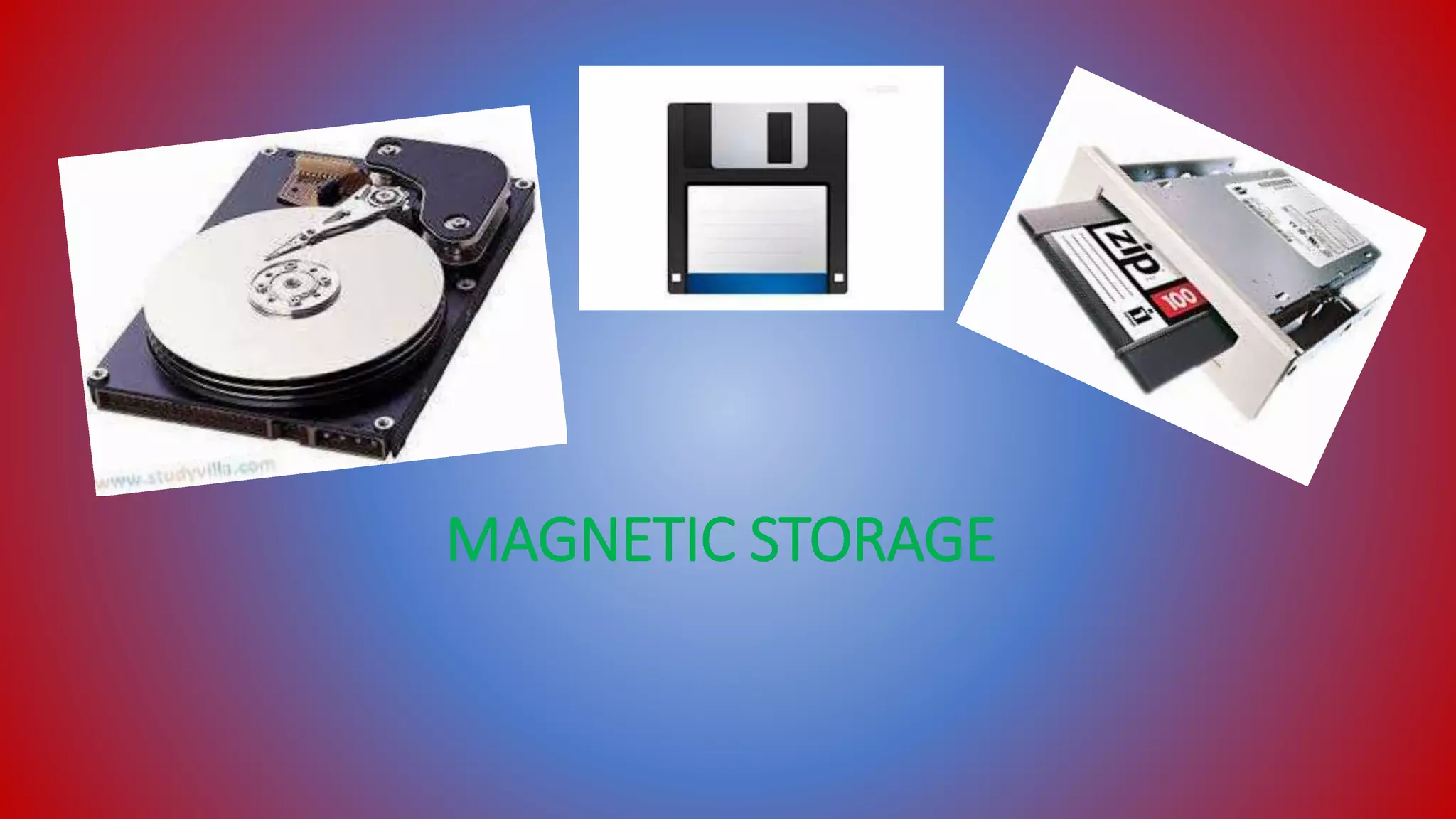
The document presents information on synchronization, asynchronous communication, synchronous communication, and external storage devices. It discusses how synchronization joins multiple processes and requires an established rhythm between devices. Asynchronous communication has no global clock and encodes timing in symbols, while synchronous communication requires synchronized clocks running at the same rate. The document also describes different types of external storage devices, including magnetic storage using disks, optical storage using laser light technology, and solid state storage like flash memory.