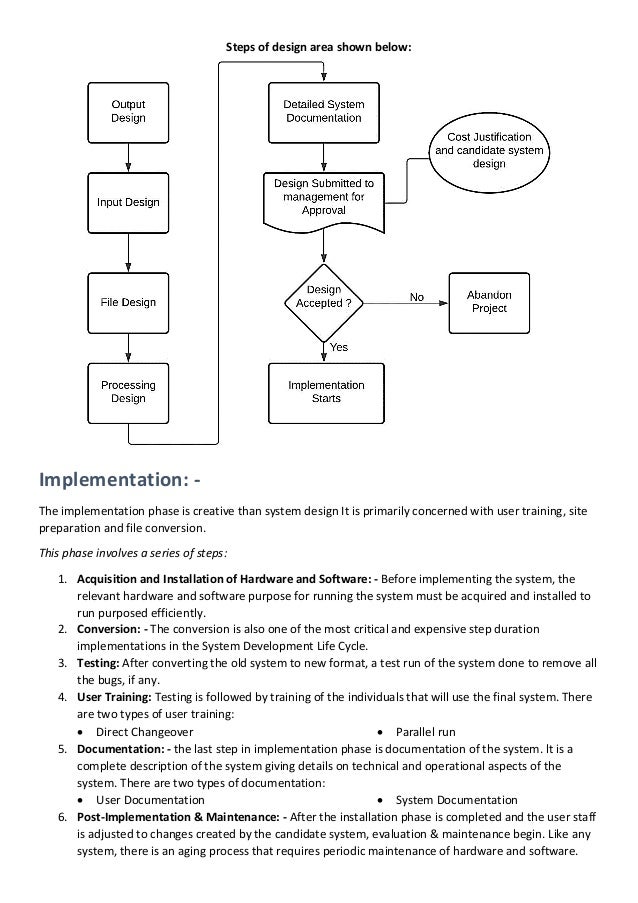
The document outlines the System Development Life Cycle (SDLC), which comprises several phases including analysis, design, implementation, and maintenance. It details the importance of recognizing needs, conducting feasibility studies (economic, technical, operational), and the steps involved in implementation such as hardware acquisition, conversion, testing, user training, and documentation. The document emphasizes that system analysis and design are interrelated and that various activities overlap throughout the life cycle of the system.