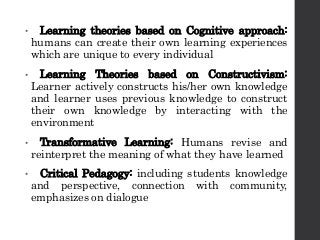
This document discusses student-centered learning (SCL) from several perspectives. It outlines the epistemic bases of SCL including idealism, naturalism, realism, and pragmatism. It also discusses the psychological bases of SCL based on learning theories like classical conditioning, operant conditioning, social learning, cognitive approaches, constructivism, transformative learning, and critical pedagogy. The document then covers the role of technology in SCL and strategies to achieve SCL like project-based learning and the teacher acting as a facilitator. It lists skills that should be developed in students through SCL like critical thinking, problem solving, and effective communication.