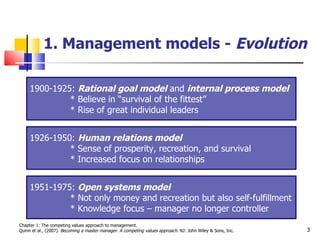
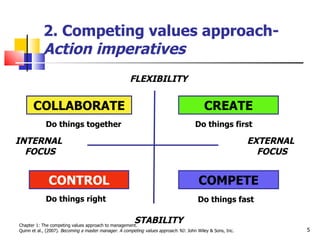
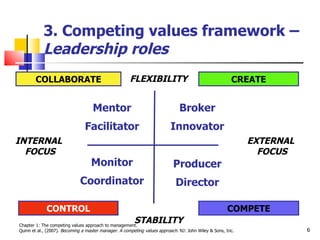
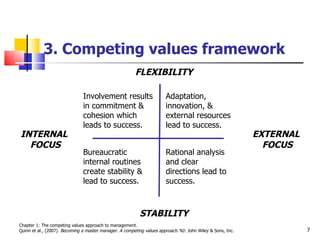
Chapter 1 of 'Becoming a Master Manager' by Quinn et al. outlines the evolution of management models and introduces the competing values approach, emphasizing the importance of balancing internal and external focus, flexibility, and stability. It explores action imperatives, leadership roles, and role expectations for managers, while underscoring the need for developing leadership competencies. The chapter also highlights the significance of aligning organizational culture with strategic goals to enhance performance and individual development.