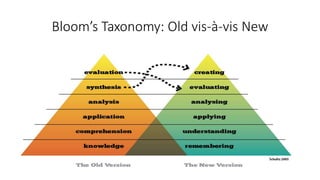
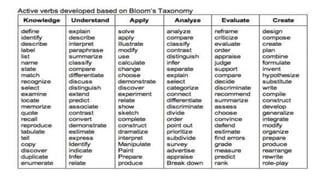
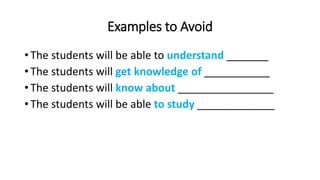
The document discusses Bloom's Taxonomy, which organizes learning objectives into six levels of cognitive complexity - Remember, Understand, Apply, Analyze, Evaluate, and Create. It provides examples of learning objectives for each level related to nouns and the Indian parliament. The objectives examples move from basic recall of facts to more complex tasks like critical thinking, problem-solving, and creation of new ideas. The document advises avoiding vague objectives that do not clearly articulate the specific cognitive process required.