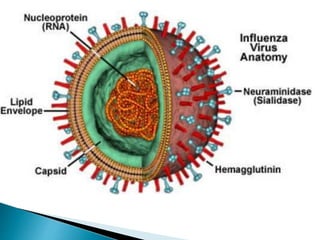
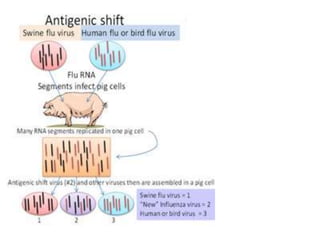
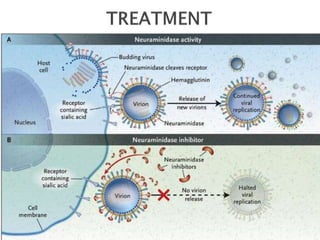
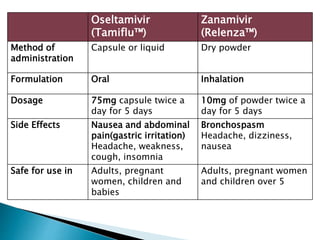
Swine flu is a respiratory disease caused by influenza viruses that infect pigs and can be transmitted to humans. The 2009 outbreak was caused by the H1N1 virus and declared a pandemic by the WHO. Swine flu viruses have segmented genomes allowing genetic material to be exchanged between human and pig viruses. It is transmitted through droplets from coughs or sneezes but not through eating pork. Symptoms include fever, cough, sore throat and fatigue. Testing and PCR assays can confirm swine flu infection. Oseltamivir and zanamivir are used to treat it. Vaccines produced in eggs or cells are used to prevent spread.