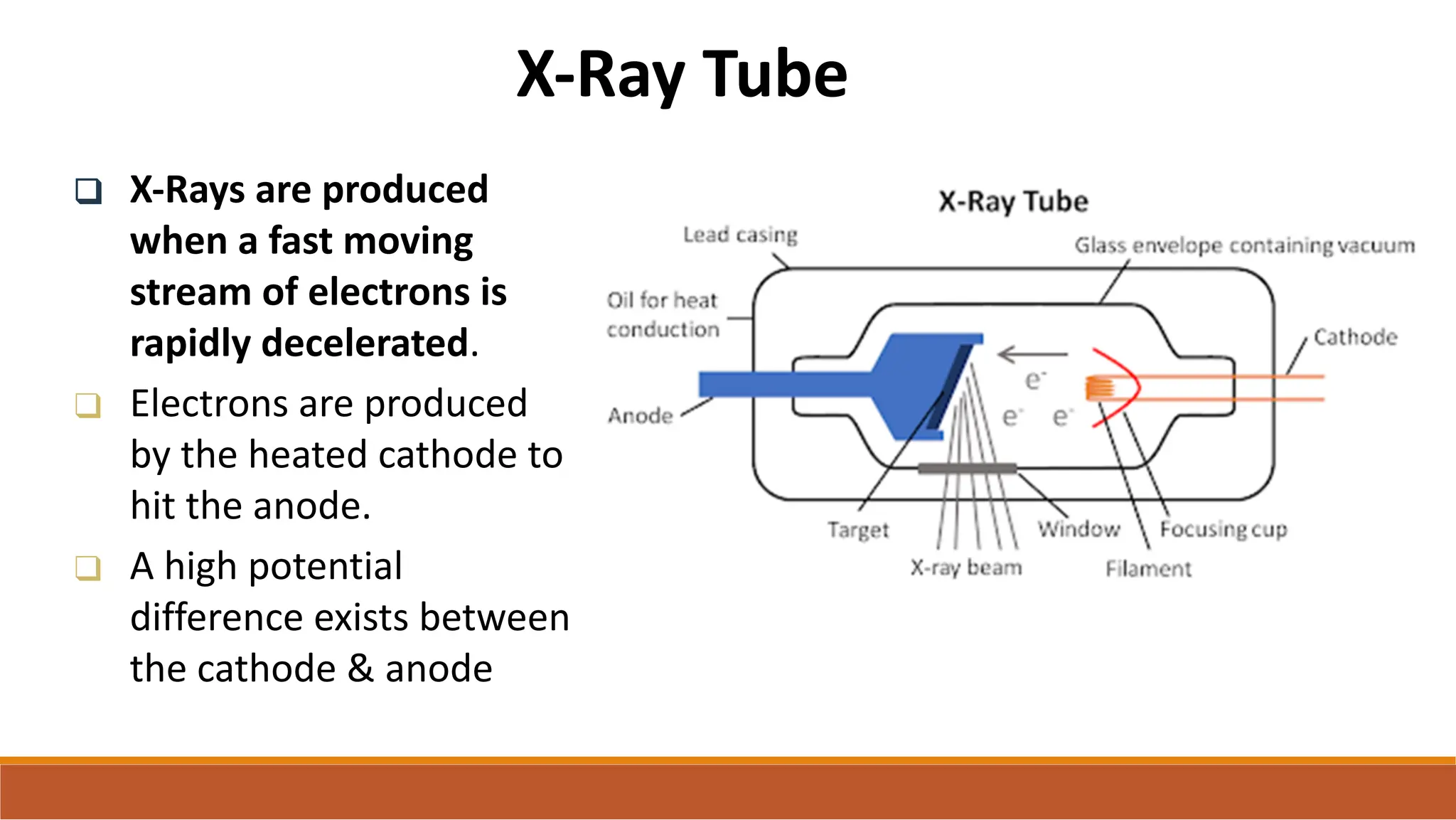
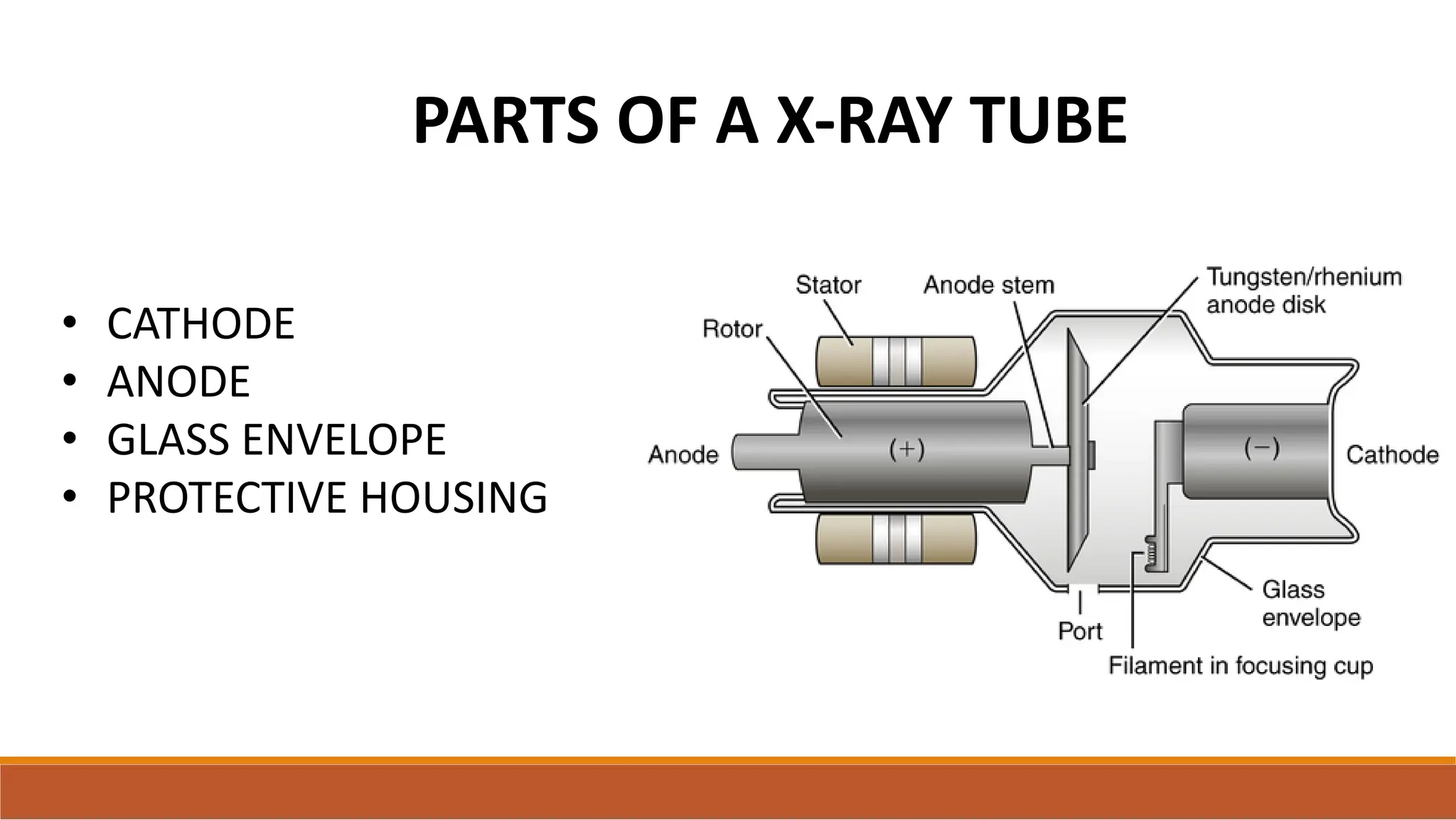
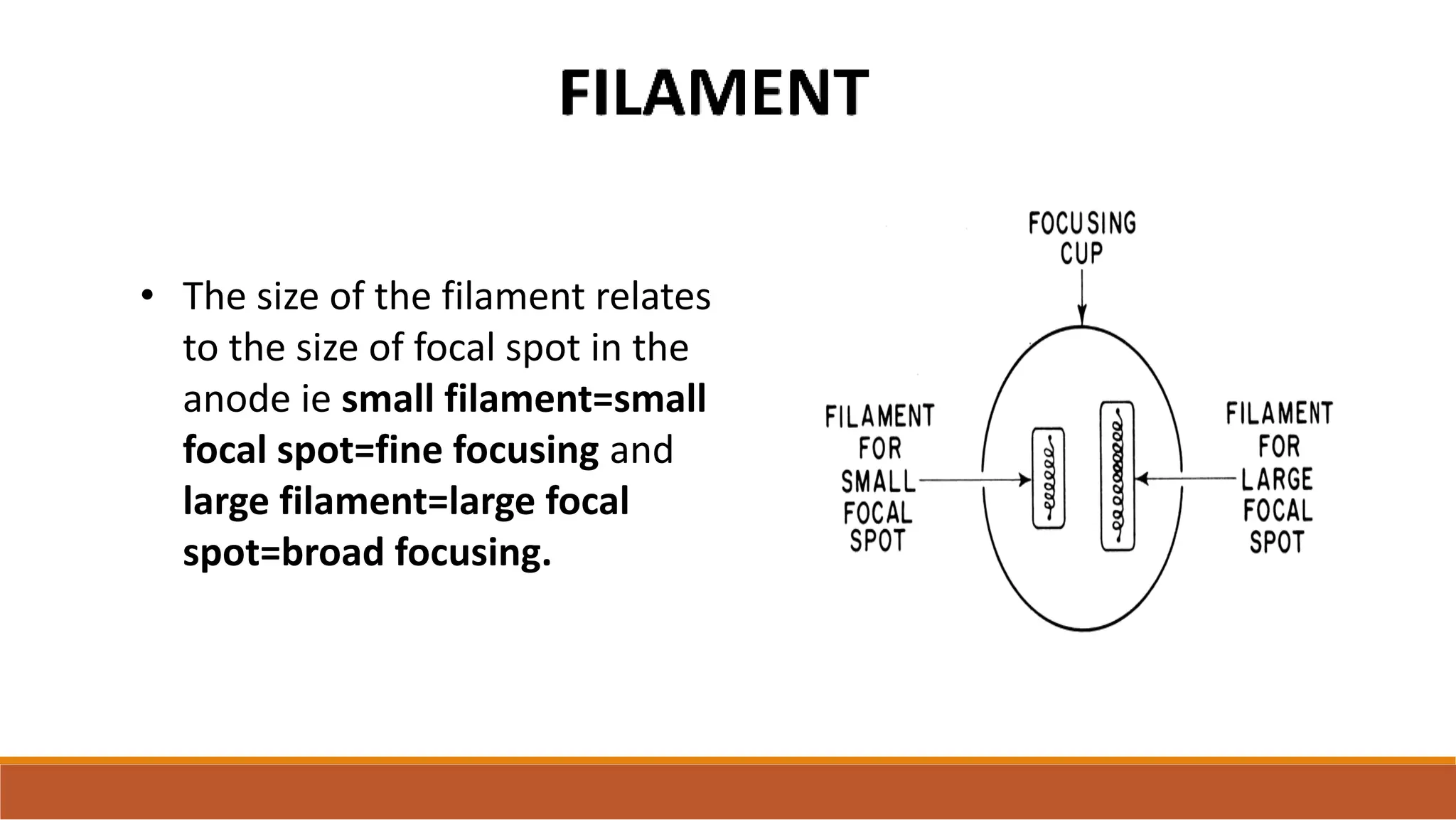
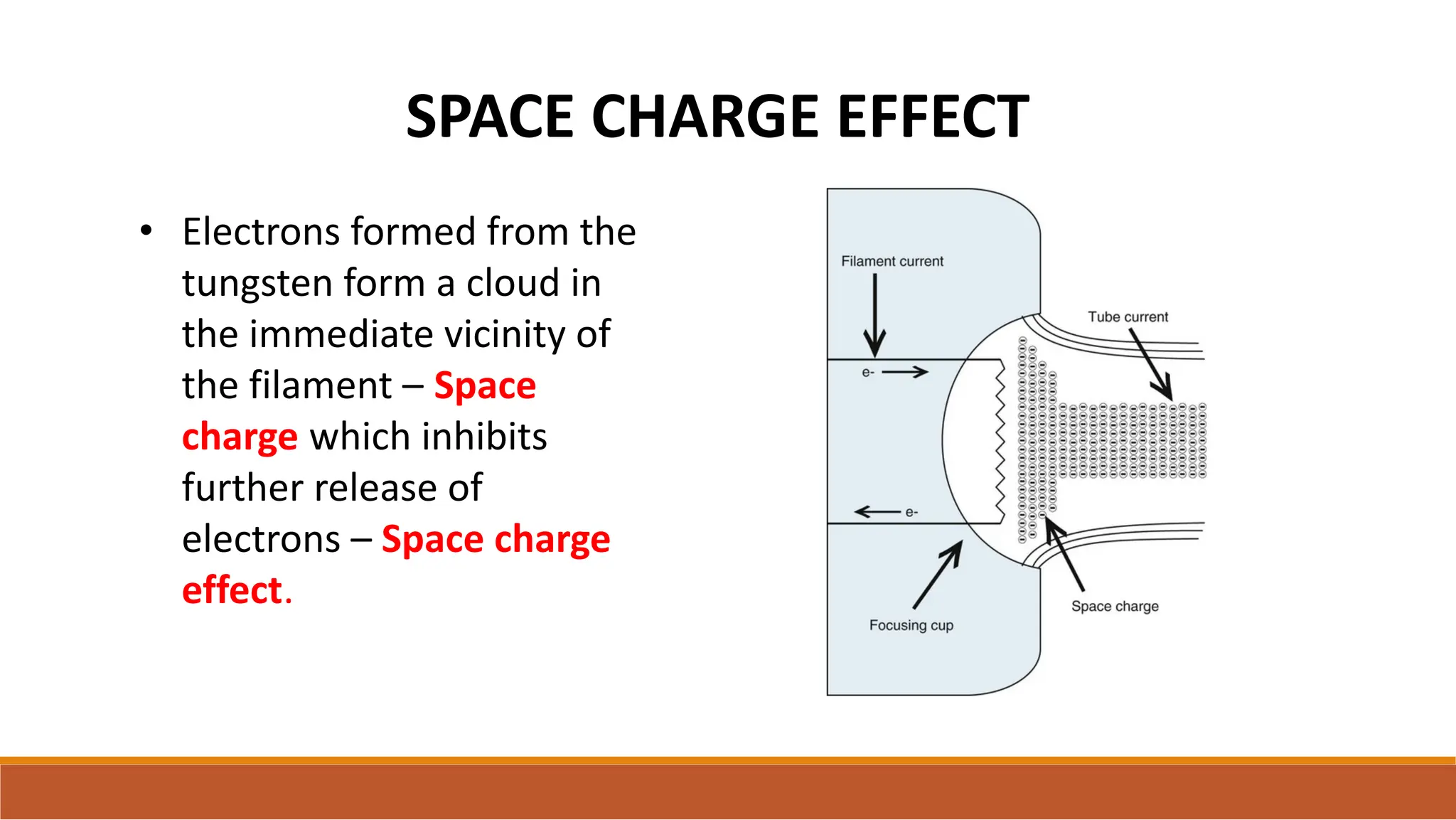
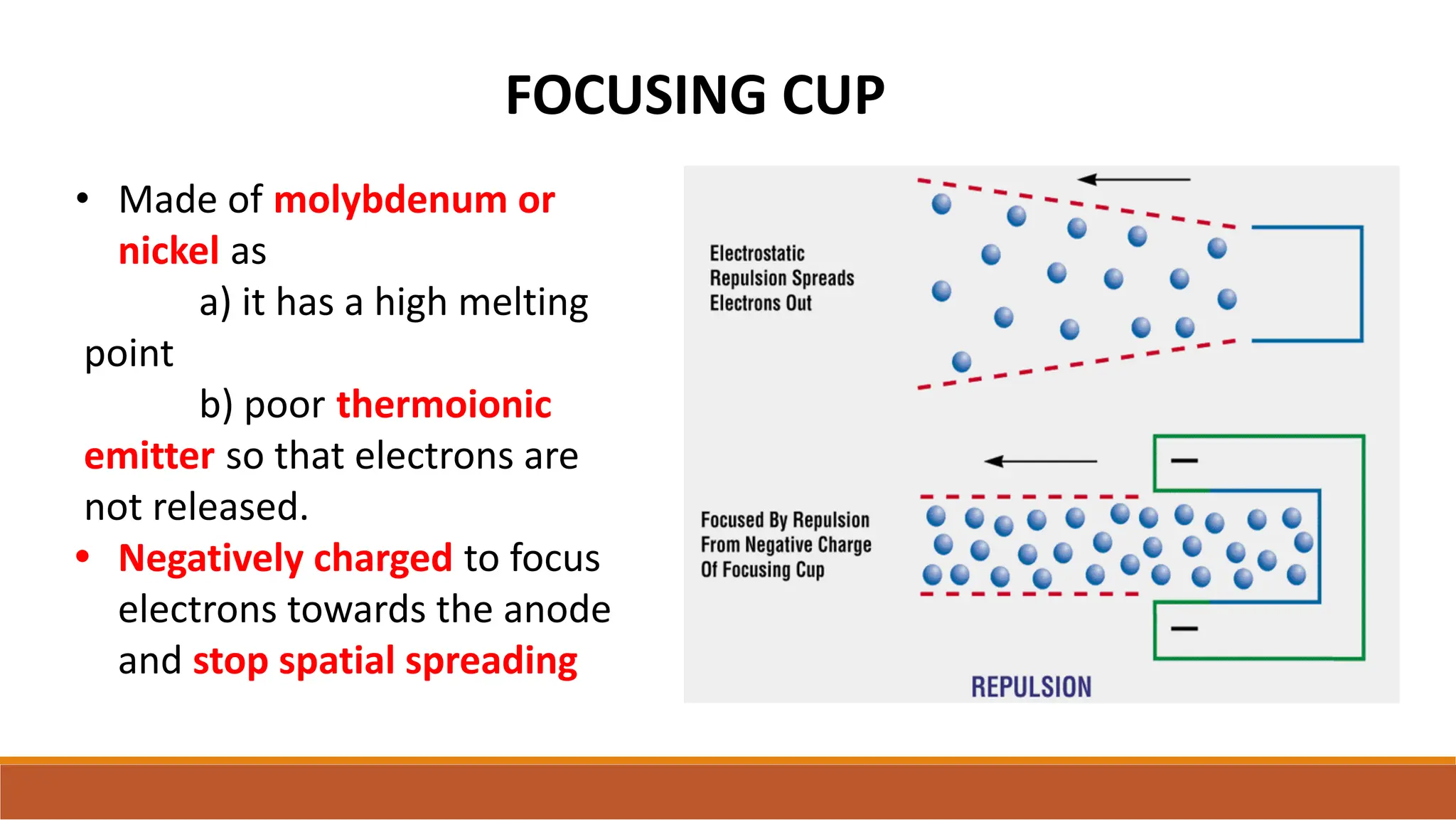
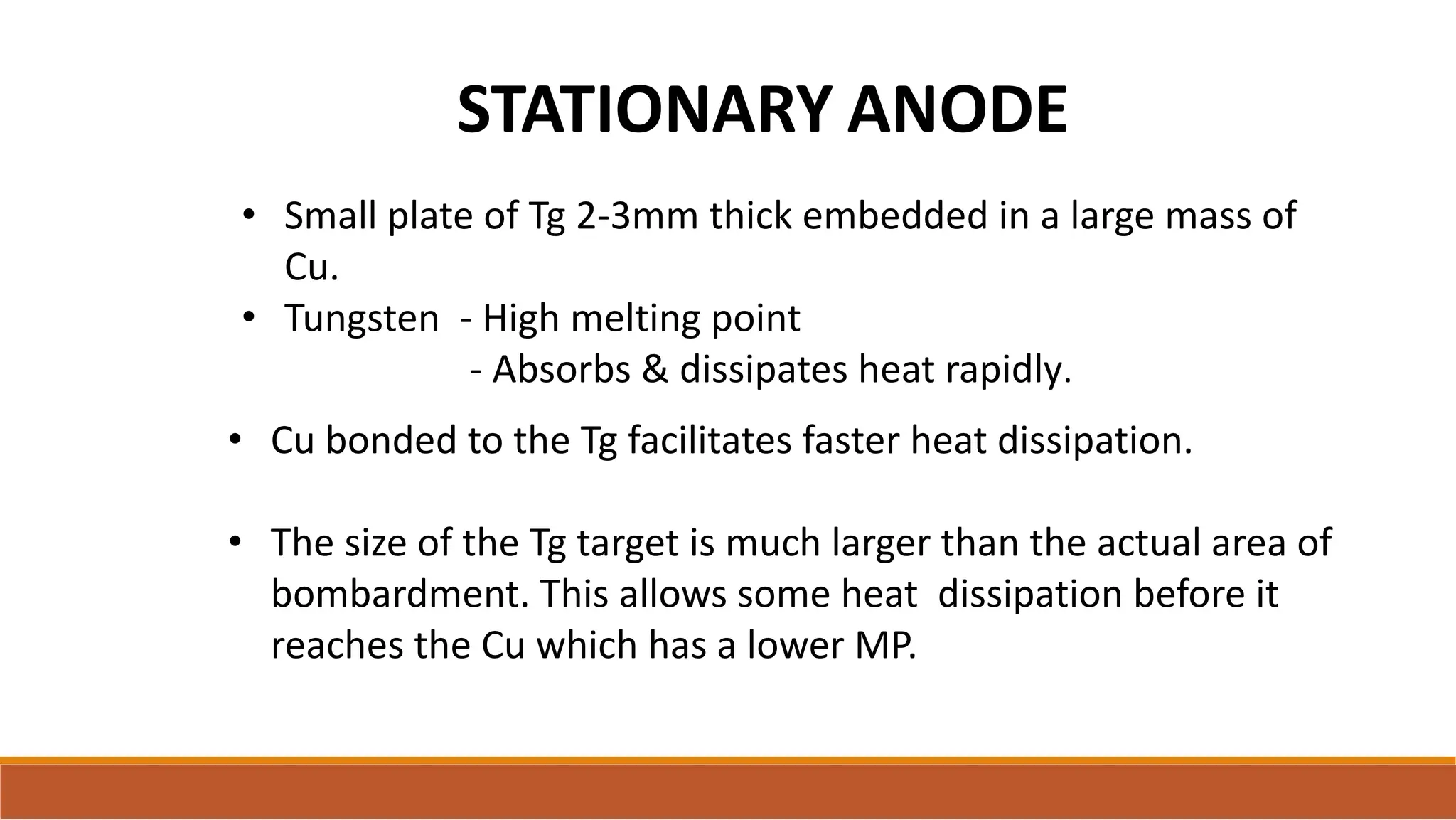
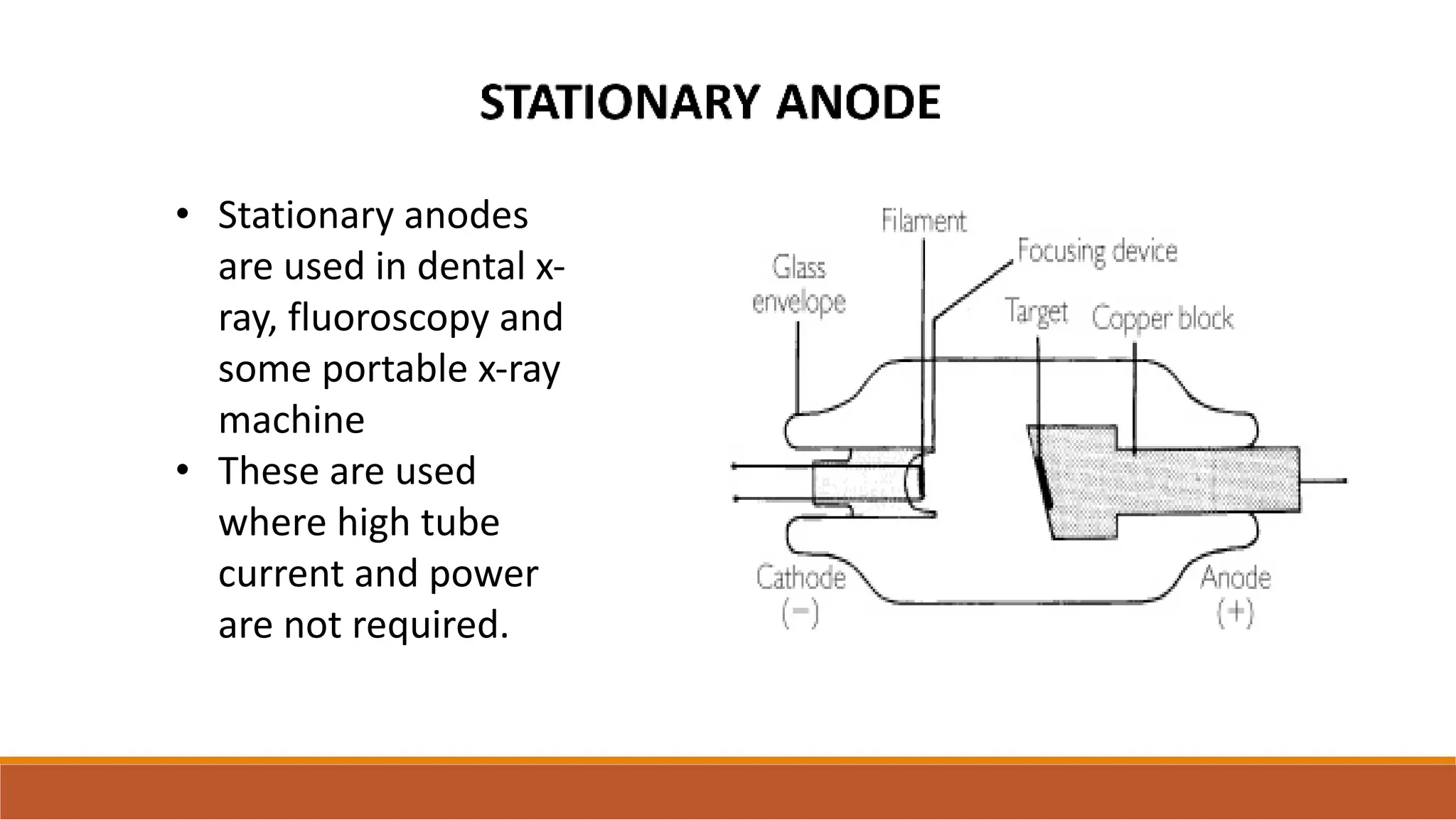
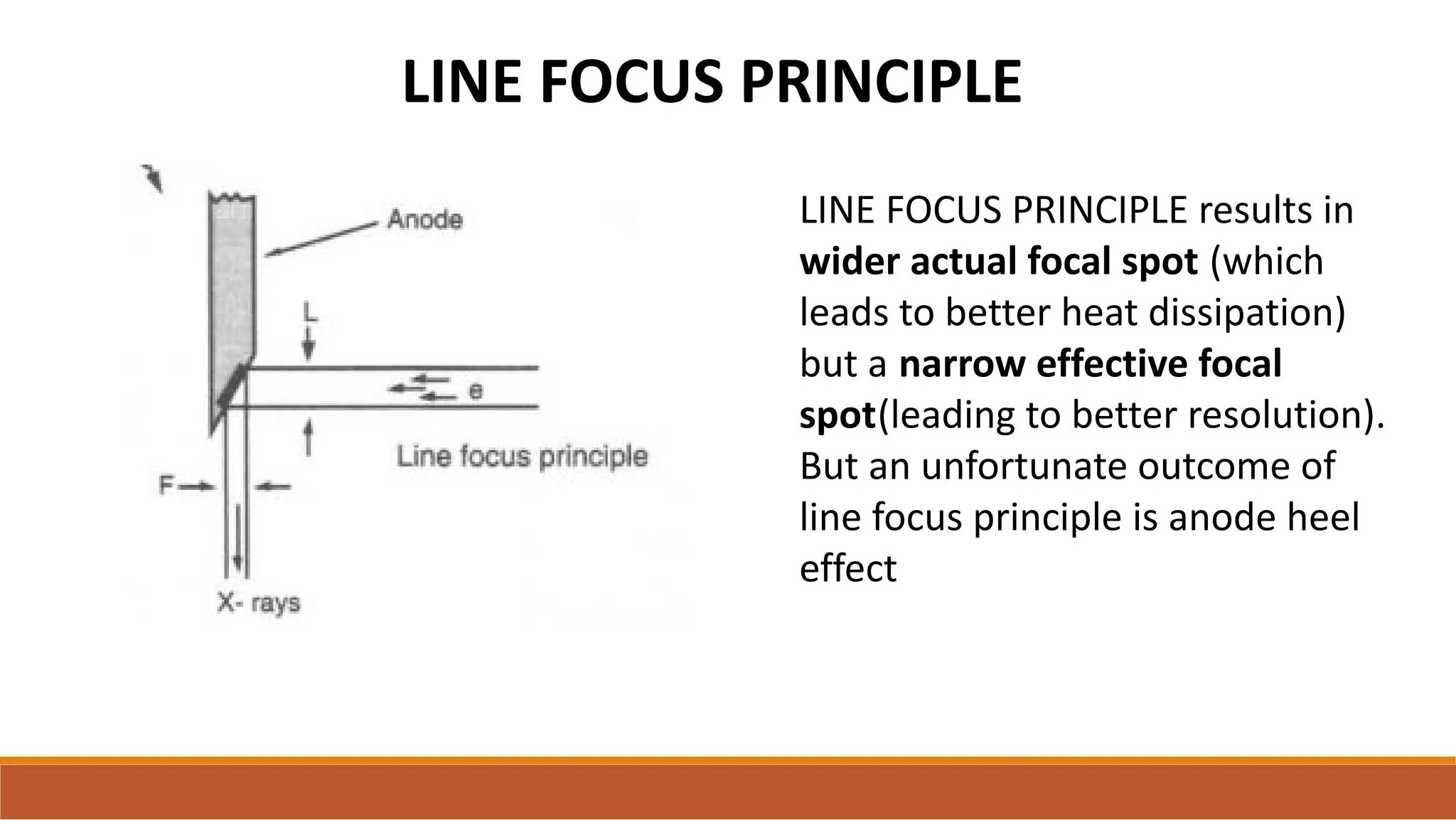
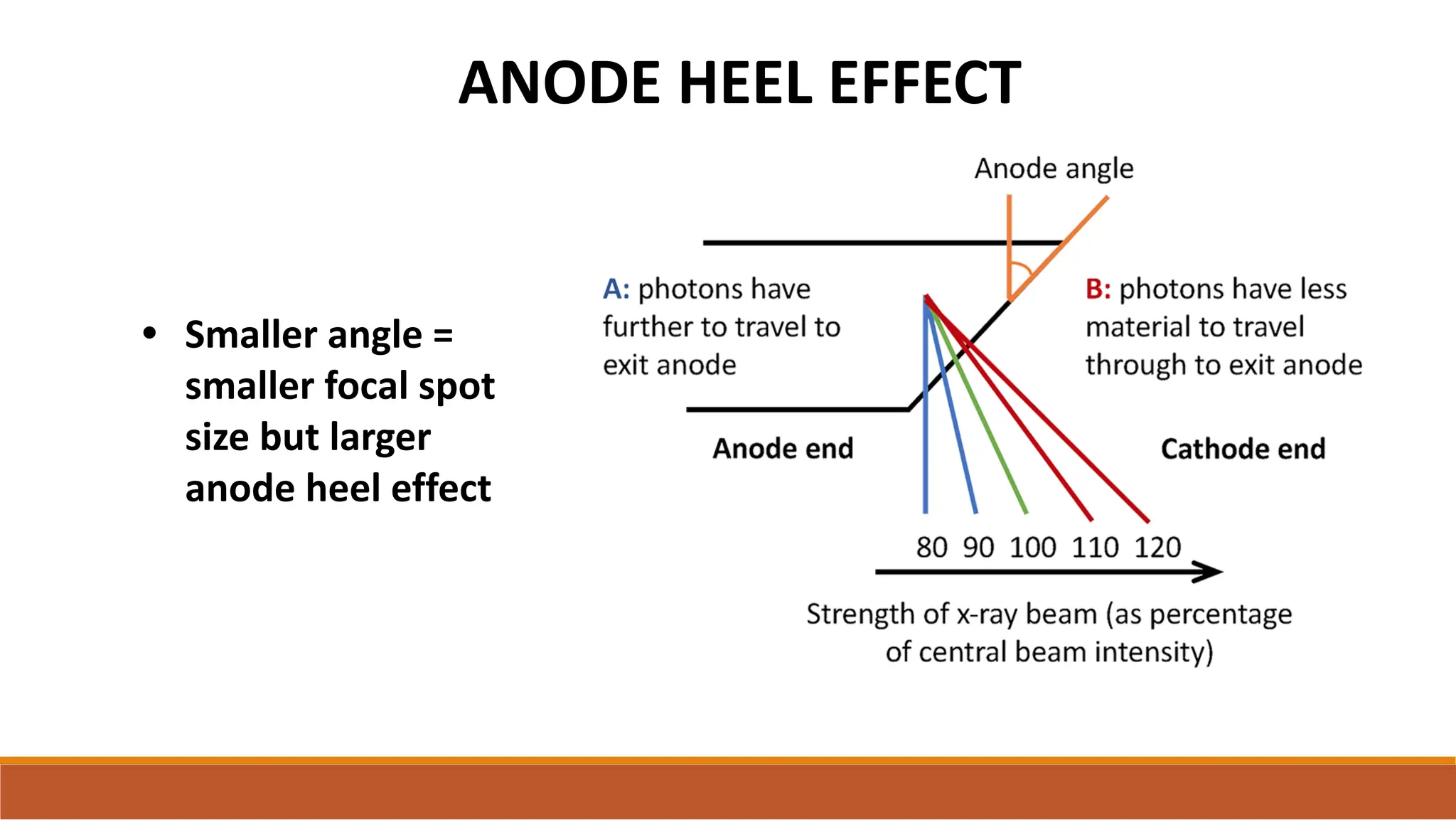
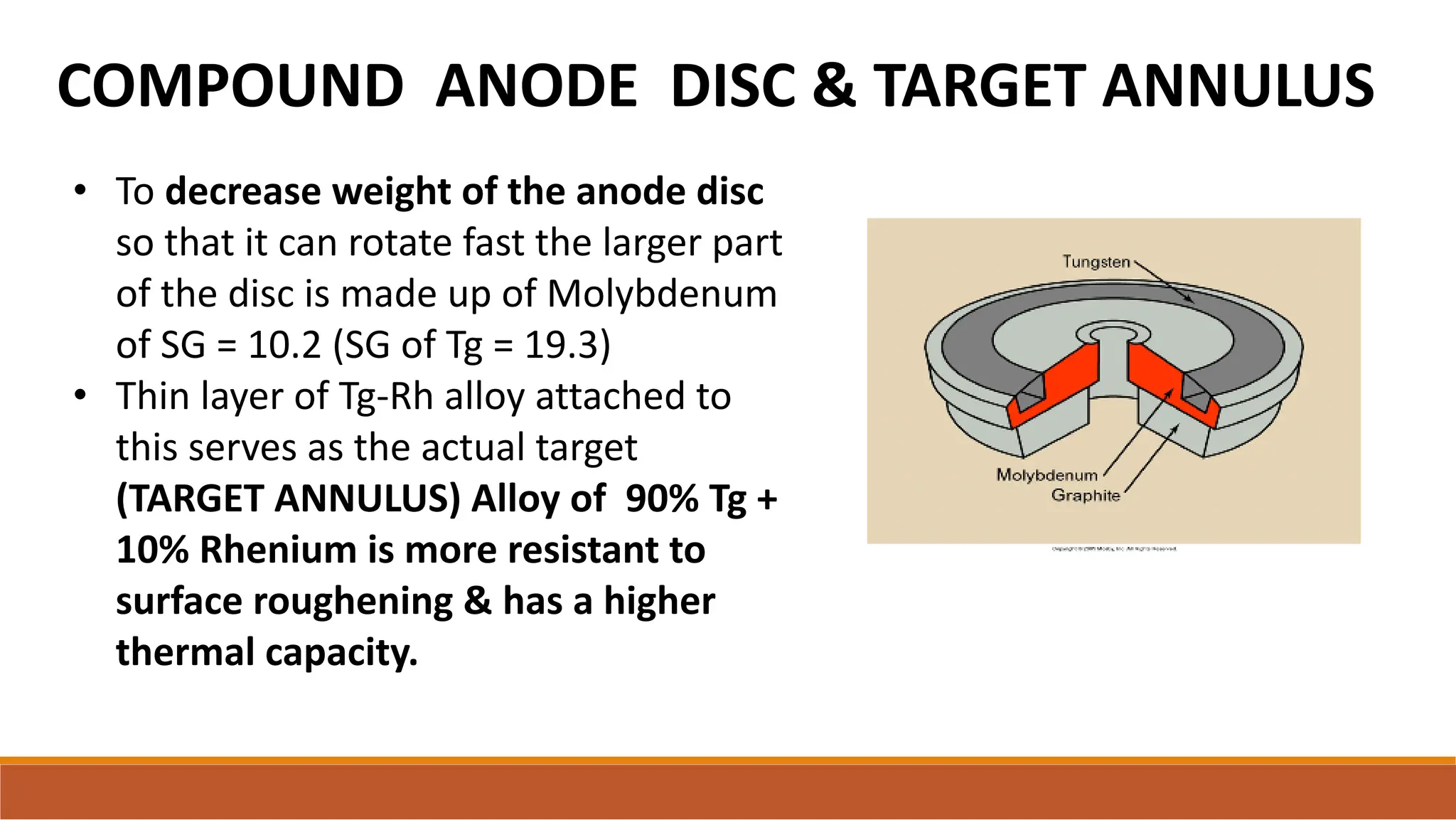
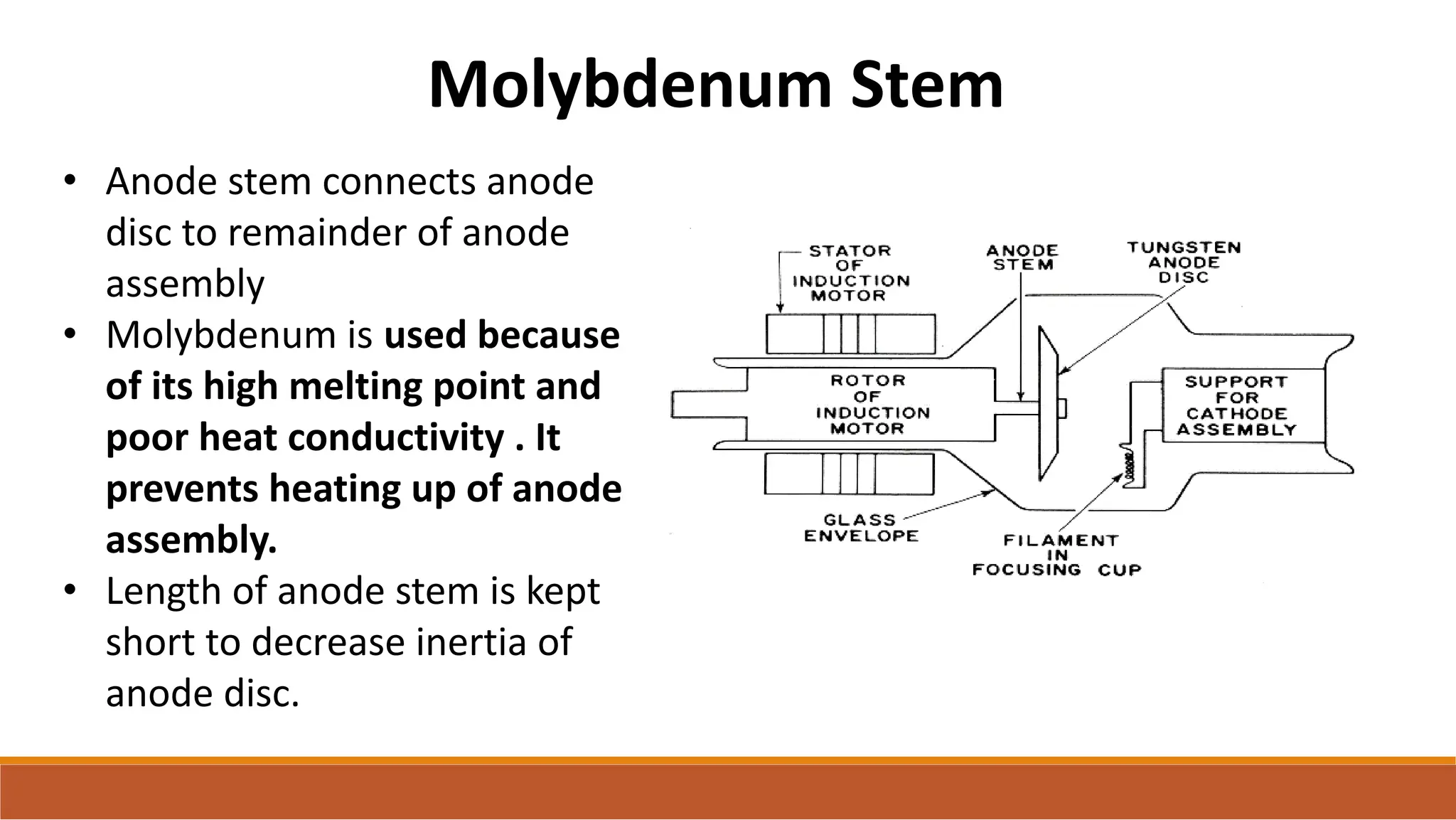
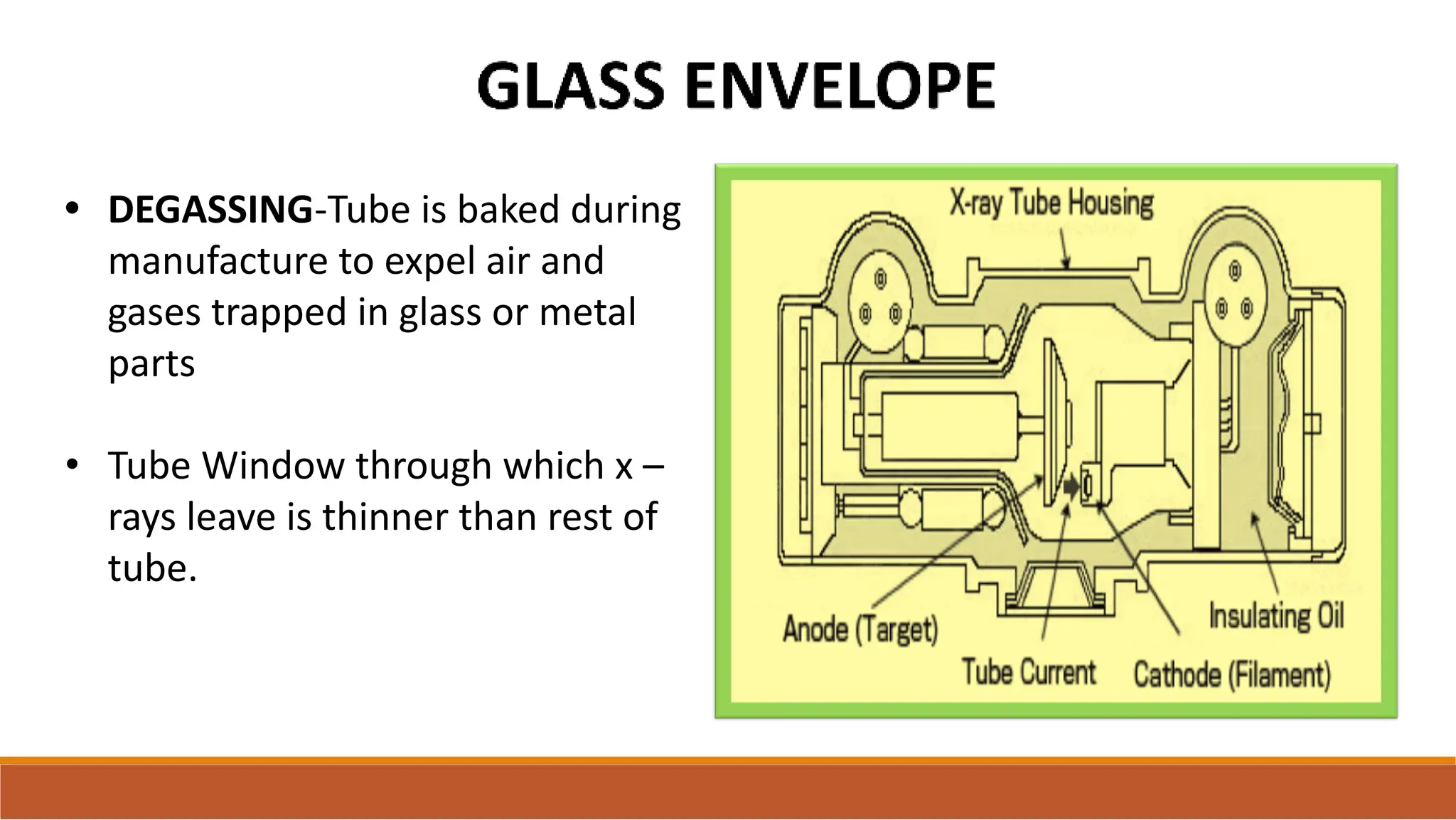
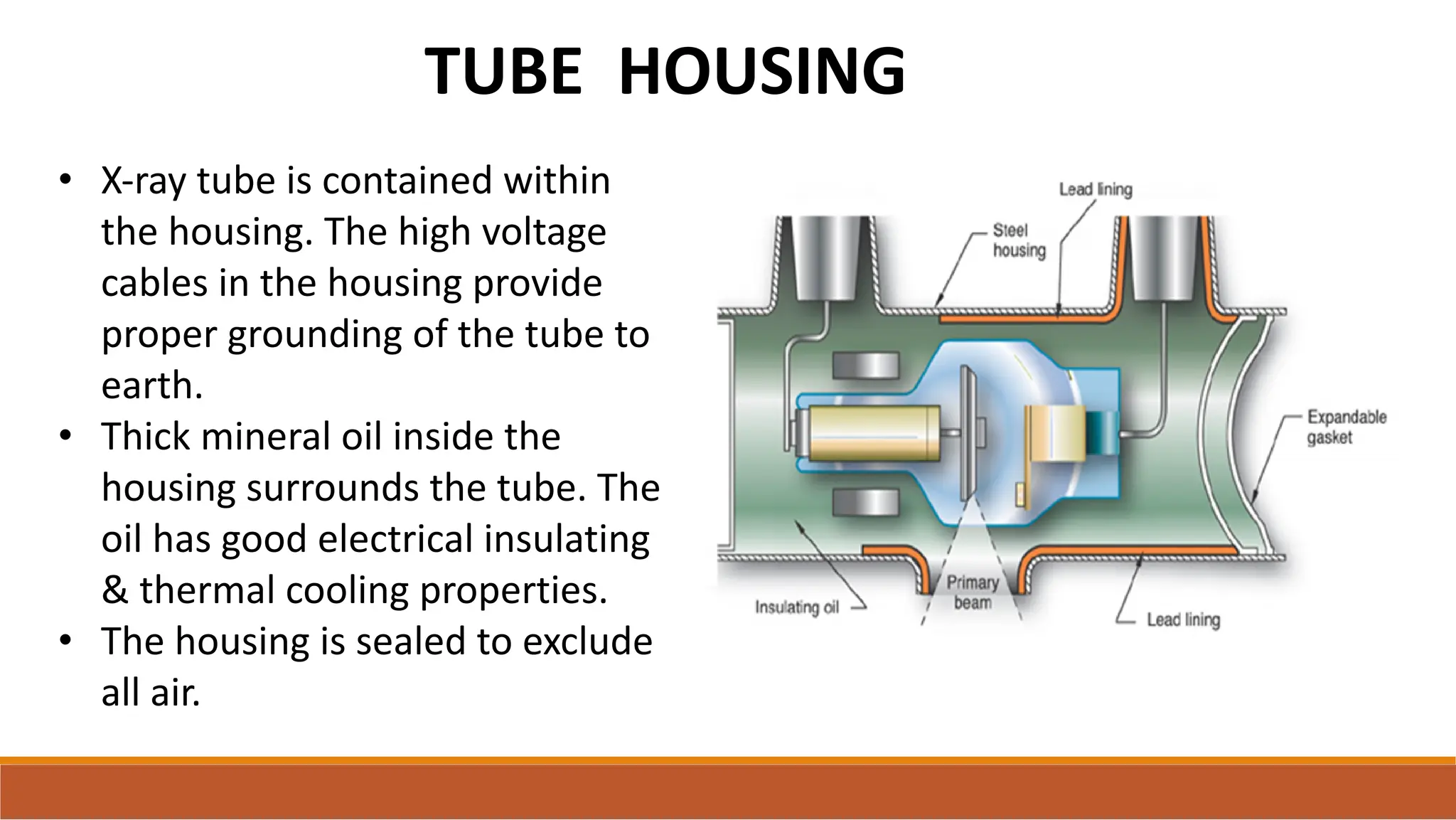
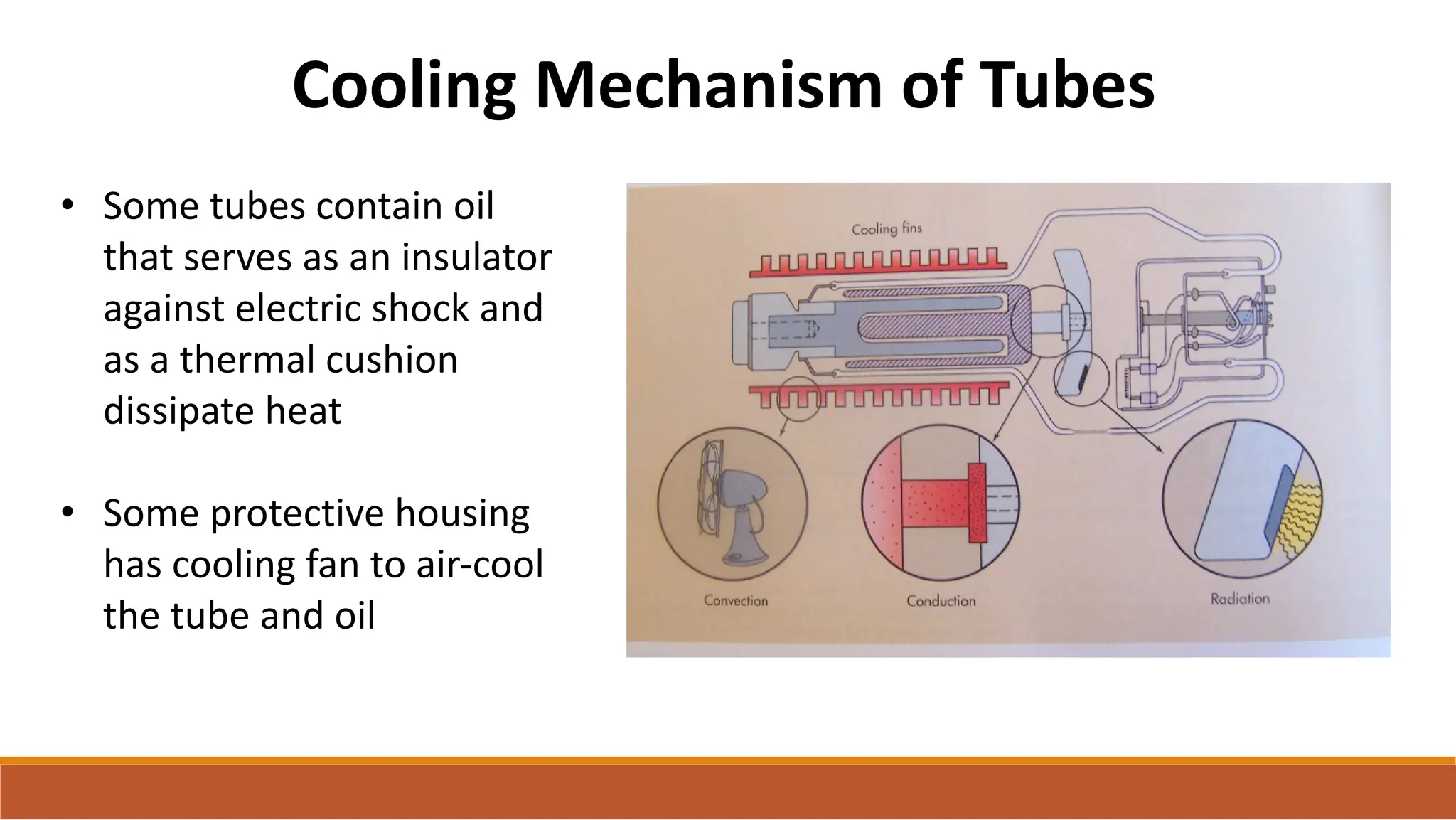
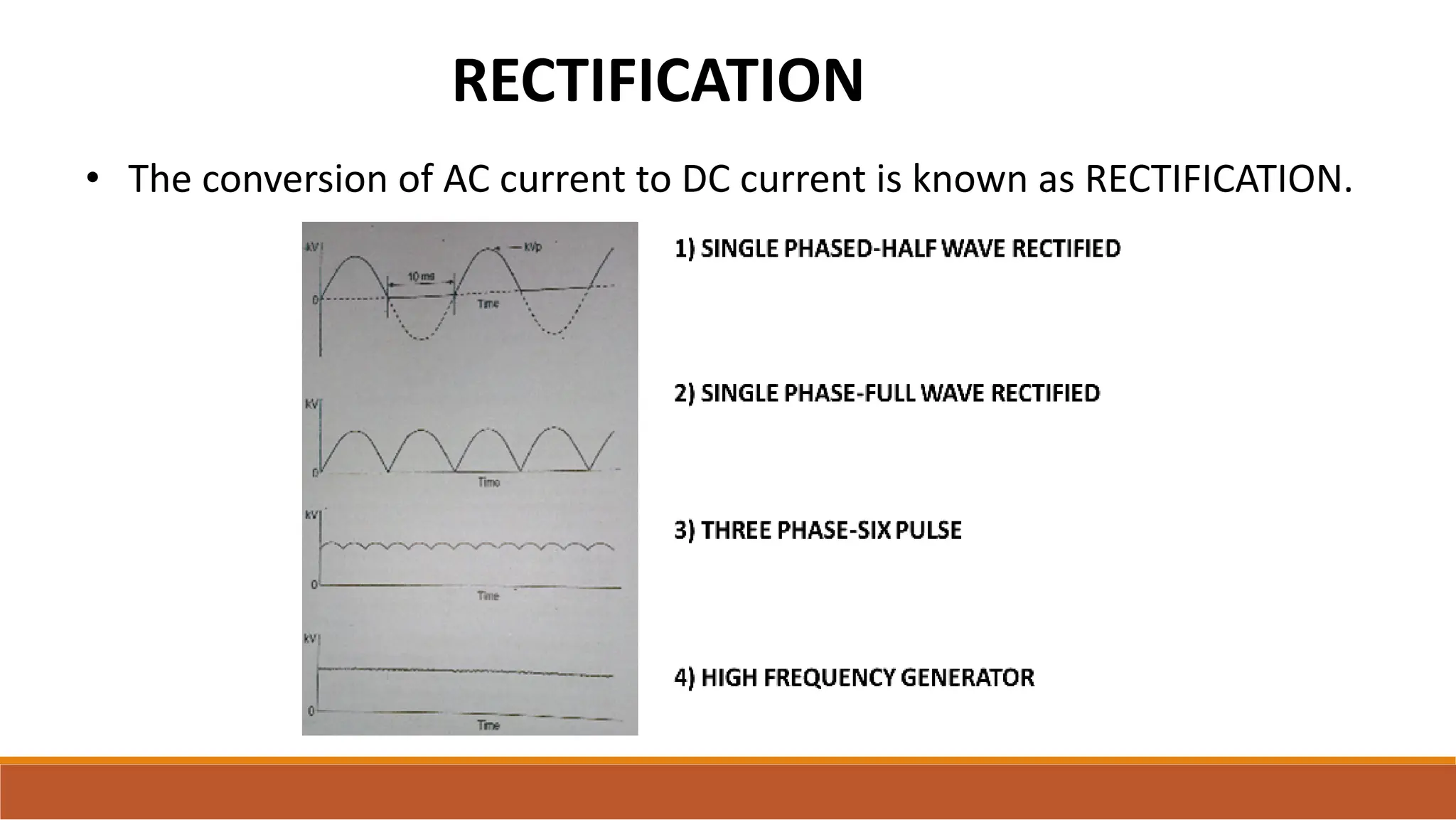
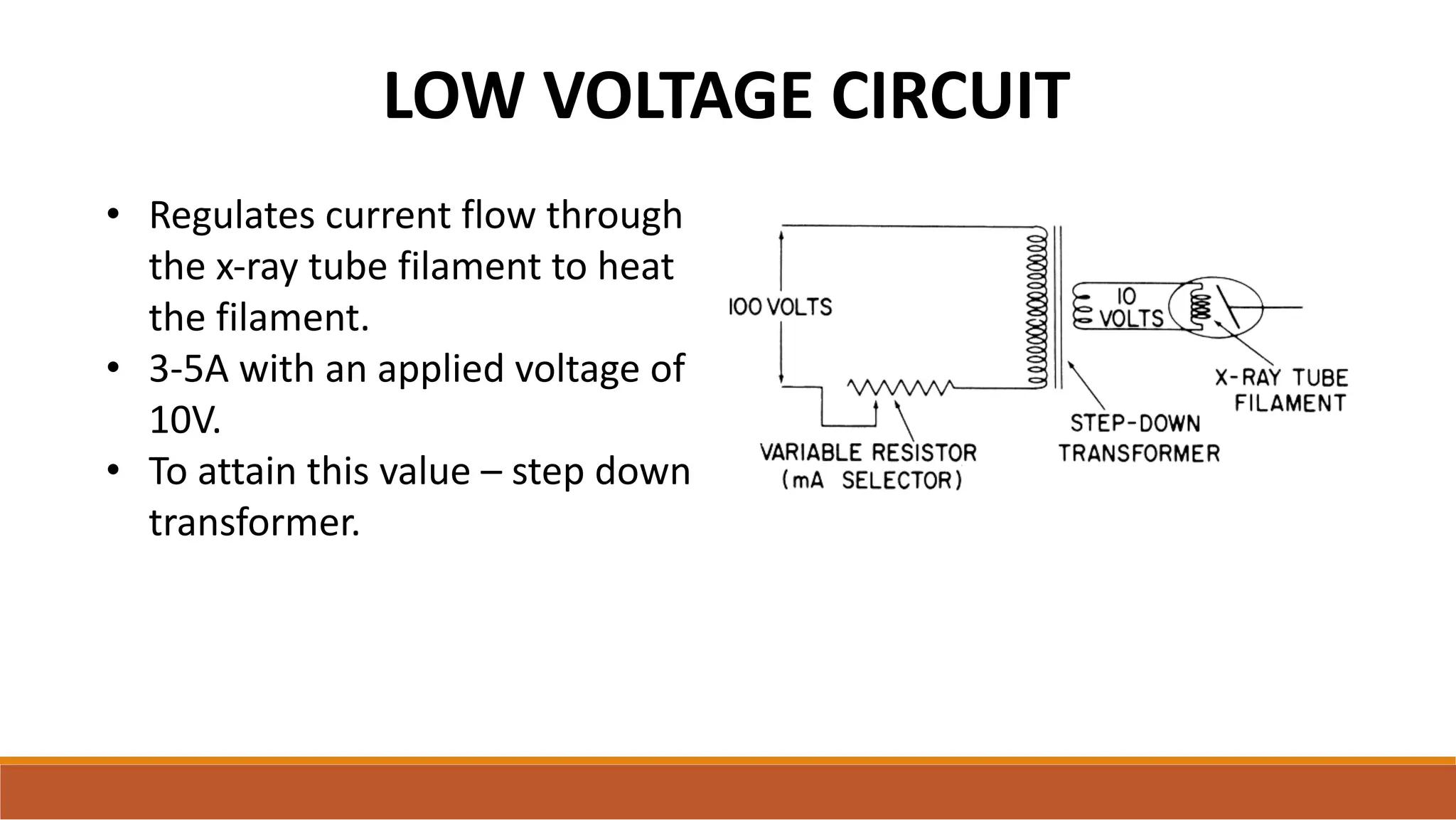
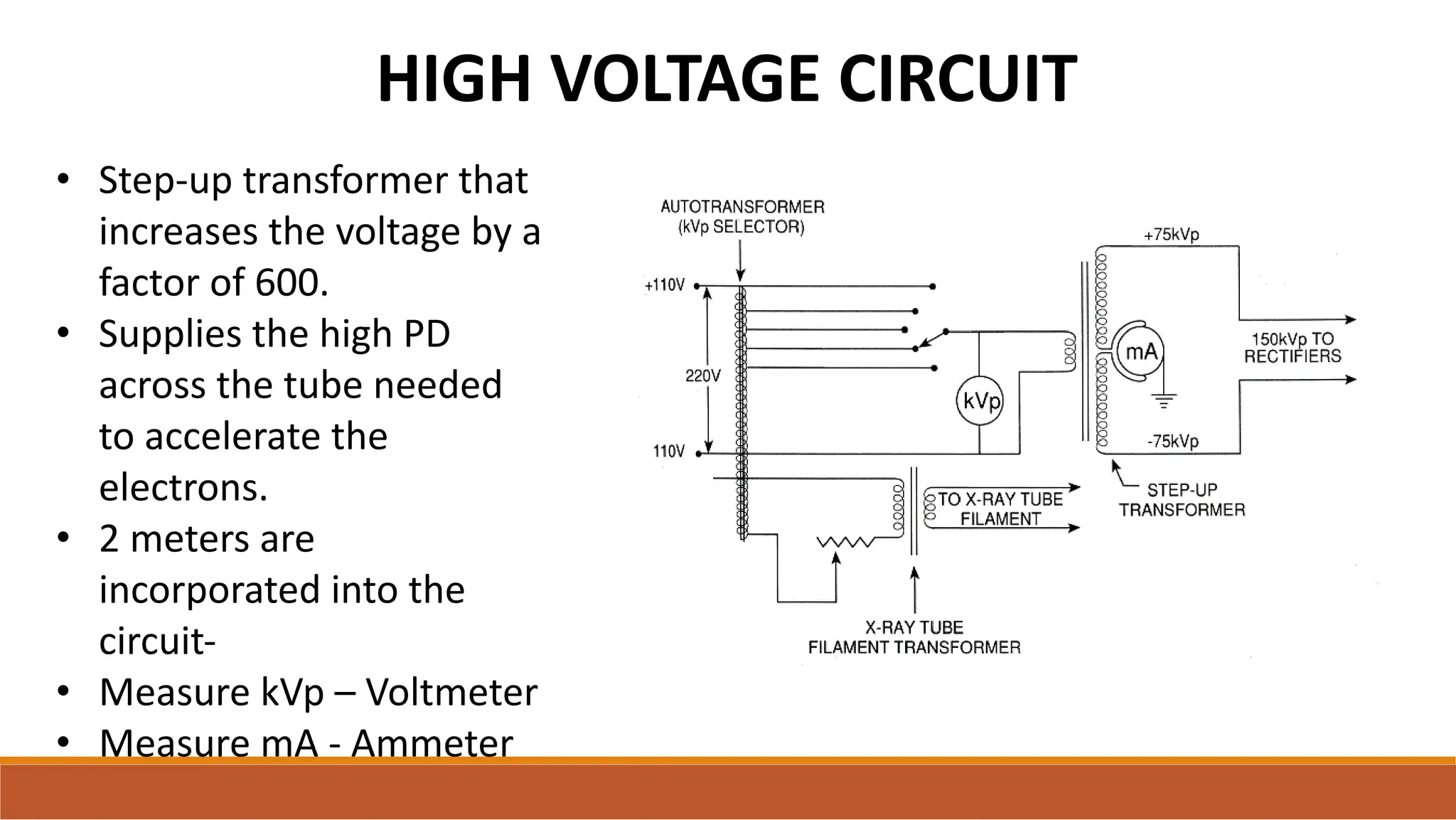
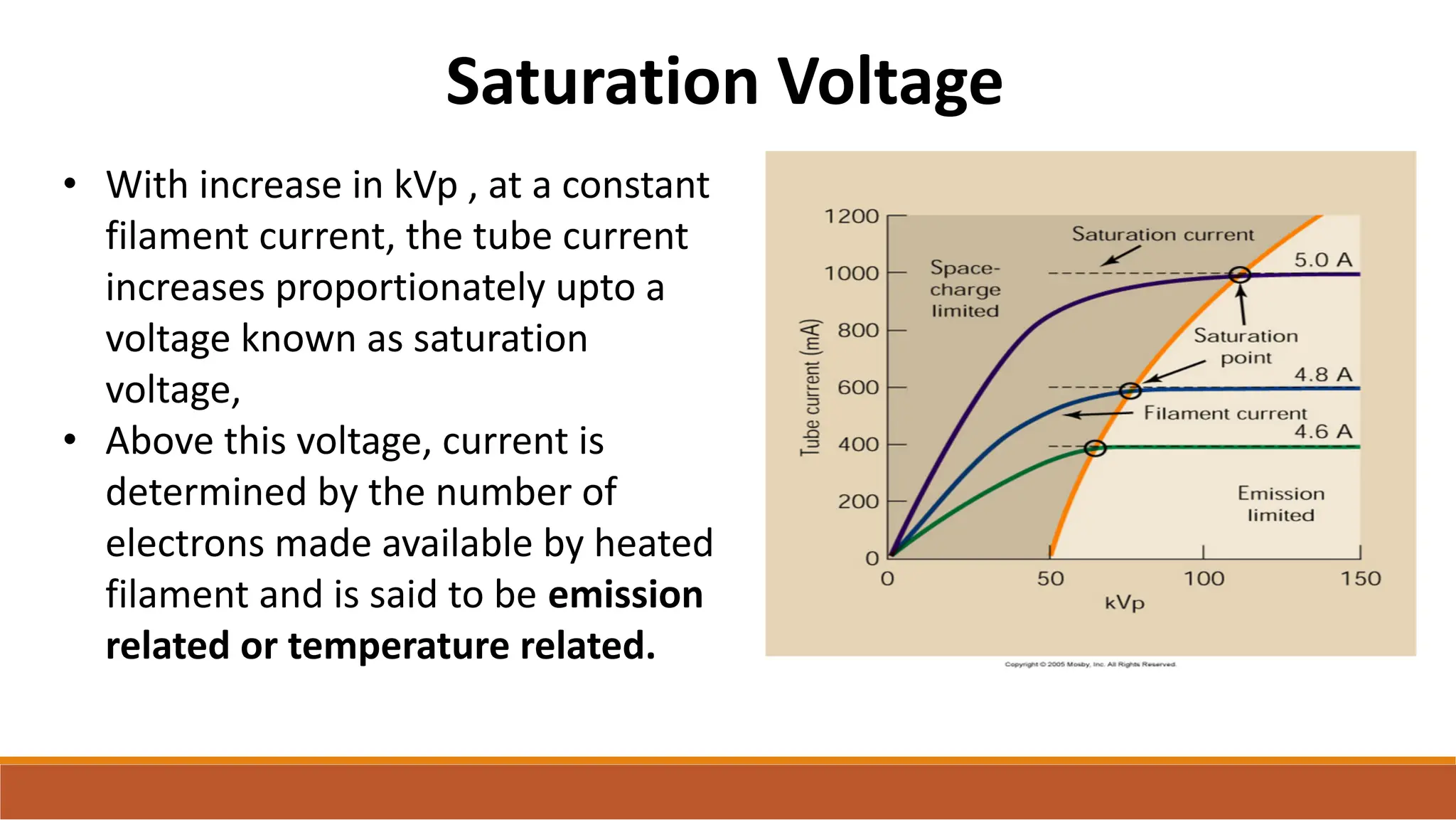
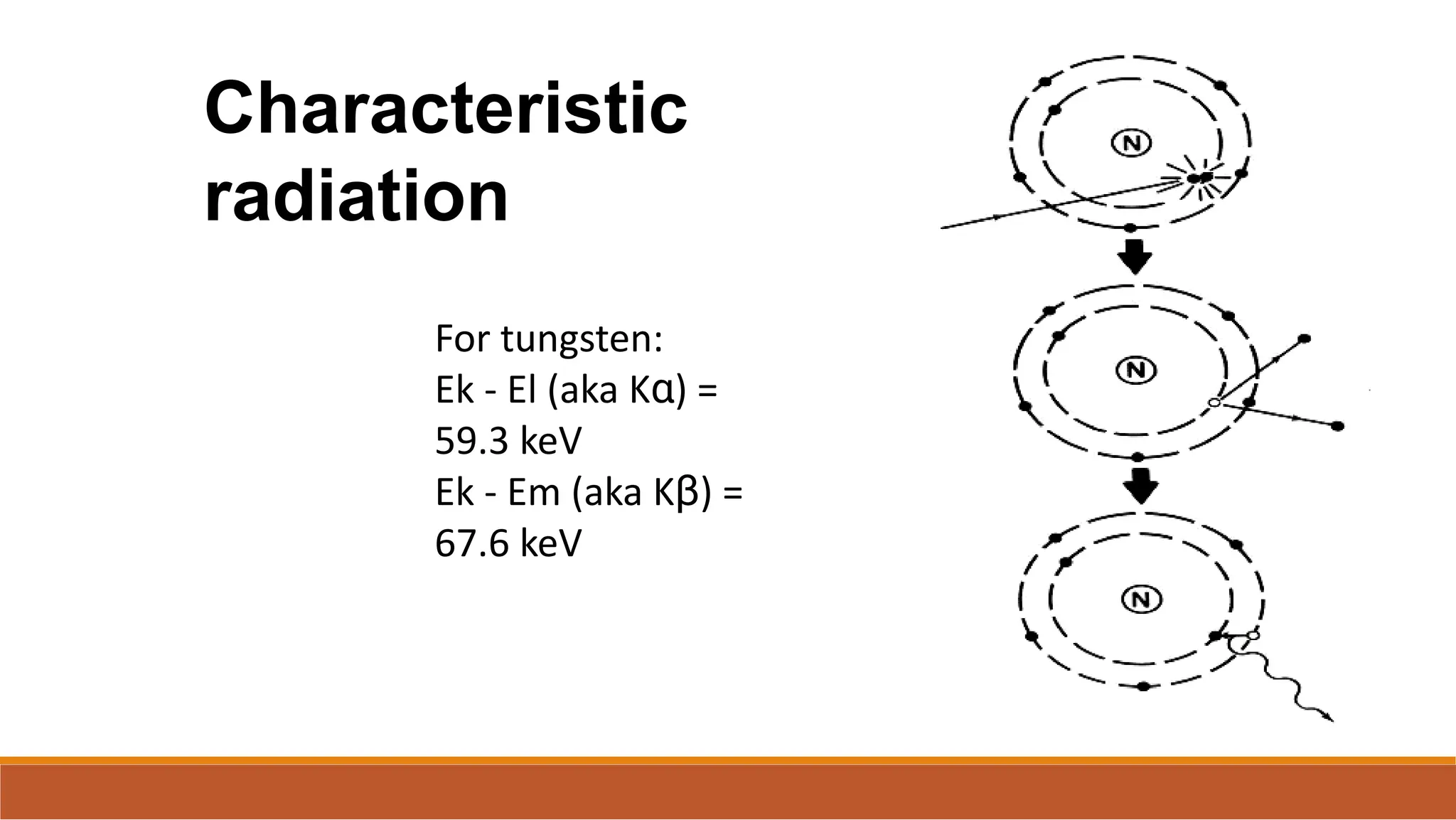
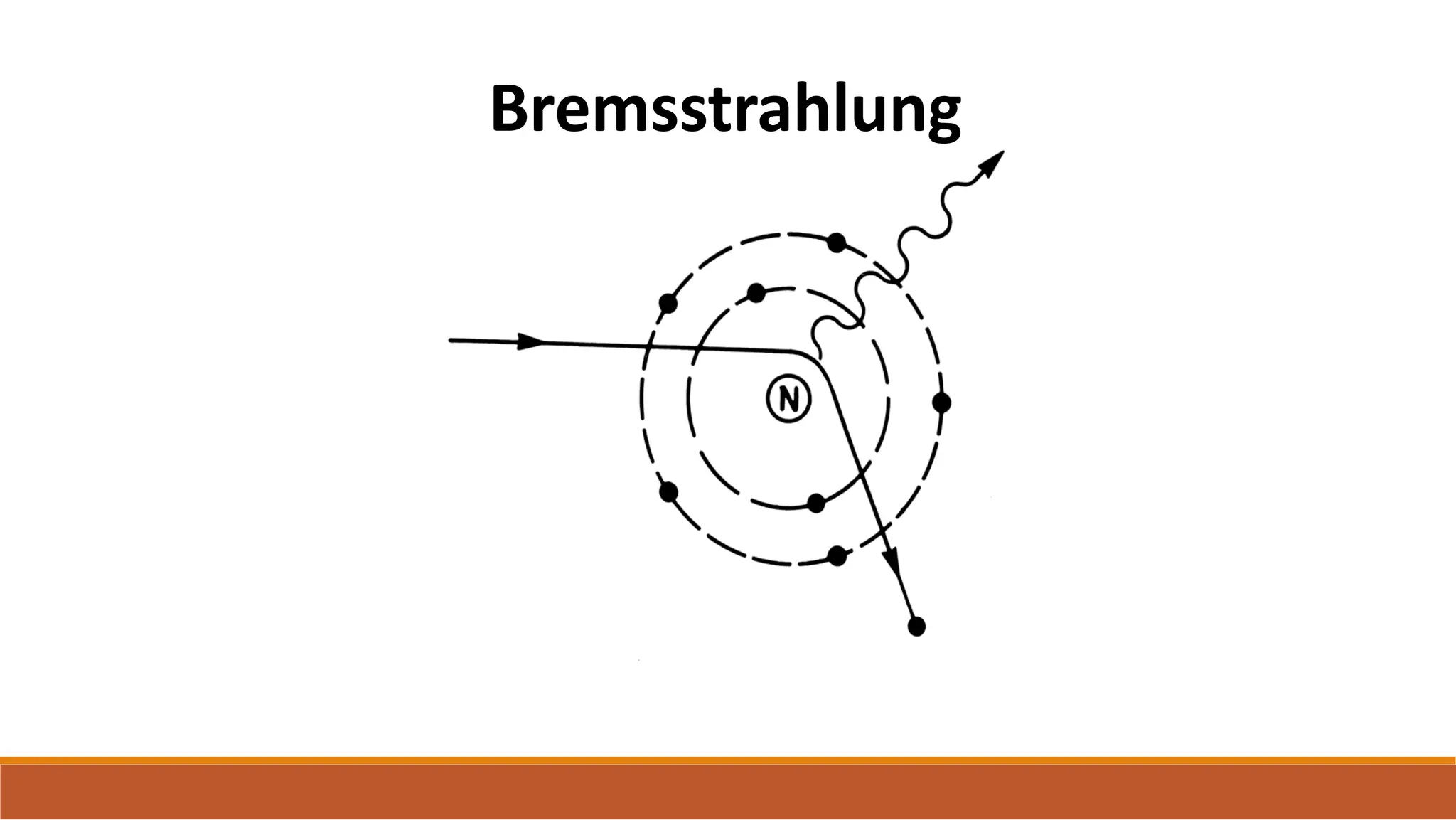
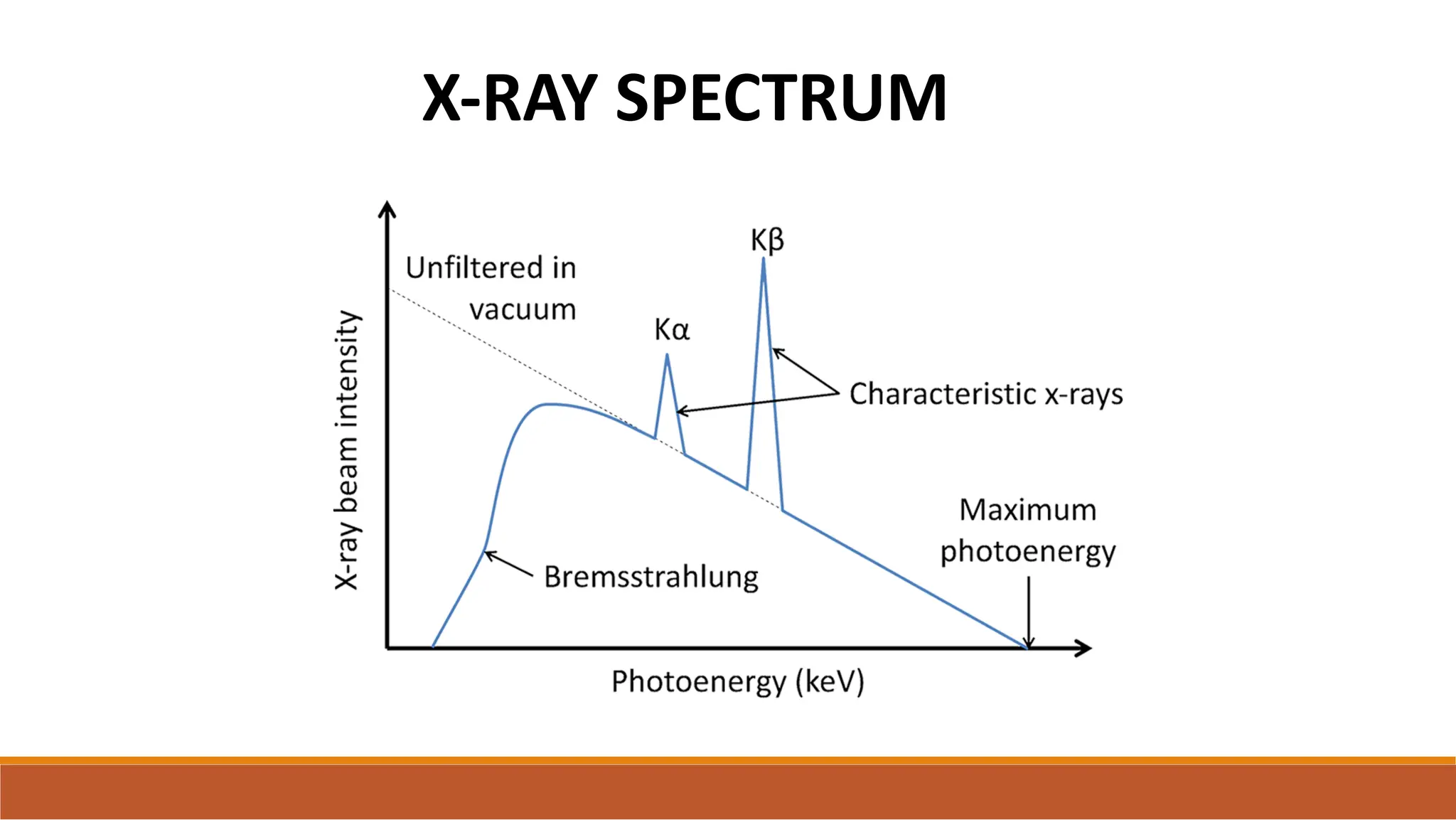
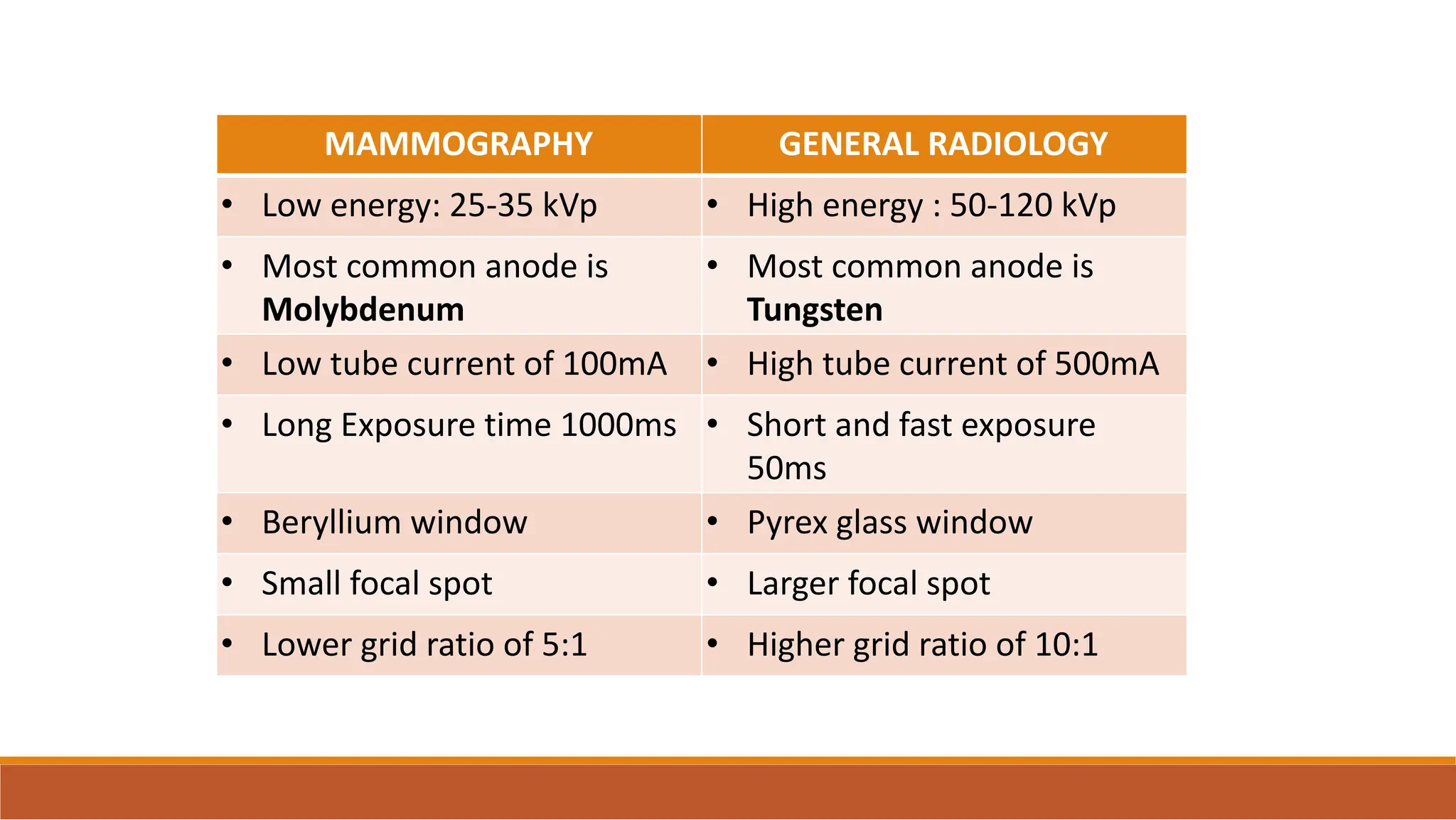
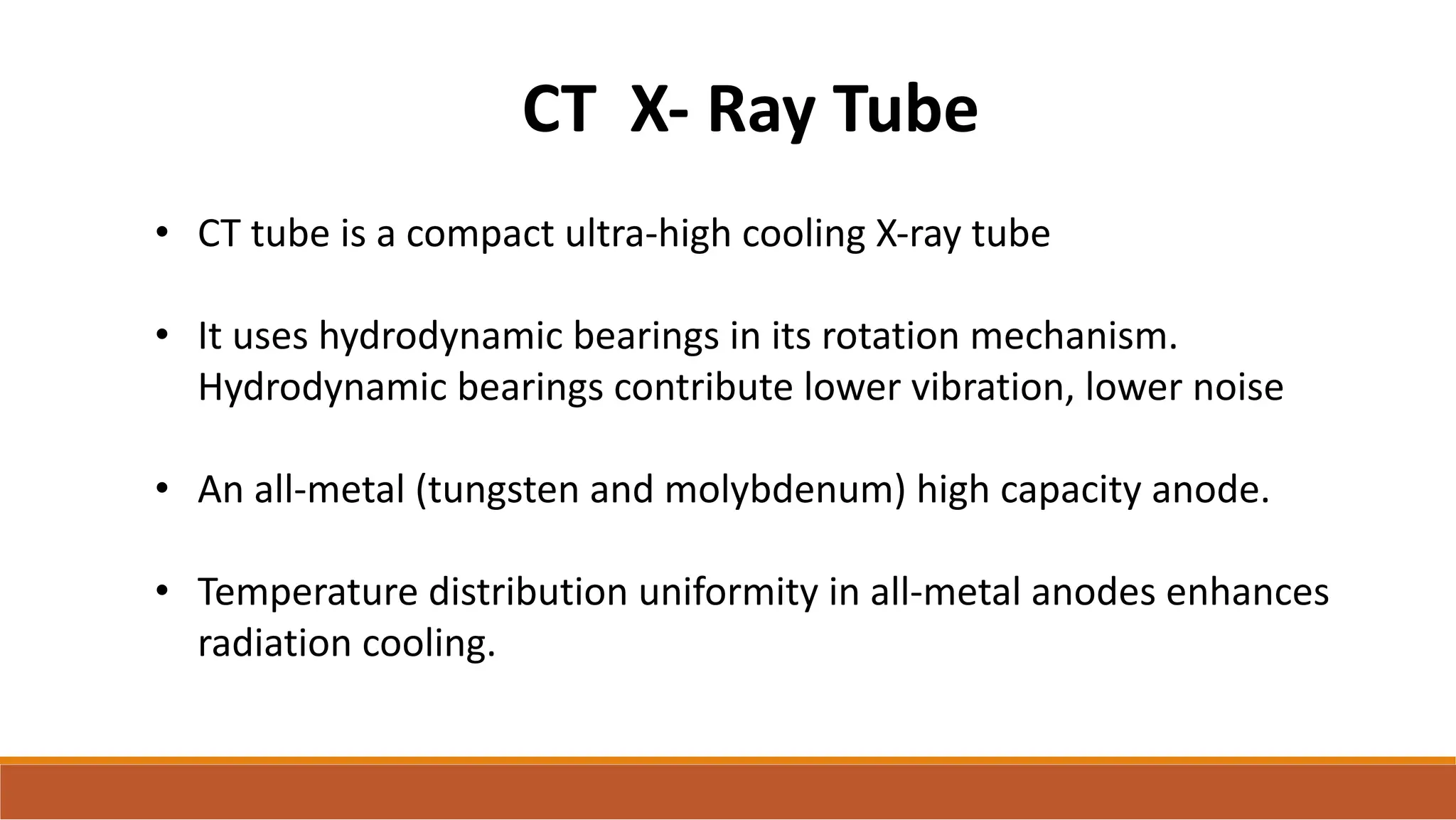
X-ray tubes produce x-rays by decelerating a high-speed stream of electrons, generated at the cathode, which then interact with the anode. The design of the tube includes components like cathodes, anodes, and protective housing to manage heat and optimize x-ray production, with various types of tubes specialized for different applications. Key principles discussed include thermionic emission, the line focus principle for resolving power, and the importance of filtering low-energy photons to ensure effective imaging.