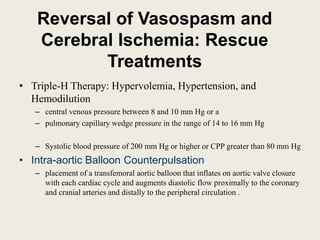
Cerebral vasospasm is a narrowing of cerebral arteries that occurs after subarachnoid hemorrhage, usually from a ruptured aneurysm. It develops in 50-90% of aneurysmal SAH cases on angiography but only 20-30% develop neurological deficits. Vasospasm typically begins 3-14 days after hemorrhage and can last up to 4 weeks. Risk is predicted by modified Fisher scale and thick subarachnoid blood. Transcranial Doppler is commonly used to screen for vasospasm. Prevention focuses on hydration, blood pressure control, nimodipine, and clot removal while treatments include "triple H" therapy and endovascular interventions like angiop