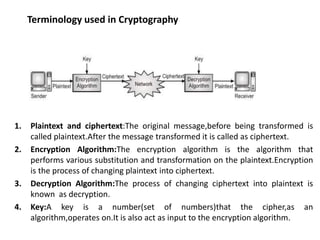
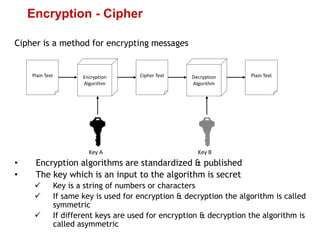
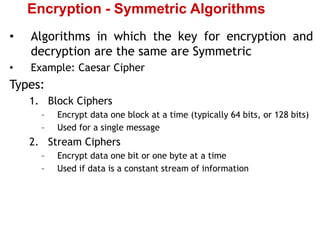
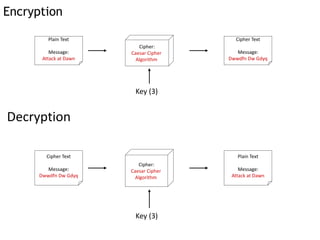
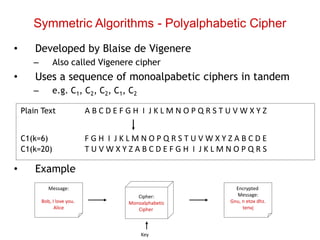
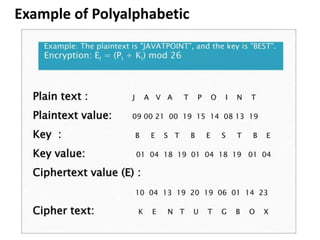
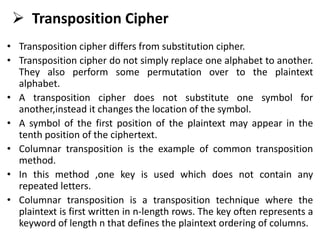
Cryptography is the practice of securing information through coding, ensuring only intended recipients can access it. It involves processes such as encryption (converting plaintext to ciphertext) and decryption (turning ciphertext back to plaintext) using keys. There are two main types of cryptographic systems: symmetric key encryption, using the same key for both processes, and asymmetric key encryption, which uses different keys.