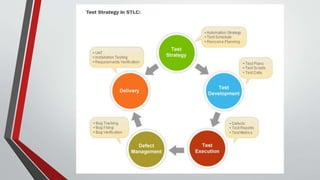
The document outlines the key steps in creating a functional testing strategy:
1. Understanding system requirements to identify business processes, data, and security needs.
2. Identifying test scenarios to describe specific business processes to test.
3. Defining test objectives to ensure the system's functionality, data accuracy, and security.