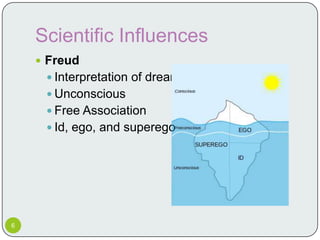
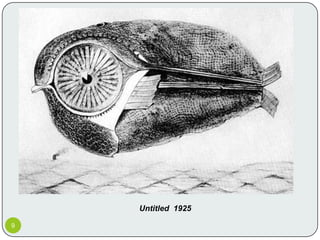
Surrealism emerged from Dada and was founded by André Breton in the 1920s. It aimed to access the unconscious mind through automatism and dream-like imagery. Major surrealist artists included Salvador Dali, Max Ernst, René Magritte, and Joan Miró. They drew influence from Freudian psychoanalysis and sought to challenge rational thought by juxtaposing reality and fantasy. While influential, surrealism has also been criticized for its treatment of women and misuse of psychoanalysis.