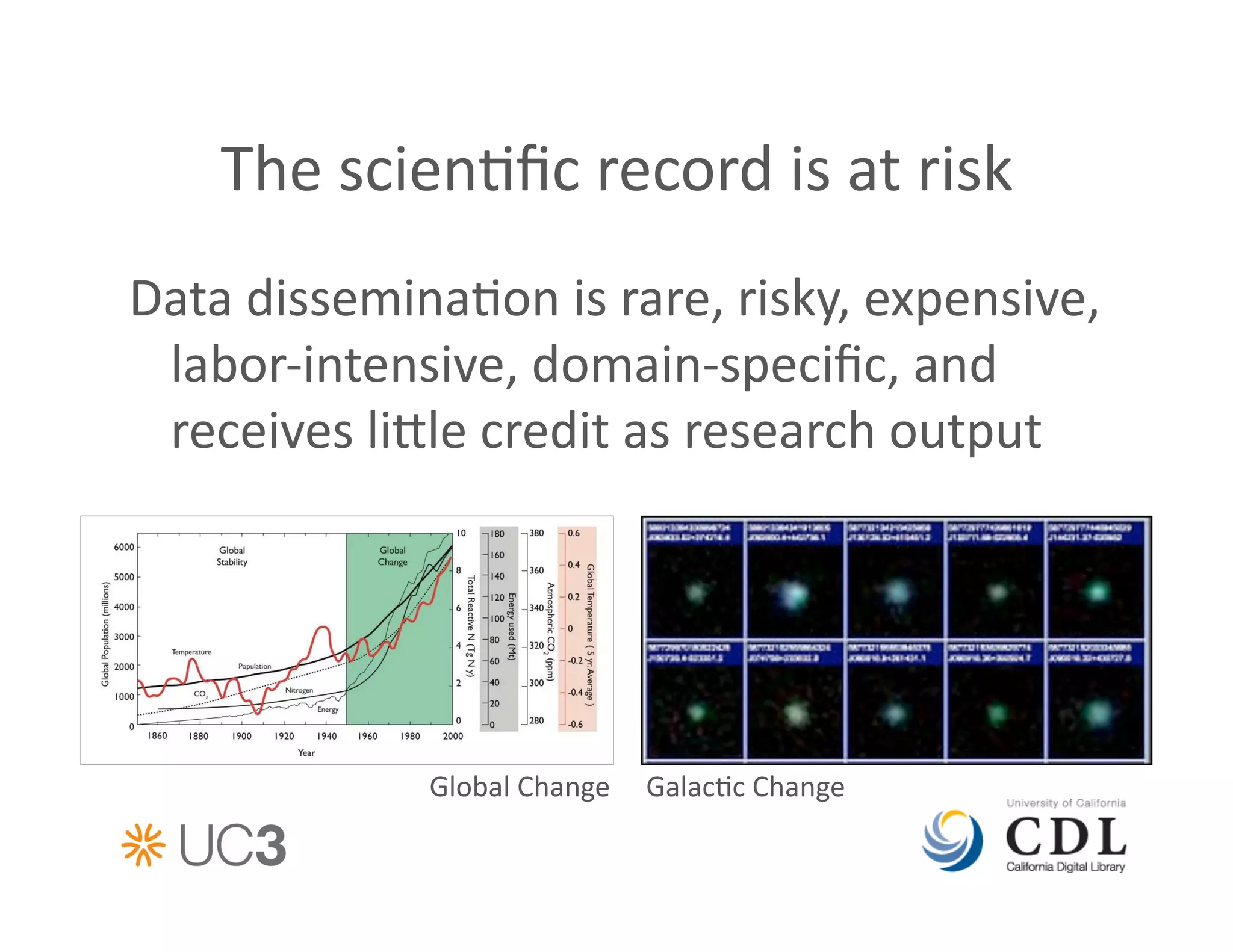
The document discusses data curation services provided by the California Digital Library (CDL). It describes CDL's Merritt repository for stable storage, EZID for assigning persistent identifiers, DMPTool for creating data management plans, and tools for data discovery, citation, and preservation cost modeling. CDL supports the full data lifecycle from deposition to long-term curation and access. The document outlines how CDL's services have expanded over time to meet the growing needs of data producers and a changing technological landscape.










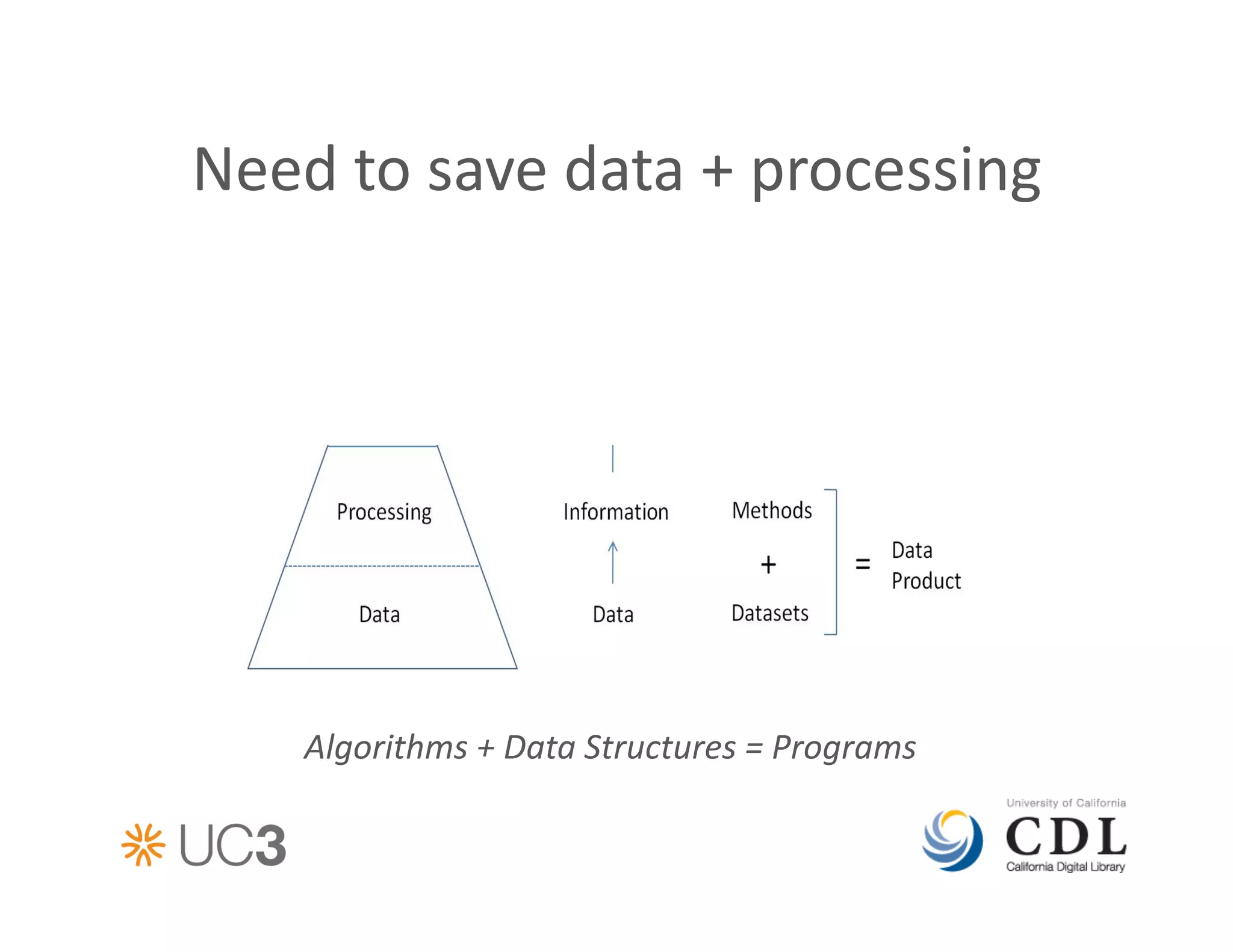




![A
data
cura&on
approach
at
CDL
• New
“data
paper”
publishing
model
[GBMF]
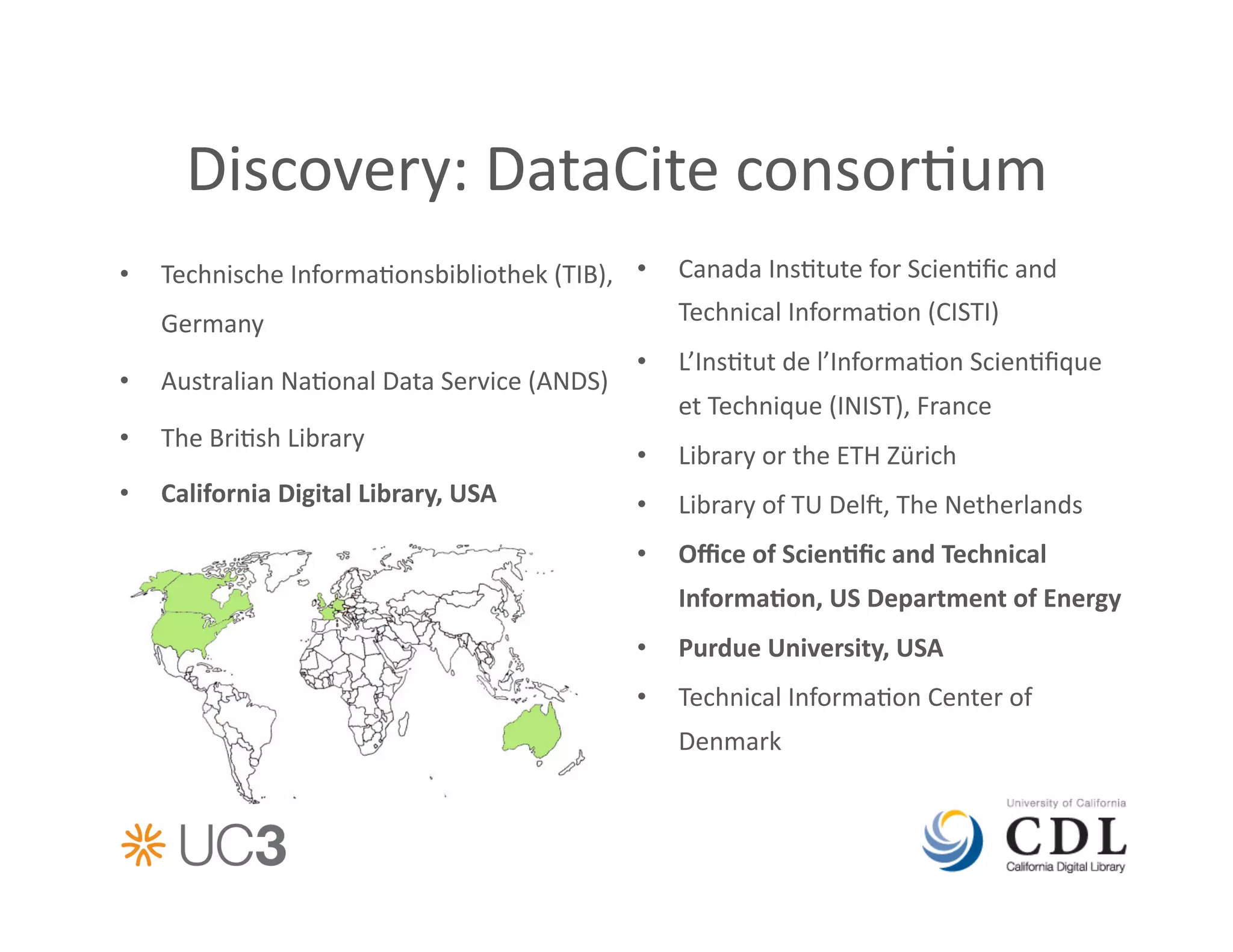
• DataCite
consor&um
and
cita&on
standards
• Other
fronts:
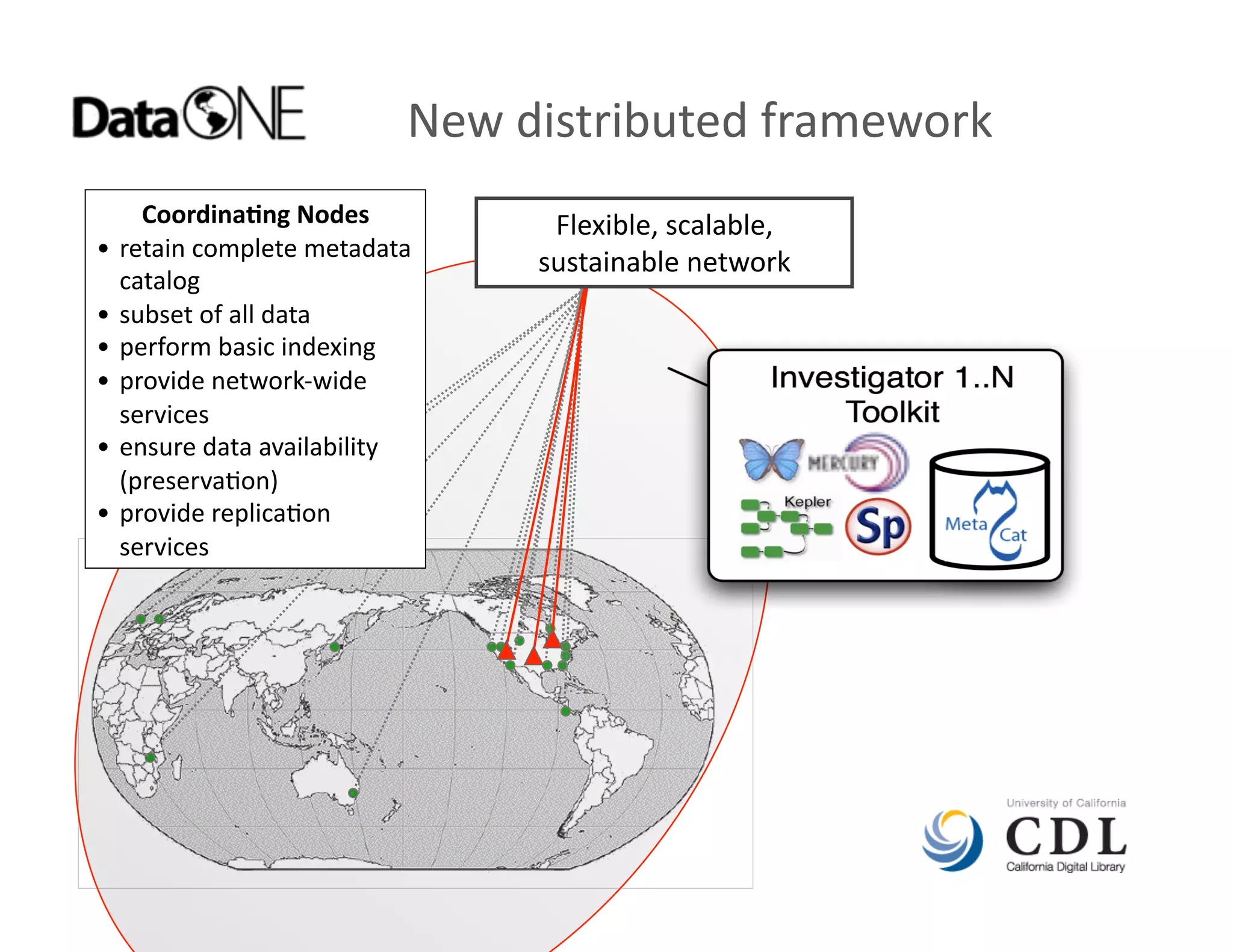
• DataONE
global
data
network
[NSF]
• Merri:
general-‐purpose
data
repository
• EZID:
scheme-‐agnos&c
&
de-‐coupled
crea&on,
resolu&on,
and
management
of
persistent
ids
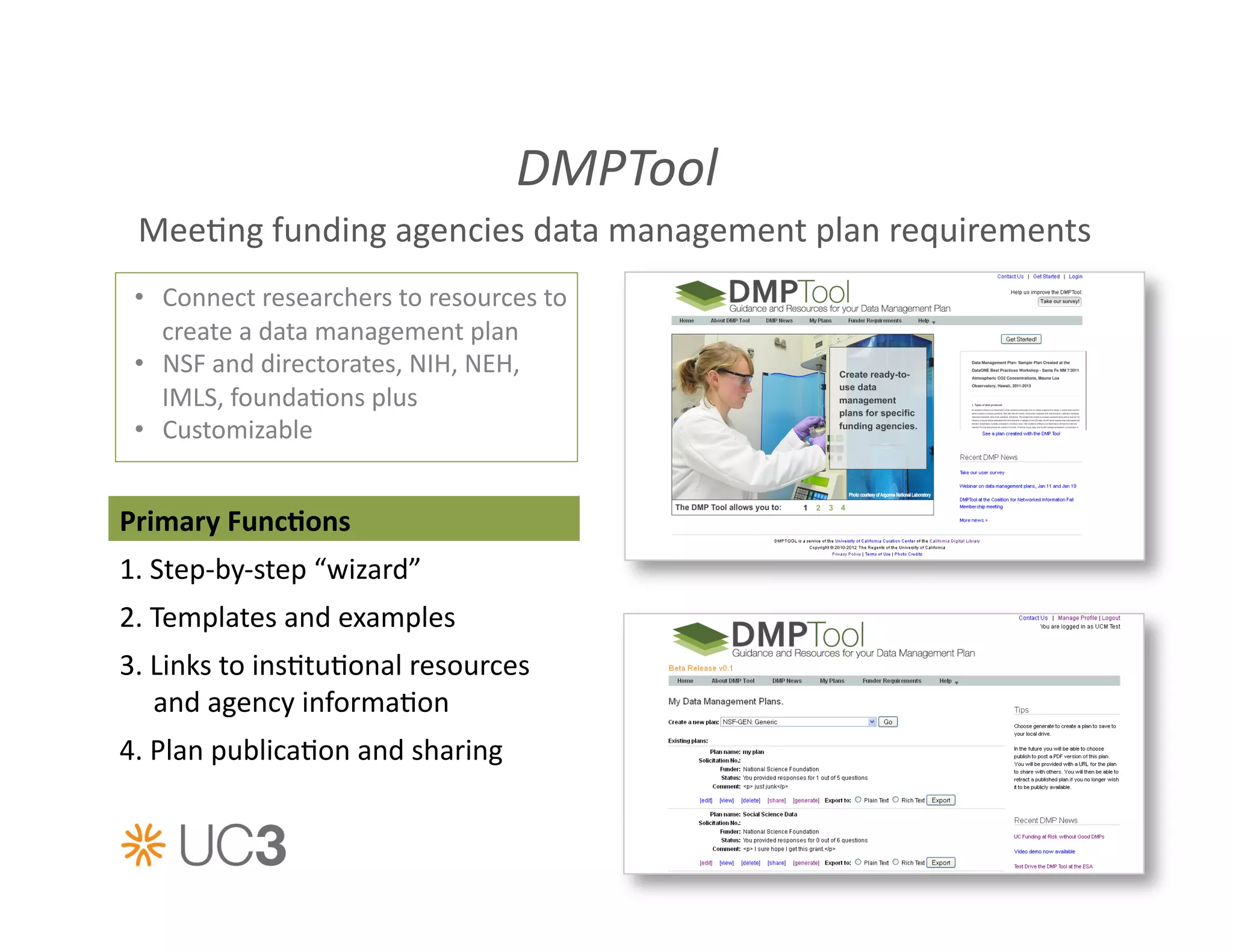
• Data
management
plan
generator
• Web
archiving
service
[Library
of
Congress]
• Open-‐source
Excel
add-‐in
[MS
Research
&
GBMF]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/jakcdldatacuration-120523181012-phpapp01/75/Supporting-Data-Rich-Research-on-Many-Fronts-24-2048.jpg)
