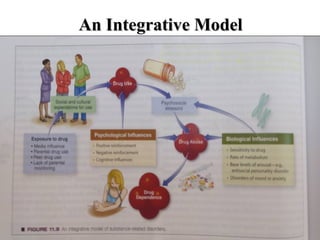
The document discusses substance-related disorders, covering their definitions, types, causes, treatments, and an Islamic perspective. It details various substance use disorders, including alcohol, opioids, and stimulants, alongside their psychological and physiological effects, withdrawal symptoms, and treatment approaches. Additionally, the document explores impulse control disorders and emphasizes the importance of psychosocial treatment and prevention strategies.