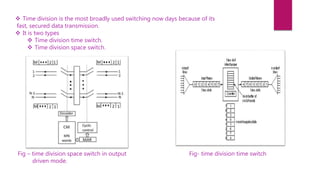
The document discusses telecommunication switching networks, focusing on the evolution and classification of switching systems, including Strowger, crossbar, and time/space division switching. It highlights the transition from point-to-point connections to automatic switching systems for better efficiency and security in communication. Additionally, it anticipates future advancements in program control switching techniques.