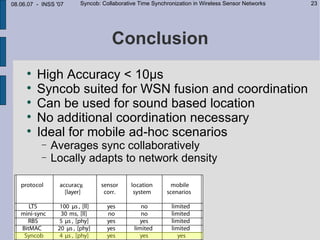
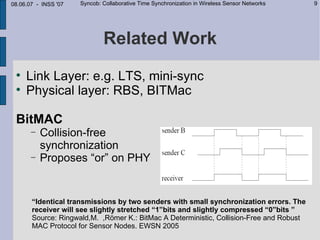
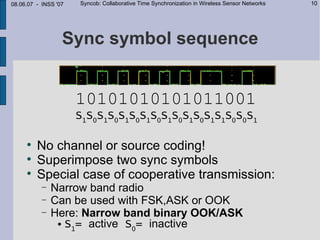
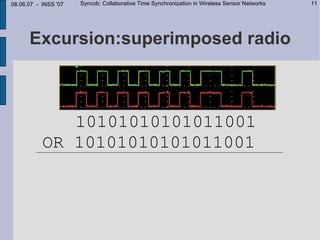
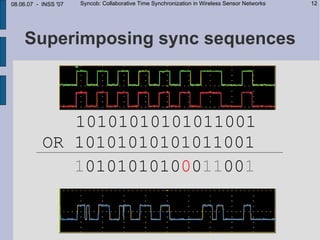
This document describes Syncob, a collaborative time synchronization technique for wireless sensor networks. Syncob allows nodes to synchronize by sending synchronization symbols simultaneously, averaging the offsets. This avoids conflicts between synchronization transmissions. The document motivates Syncob by describing applications requiring accurate synchronization like collaborative sensing and ultrasound location. It also discusses related work and outlines the Syncob algorithm, addressing issues like distributed operation, handling time shifts, and periodic resynchronization. An implementation on Particle sensor nodes achieves synchronization accuracy below 10 microseconds. Syncob is well-suited for sensor network applications involving fusion and coordination in mobile ad-hoc networks.






![08.06.07 - INSS '07 Syncob: Collaborative Time Synchronization in Wireless Sensor Networks 21
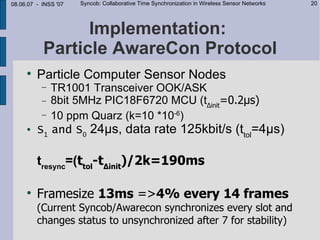
Implementation:
Sync propagation time
Sync to network Sync to single partner
1
cumulated probability functions
0 20 Delay [ms] 100](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/syncobfinal2-120404100027-phpapp02/85/Syncob-21-320.jpg)