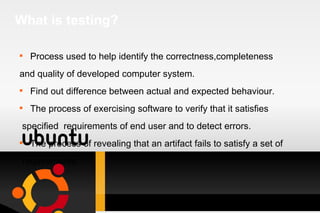
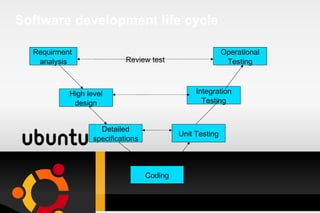
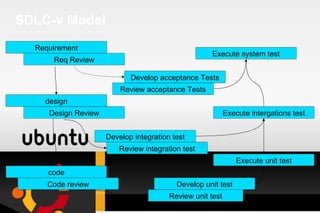
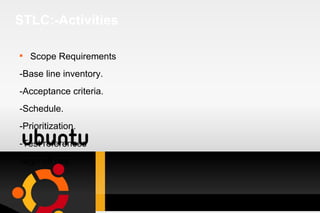
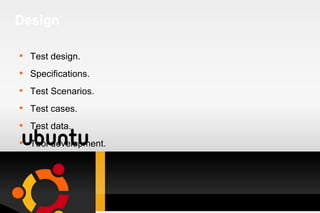
Testing is a process used to identify errors, ensure quality, and verify that a system meets its requirements. It involves executing a program or system to evaluate its attributes and determine if it functions as intended. There are various types of testing such as unit testing, integration testing, system testing, and acceptance testing. An effective test approach considers objectives, activities, resources, and methods to thoroughly test a system. Requirements analysis is also important to ensure testing covers all necessary functionality.