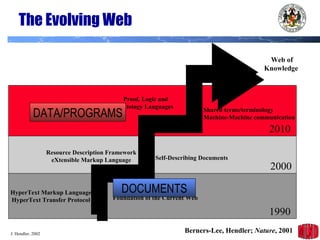
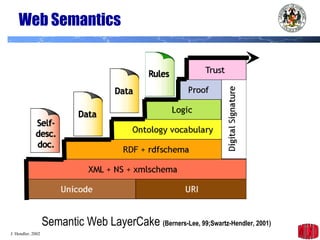
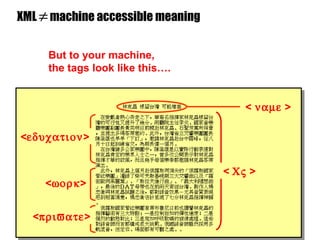
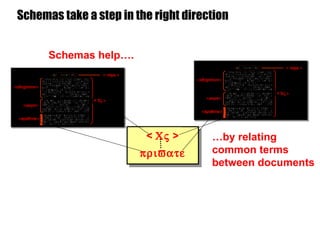
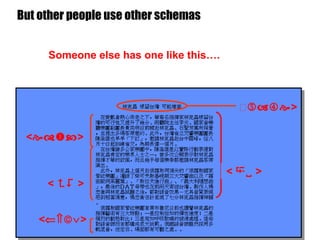
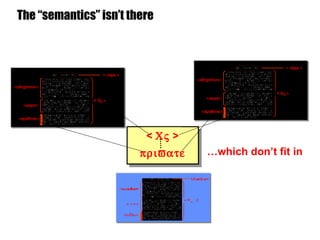
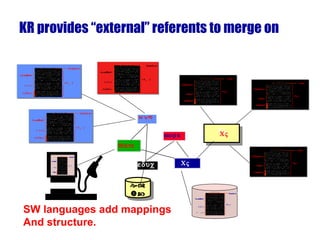
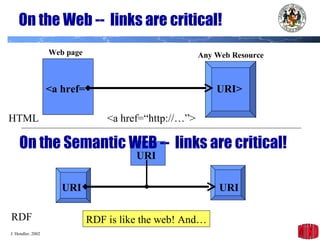
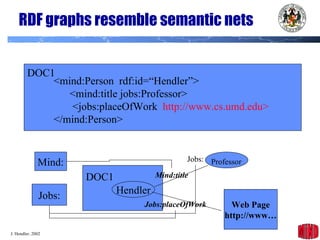
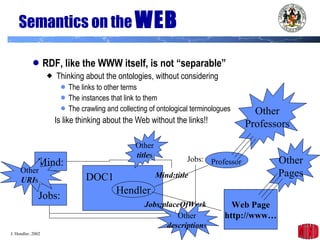
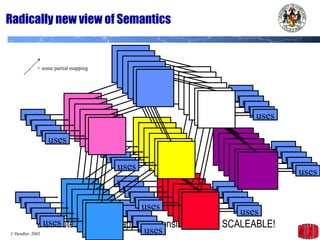
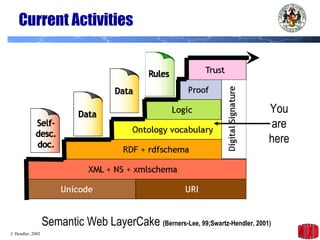
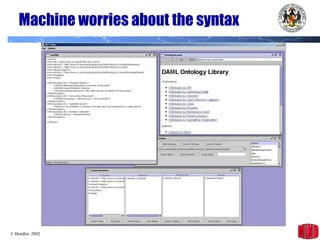
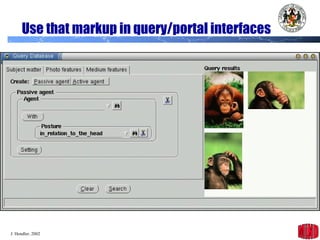
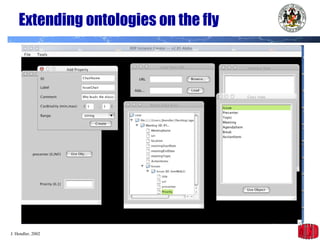
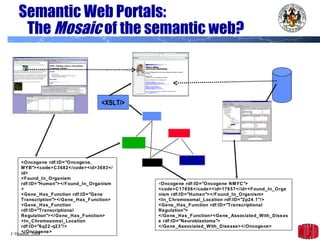
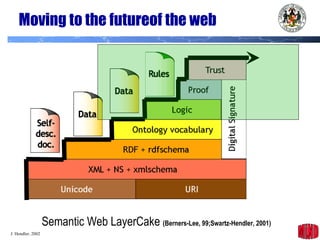
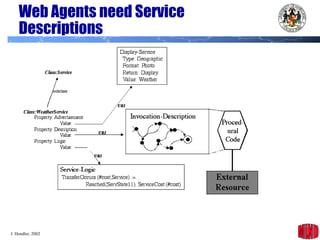
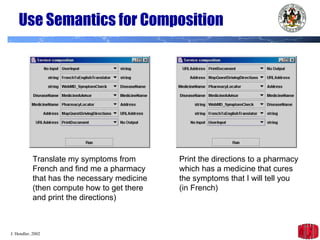
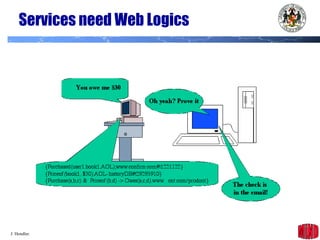
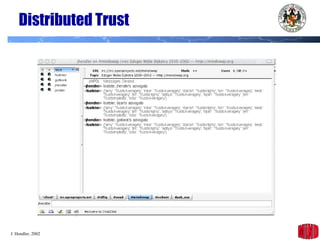
The document introduces the Semantic Web and its goals of making web content machine-readable through the use of ontologies and semantic annotations. It describes the evolution of the web from human-readable documents and links to machine-processable data through technologies like XML, RDF, and OWL. It outlines current work by the W3C to develop standards and an active working group to develop the Semantic Web.