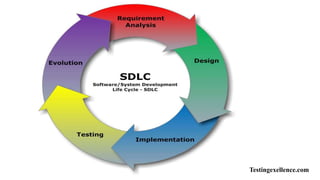
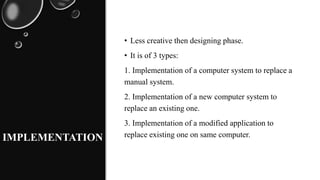
The document discusses the system development life cycle (SDLC), which consists of several phases for developing software projects. It includes recognition of need, feasibility study, analysis, design, implementation, testing, and maintenance. In the analysis phase, tools are used to obtain an in-depth understanding of business needs. The design phase defines the final system and technical specifications. Testing verifies that requirements are met and defects are fixed before software is delivered to customers.