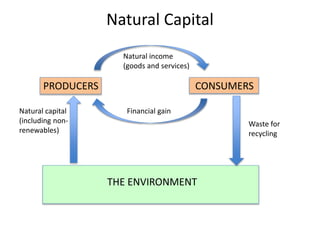
Natural capital refers to the resources available for human exploitation including those in the biosphere, lithosphere, and atmosphere. Some natural capital such as timber and food crops is renewable as it can regenerate quickly through natural processes like photosynthesis. Other resources like solar and geothermal energy are replenishable through abiotic processes. Fossil fuels and minerals are non-renewable as they cannot be replaced within human timescales. Natural capital provides both goods like timber and services like climate stabilization. Sustainability requires balancing the exploitation of renewable resources with their regeneration rates to ensure their availability for future generations.