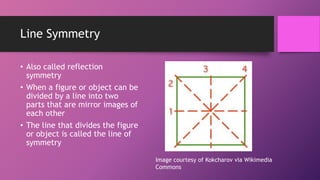
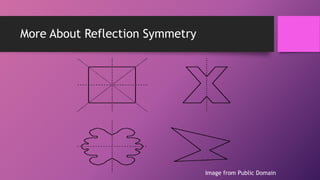
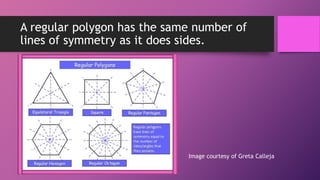
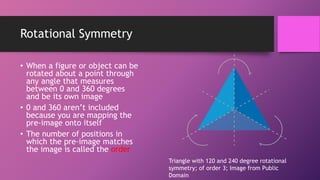
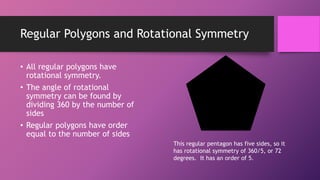
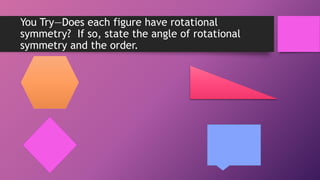
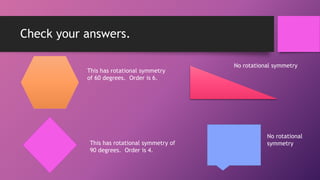
This document discusses two types of geometric symmetry: line symmetry and rotational symmetry. It defines line symmetry as when a figure can be divided into two mirror image parts by a line, called the line of symmetry. Rotational symmetry occurs when a figure looks the same after being rotated partway around a center point. Regular polygons have both types of symmetry: their number of lines of symmetry equals their number of sides, and their rotational symmetry angle is 360 degrees divided by the number of sides. The document provides examples and exercises to help understand and identify these symmetries.