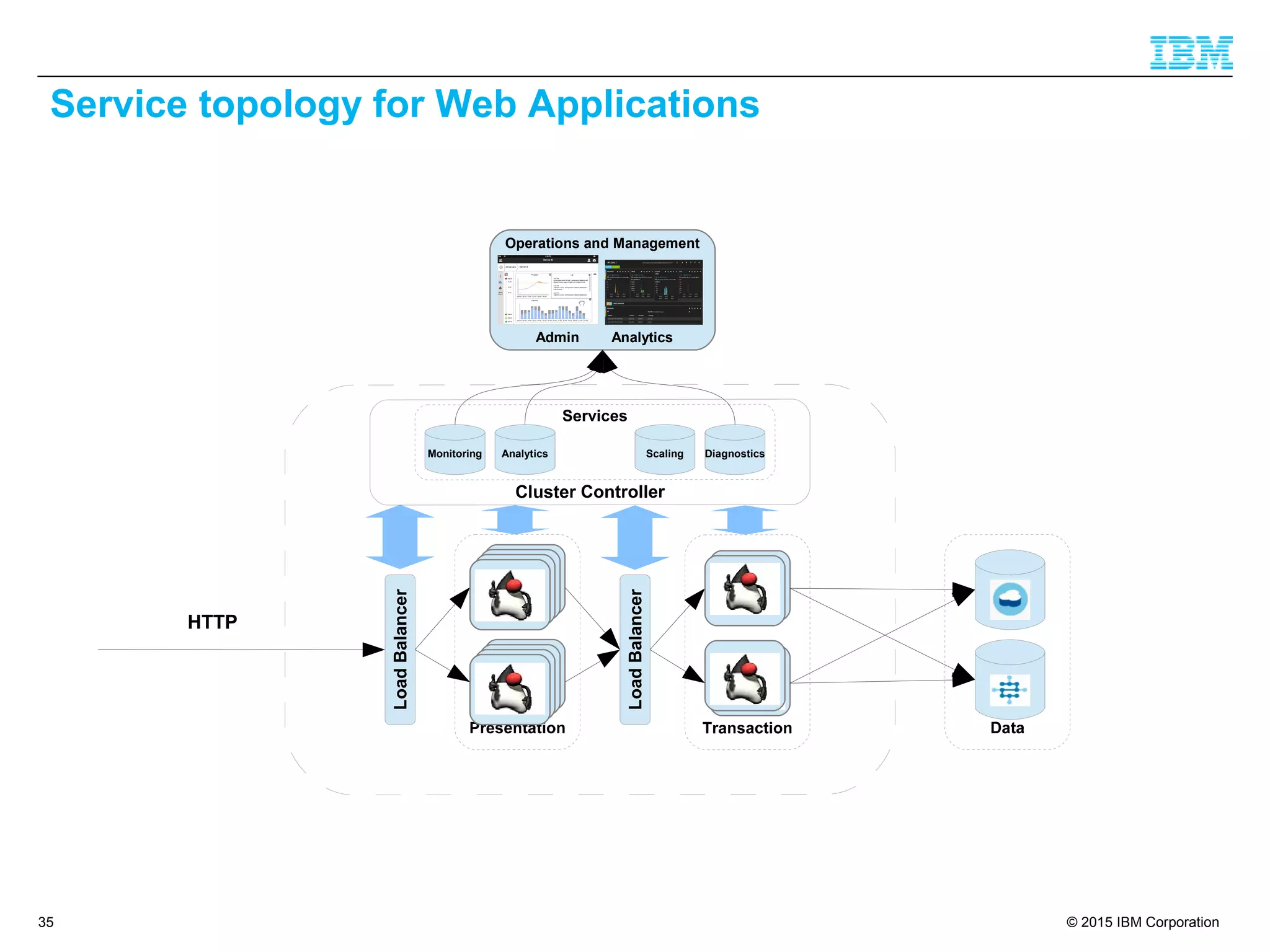
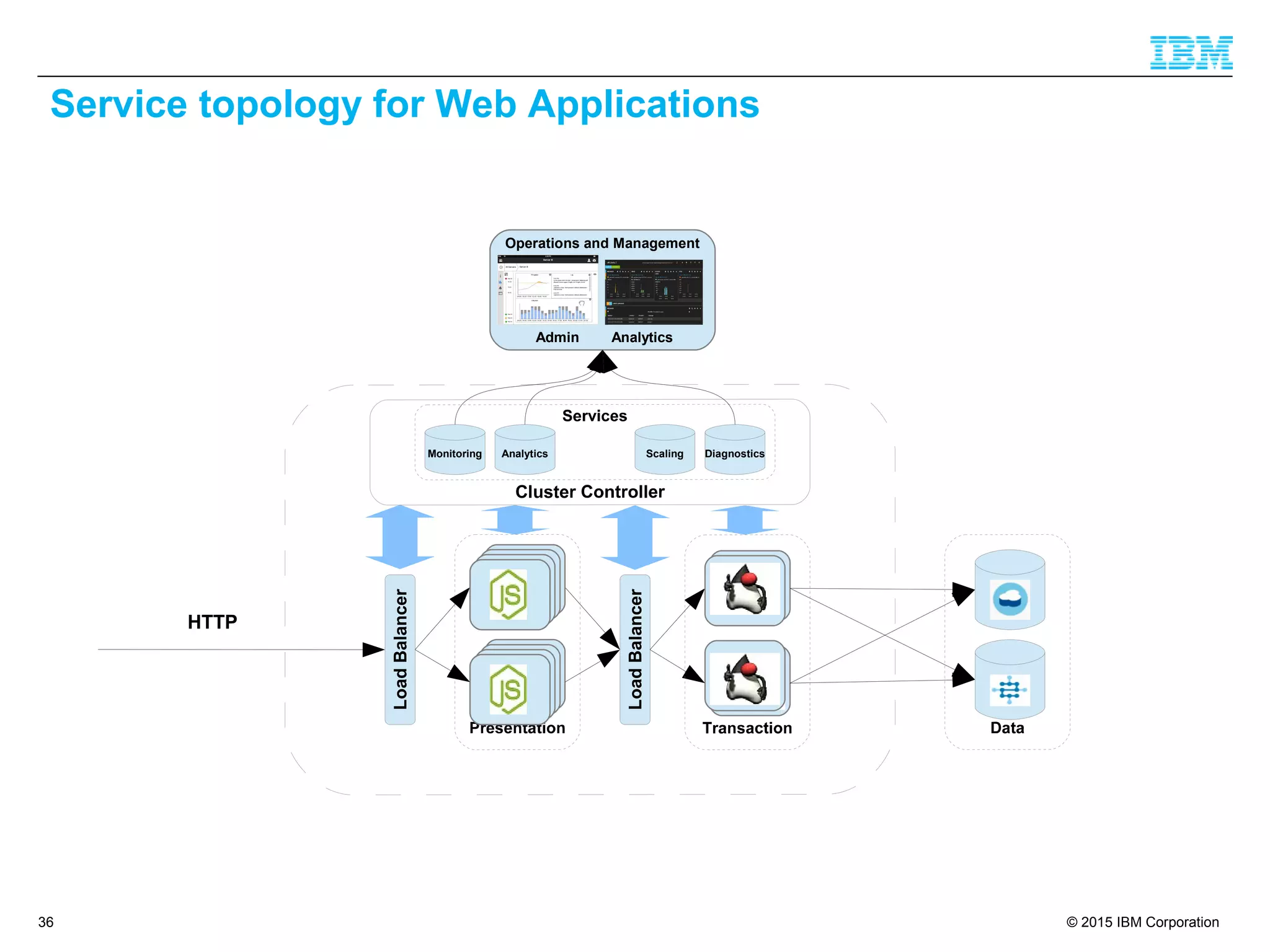
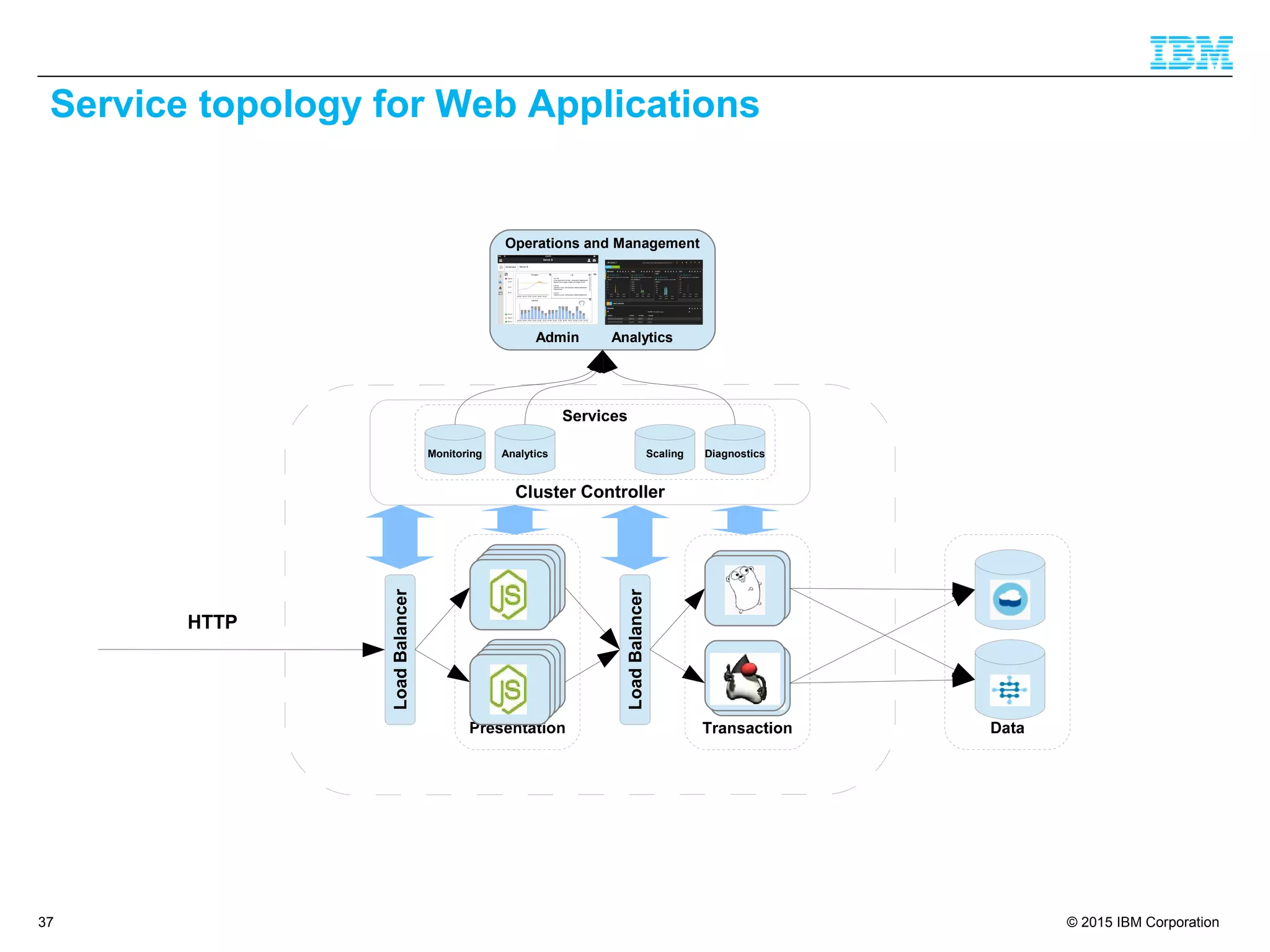
The document discusses trends in enterprise web application development, highlighting the increasing demand for polyglot ecosystems and the importance of high-performance infrastructure tailored for various language runtimes. It emphasizes the rise of JavaScript and Node.js for scalable applications, as well as cloud computing benefits and the microservices architecture model. Additionally, it compares dynamically typed and statically typed languages, noting their respective advantages and challenges in performance and data integrity.