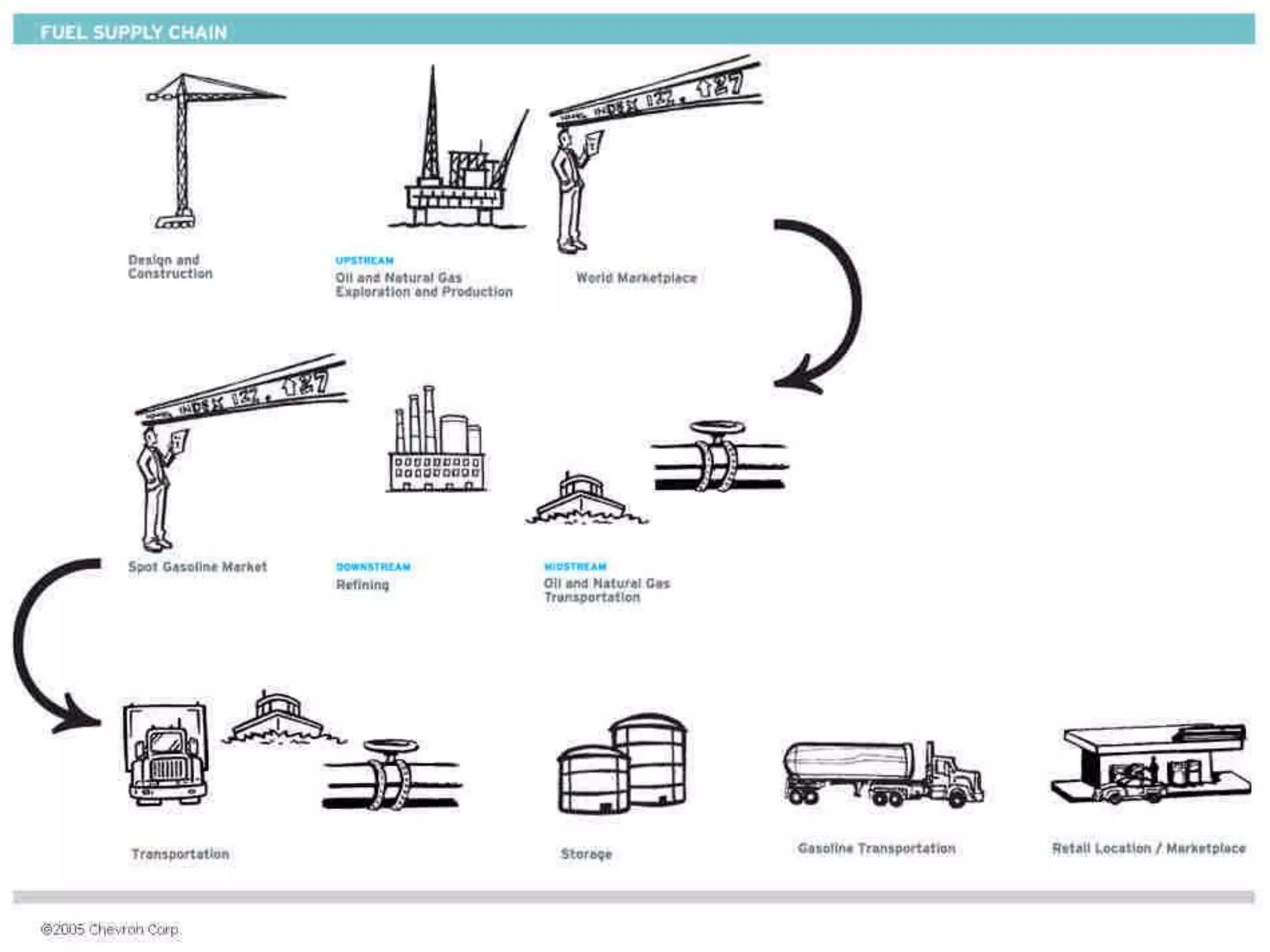
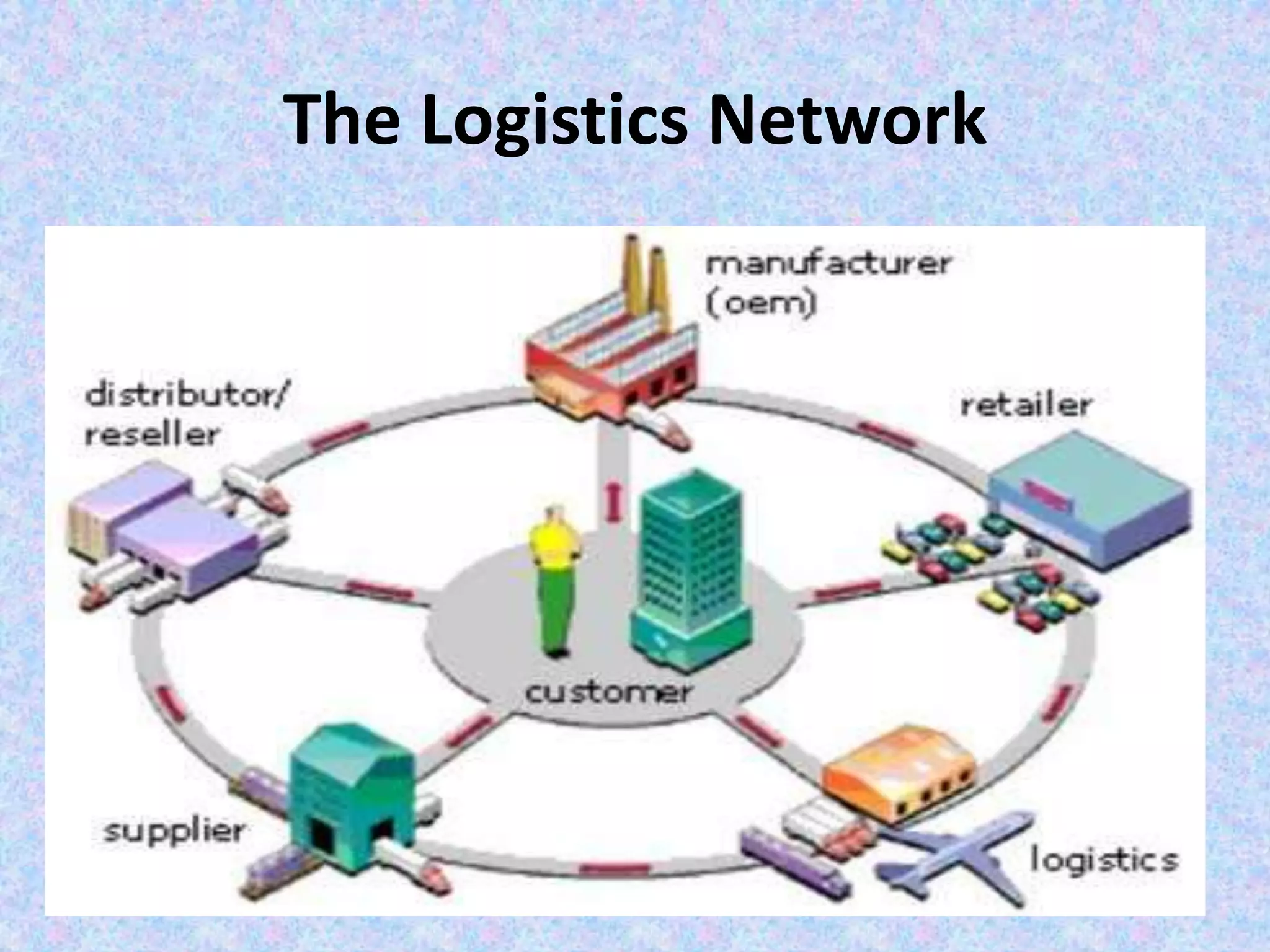
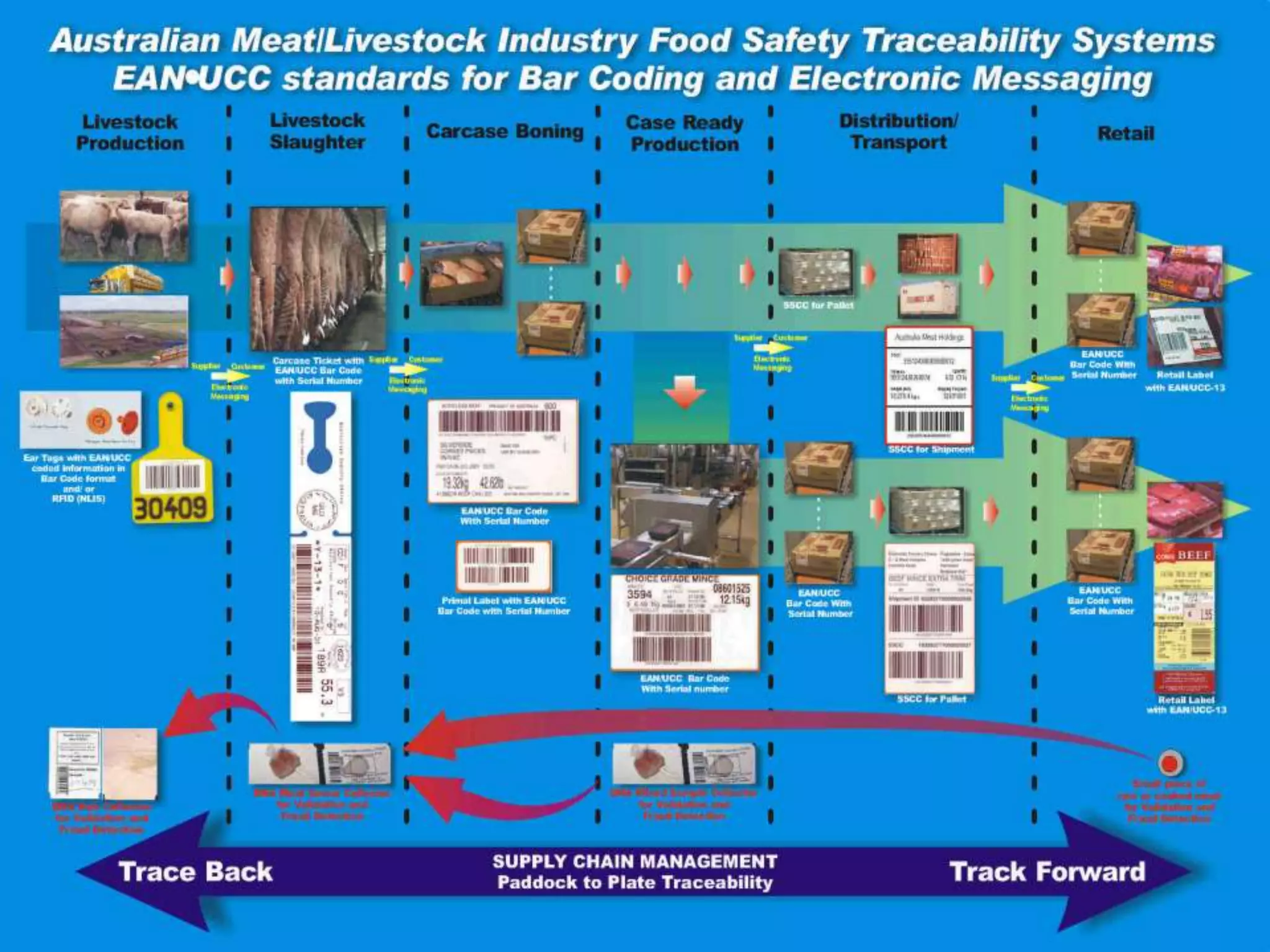
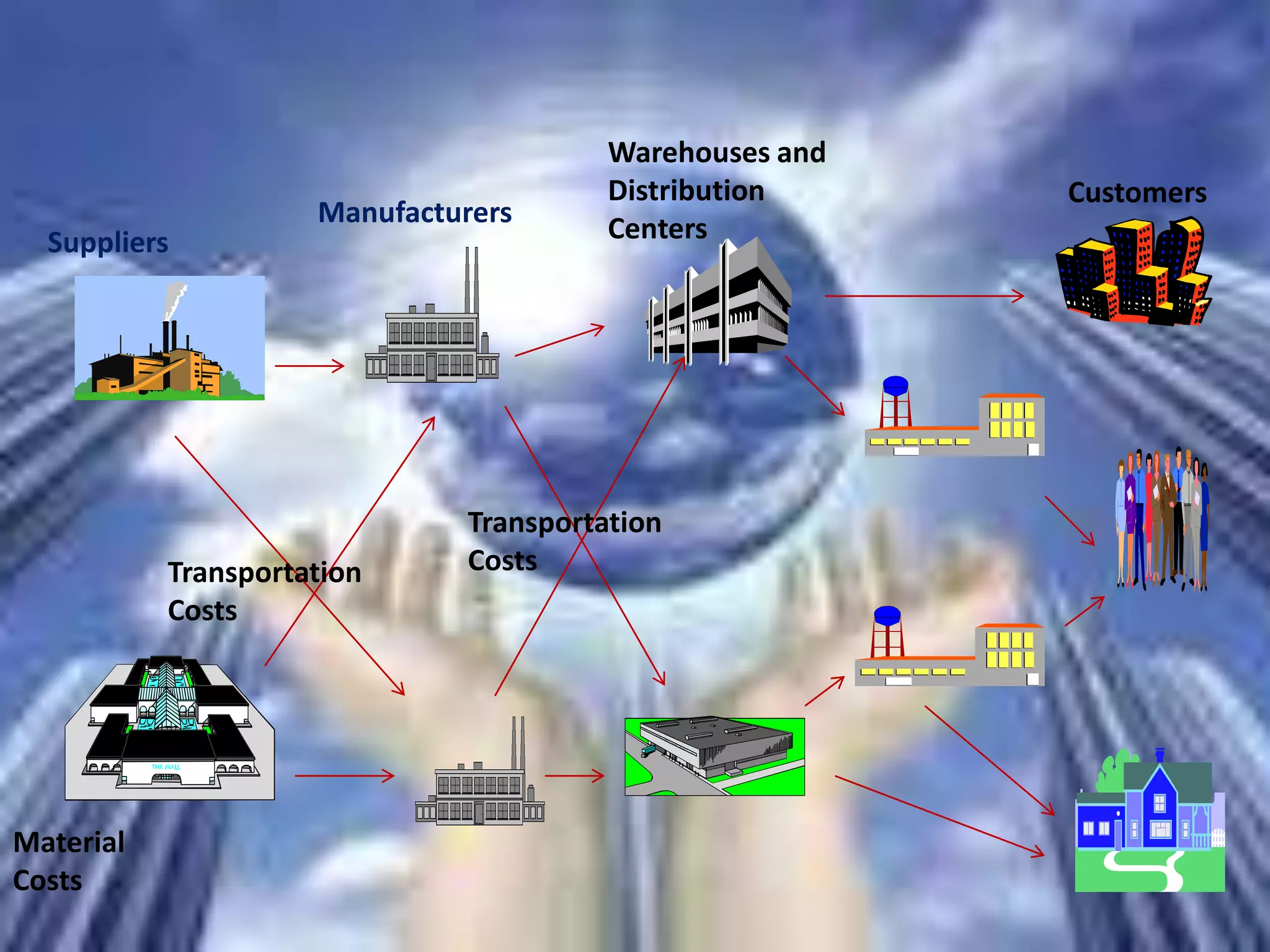
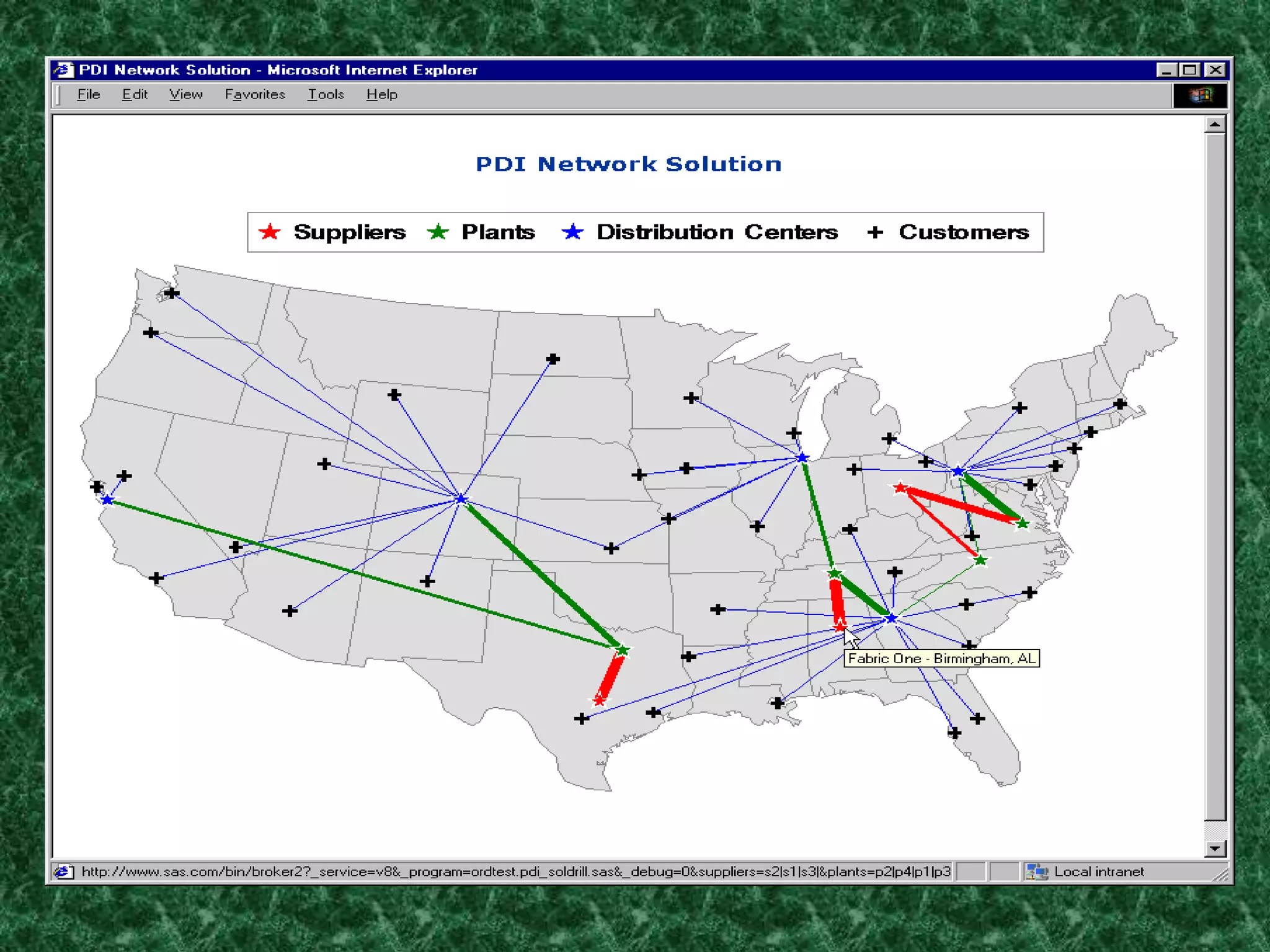
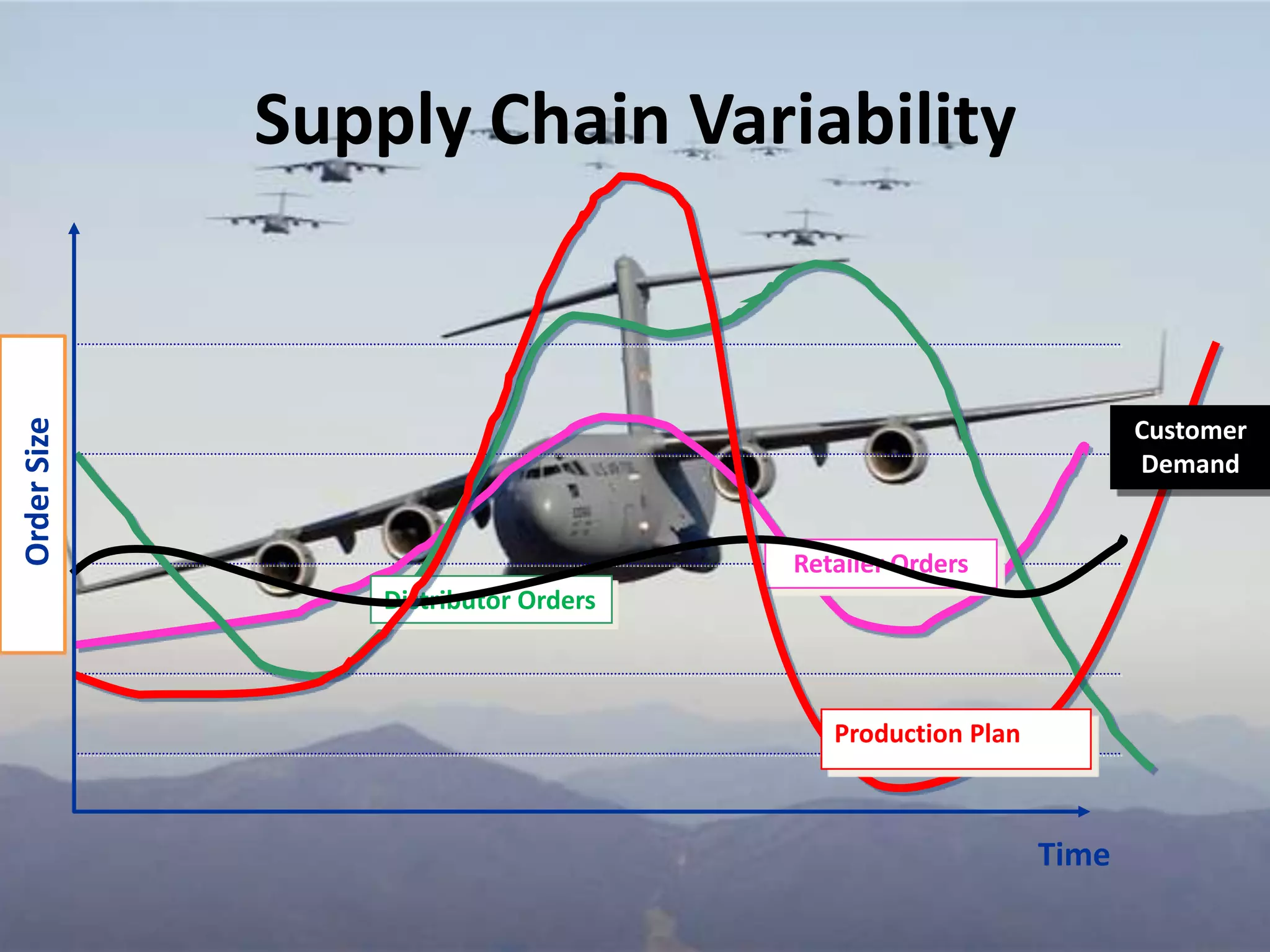
The document provides an introduction to supply chain management. It defines a supply chain as the system of suppliers, manufacturers, transportation, distributors, and vendors that transforms raw materials into final products for customers. The goal of supply chain management is to efficiently integrate these entities to minimize costs and satisfy customer demands. It discusses challenges like conflicting objectives between different parts of the supply chain, uncertainty, and variability over time. It also outlines key issues and new concepts in supply chain management.