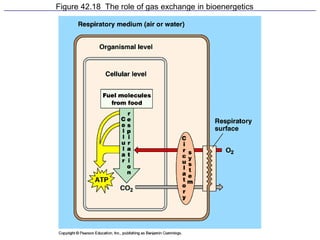
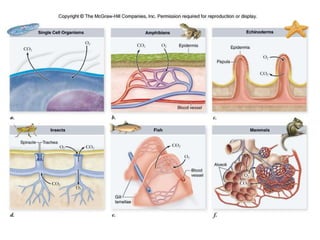
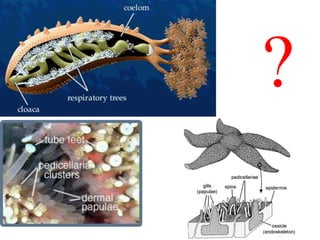
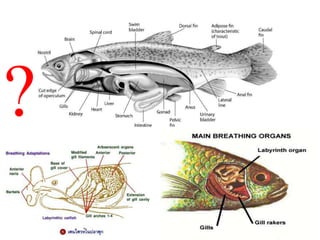
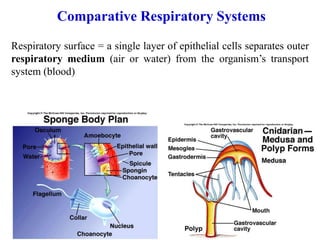
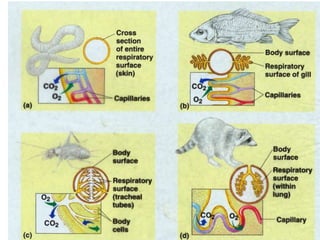
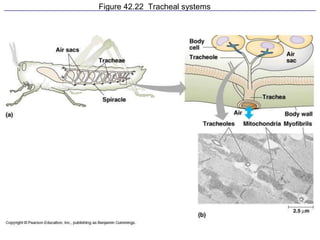
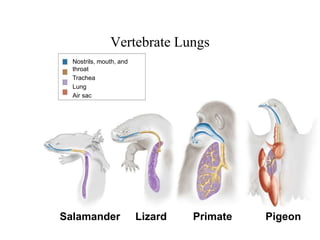
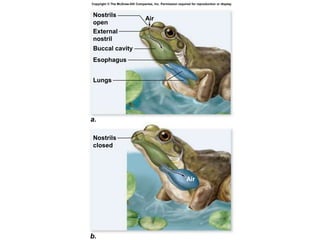
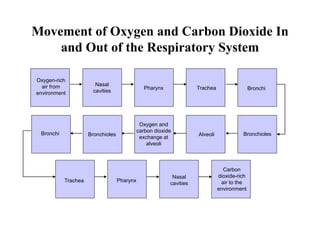
1. Respiration involves the exchange of gases between an organism and its environment. Respiratory systems have evolved specialized structures with large surface areas to facilitate gas exchange through diffusion.
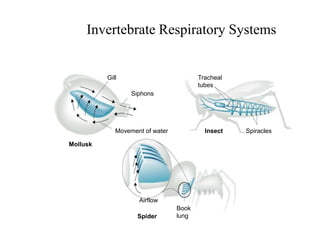
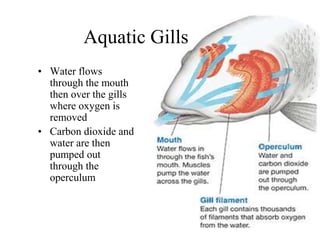
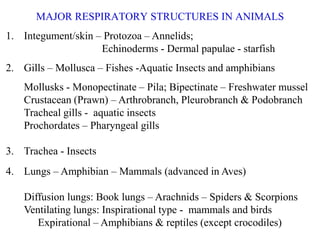
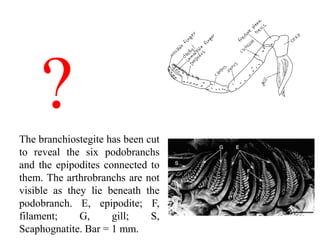
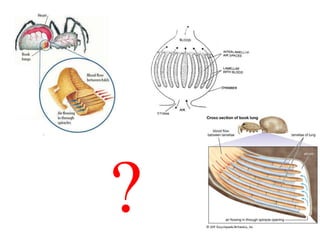
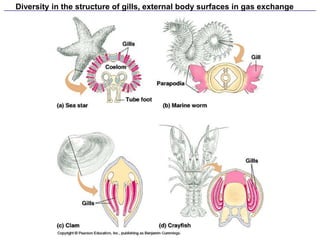
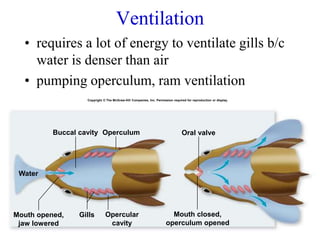
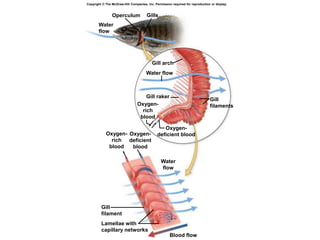
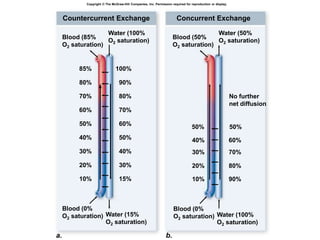
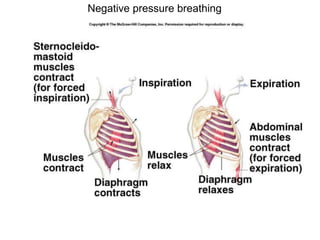
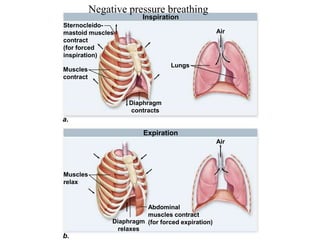
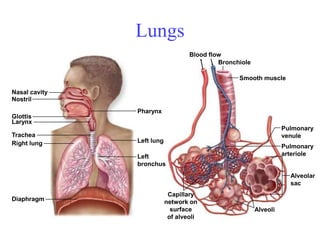
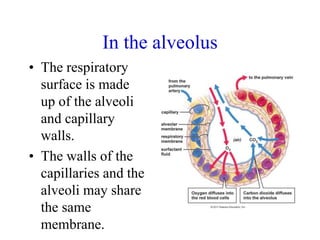
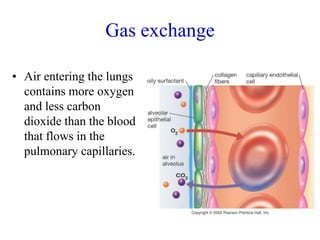
2. Aquatic organisms rely on gills for respiration, while terrestrial organisms rely on lungs or tracheal systems. Gills provide a moist surface and countercurrent flow maximizes oxygen uptake. Lungs have a large surface area provided by alveoli.
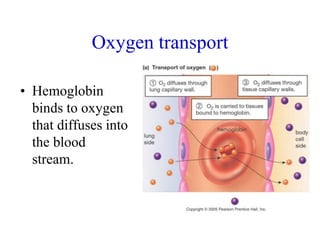
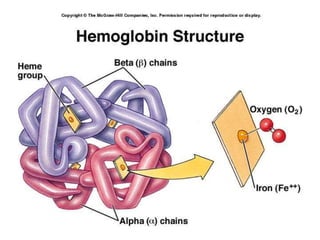
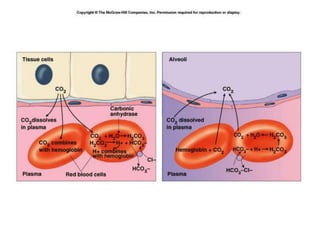
3. Oxygen is transported via hemoglobin in red blood cells, while carbon dioxide is transported as bicarbonate ions and by binding to hemoglobin. Respiratory pigments like hemoglobin enhance the diffusion of gases in the circulatory system.