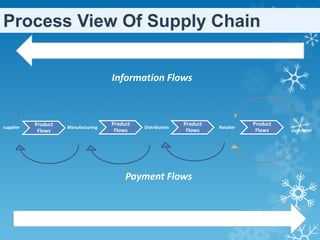
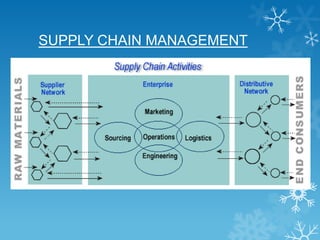
Supply chain management involves integrating suppliers, factories, warehouses, and stores to efficiently produce and distribute the right products in the right quantities to the right locations at the right time. The goals are to minimize total system costs and satisfy customer needs. A supply chain includes suppliers, internal operations like manufacturing, distribution systems, and end users. It involves the flow of materials, services, information, and funds. Effective supply chain management provides benefits like revenue growth, lower costs, and better asset usage.