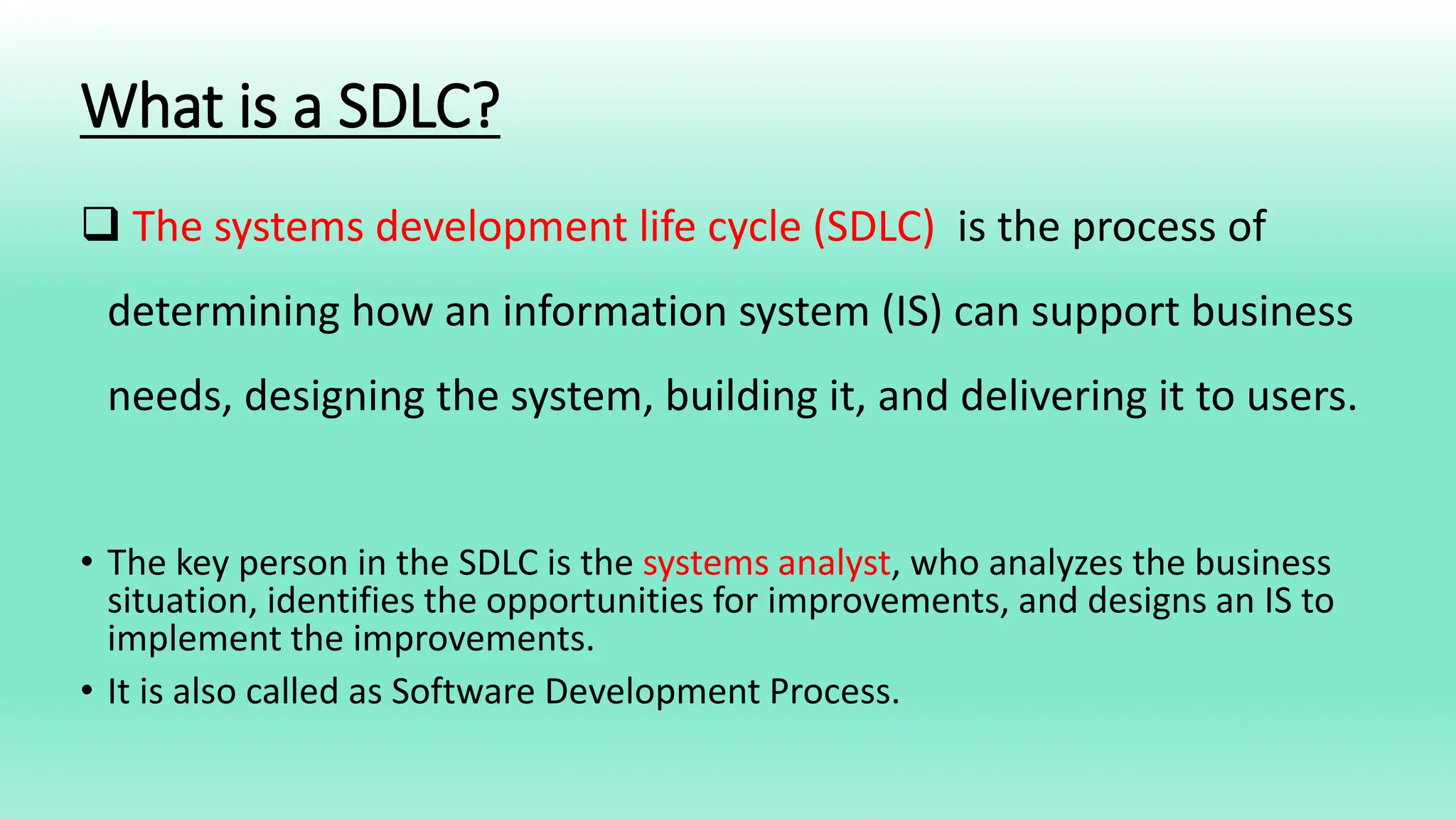
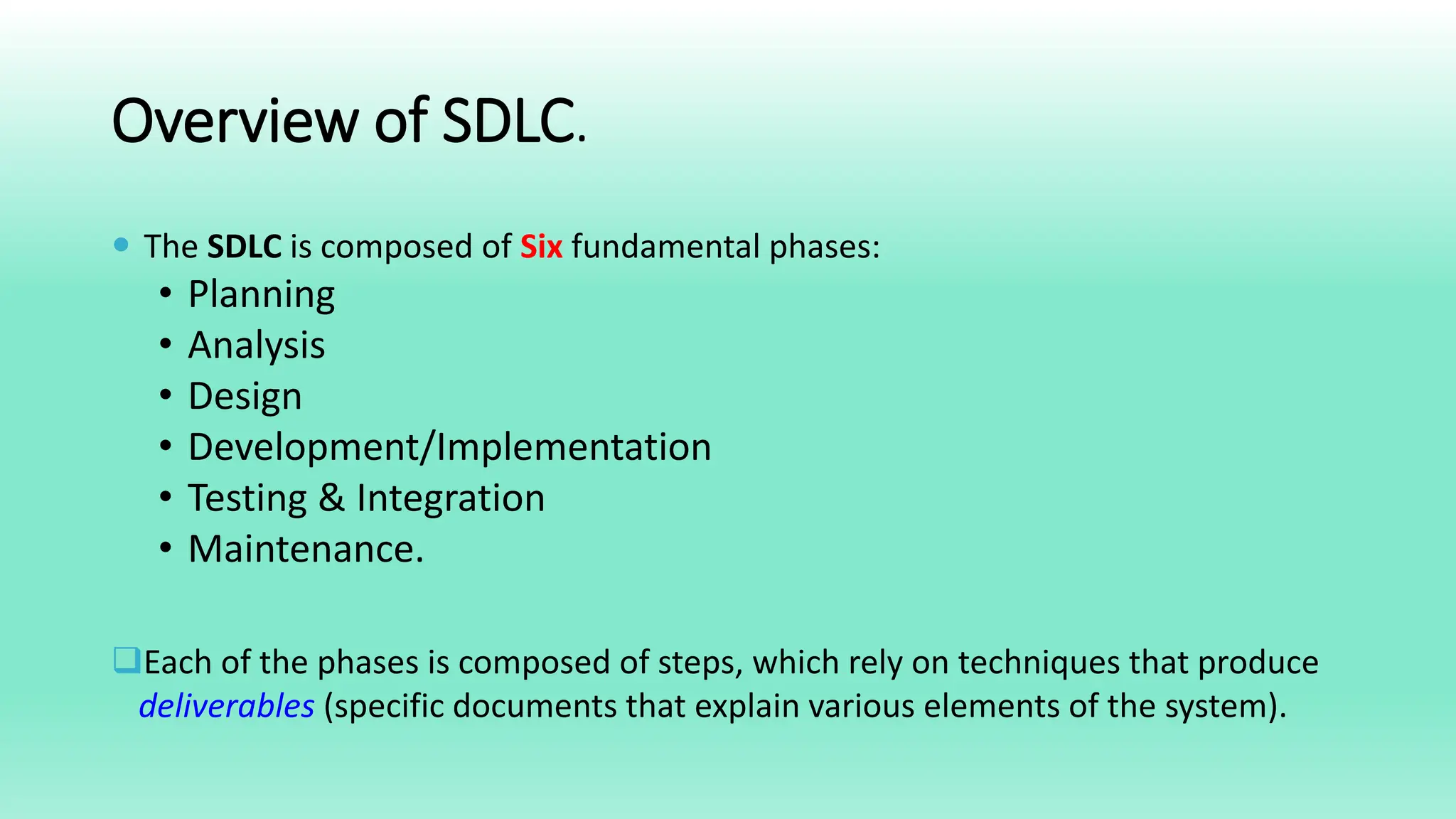
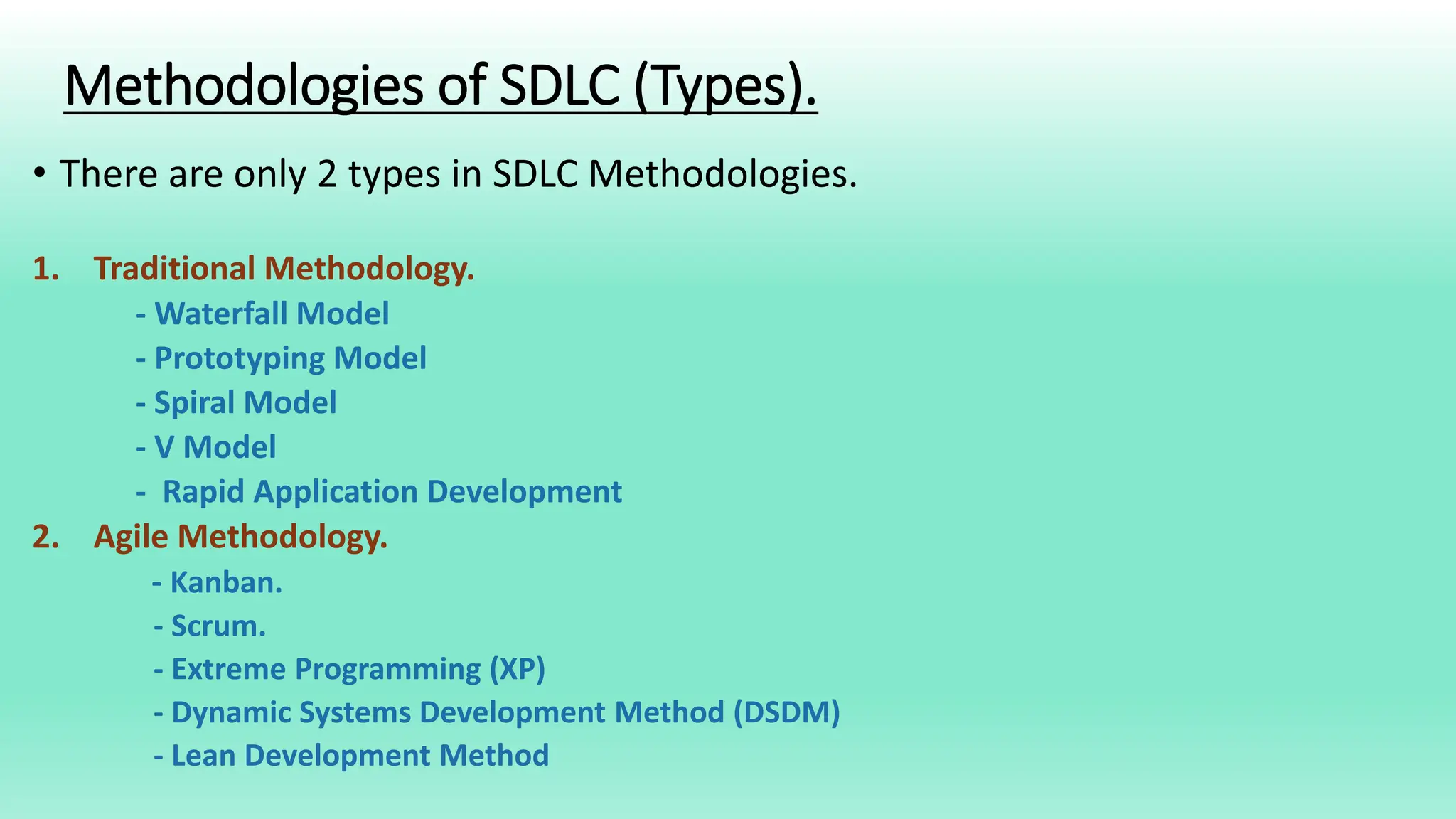
The Systems Development Life Cycle (SDLC) is a process for developing information systems that includes six key phases: planning, analysis, design, development/implementation, testing & integration, and maintenance. Each phase focuses on specific questions and tasks essential for building a system that meets business needs, and involves methodologies such as traditional and agile approaches. Advantages of SDLC include enhanced control over projects, defined goals, and thorough documentation throughout the process.
![System Development Life Cycle
(SDLC)
Kavindu Chethiya Yakupitiya
BSc (Hons) IT [KDU] , PGD In Cyber Security [SLIIT] , MSc (Hons) in Cyber Security - Reading [SLIIT]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sdlclecture2-240531142407-154a10ad/75/System-development-life-cycle-SDLC-pdf-1-2048.jpg)