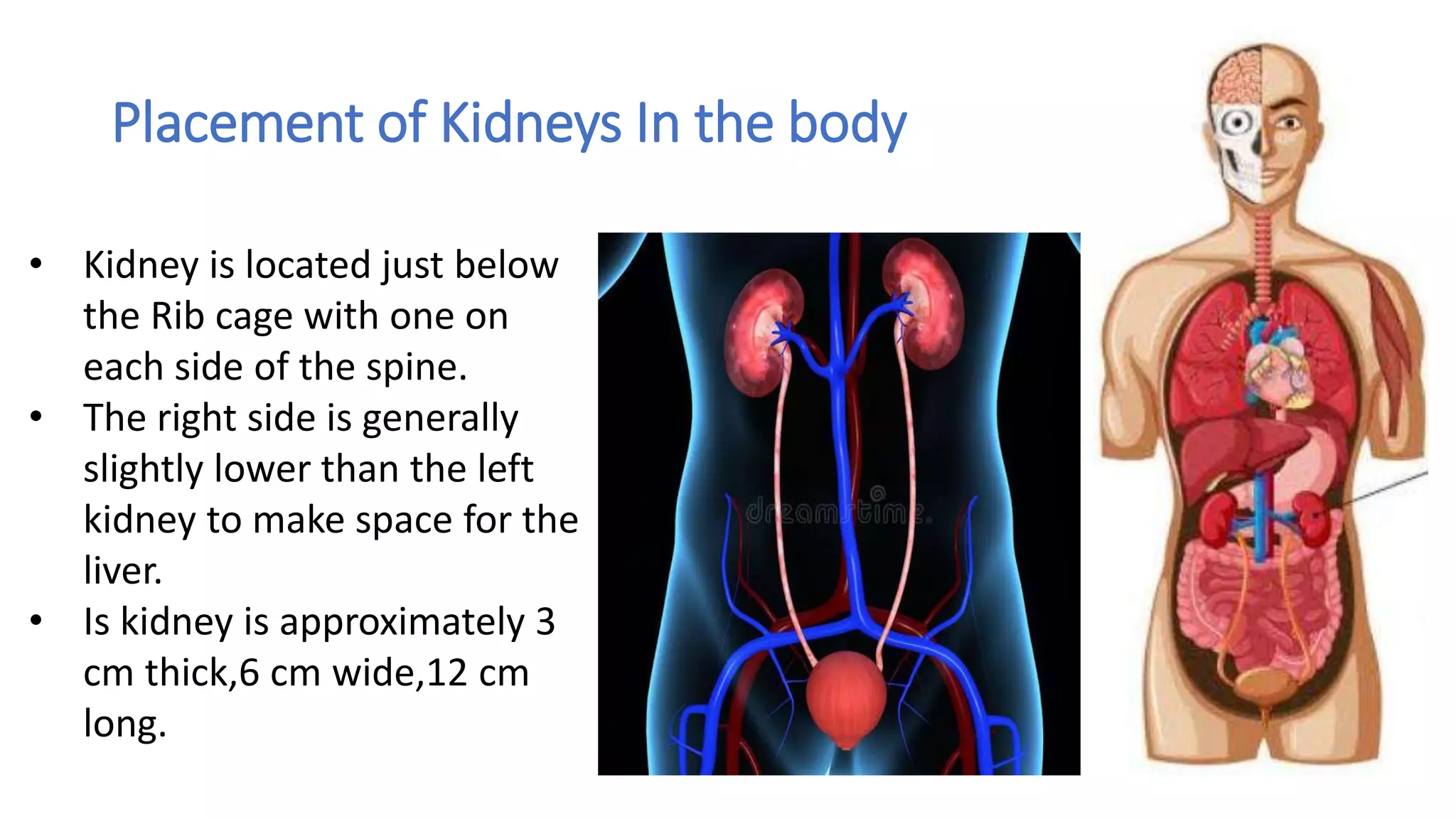
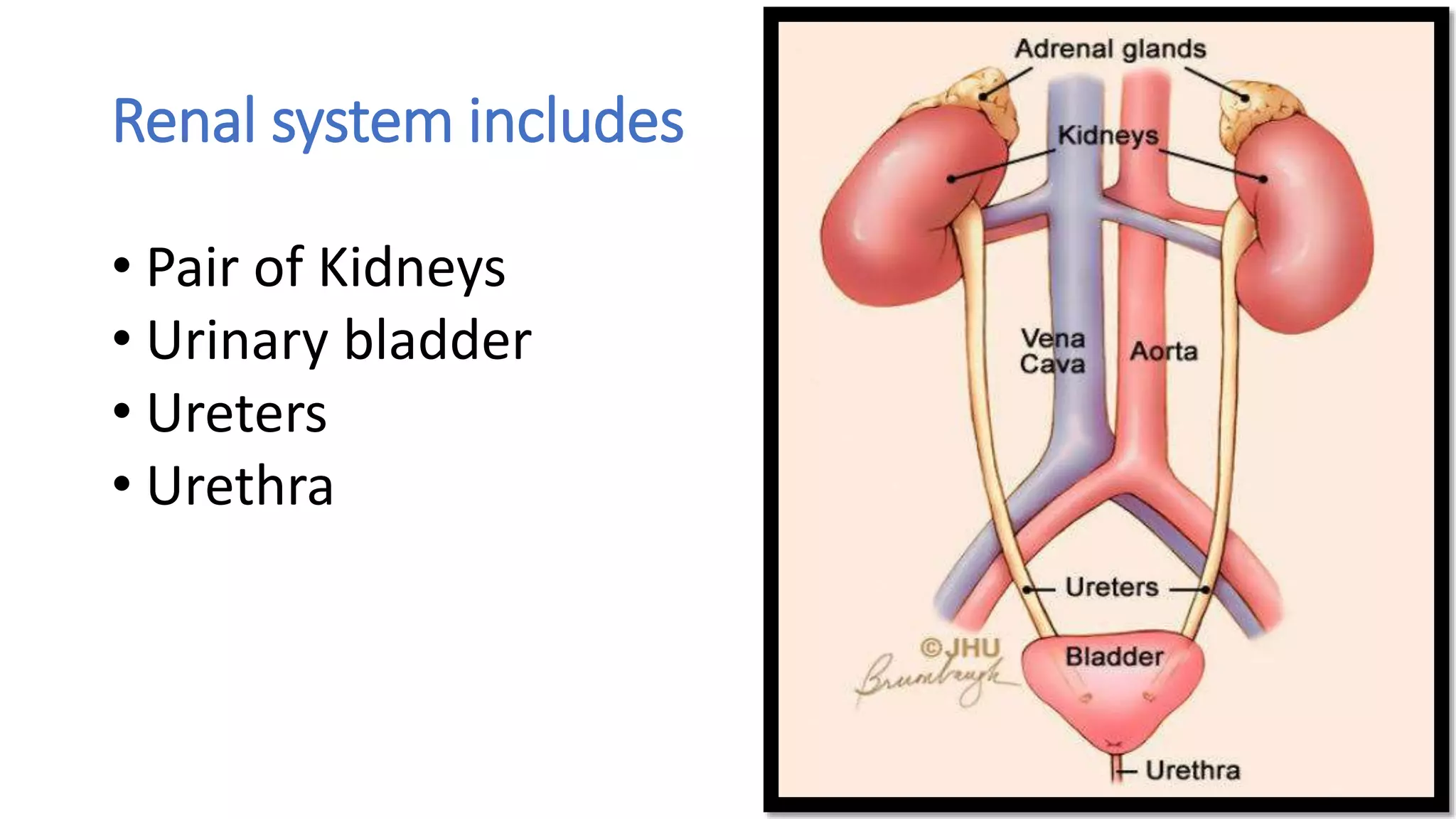
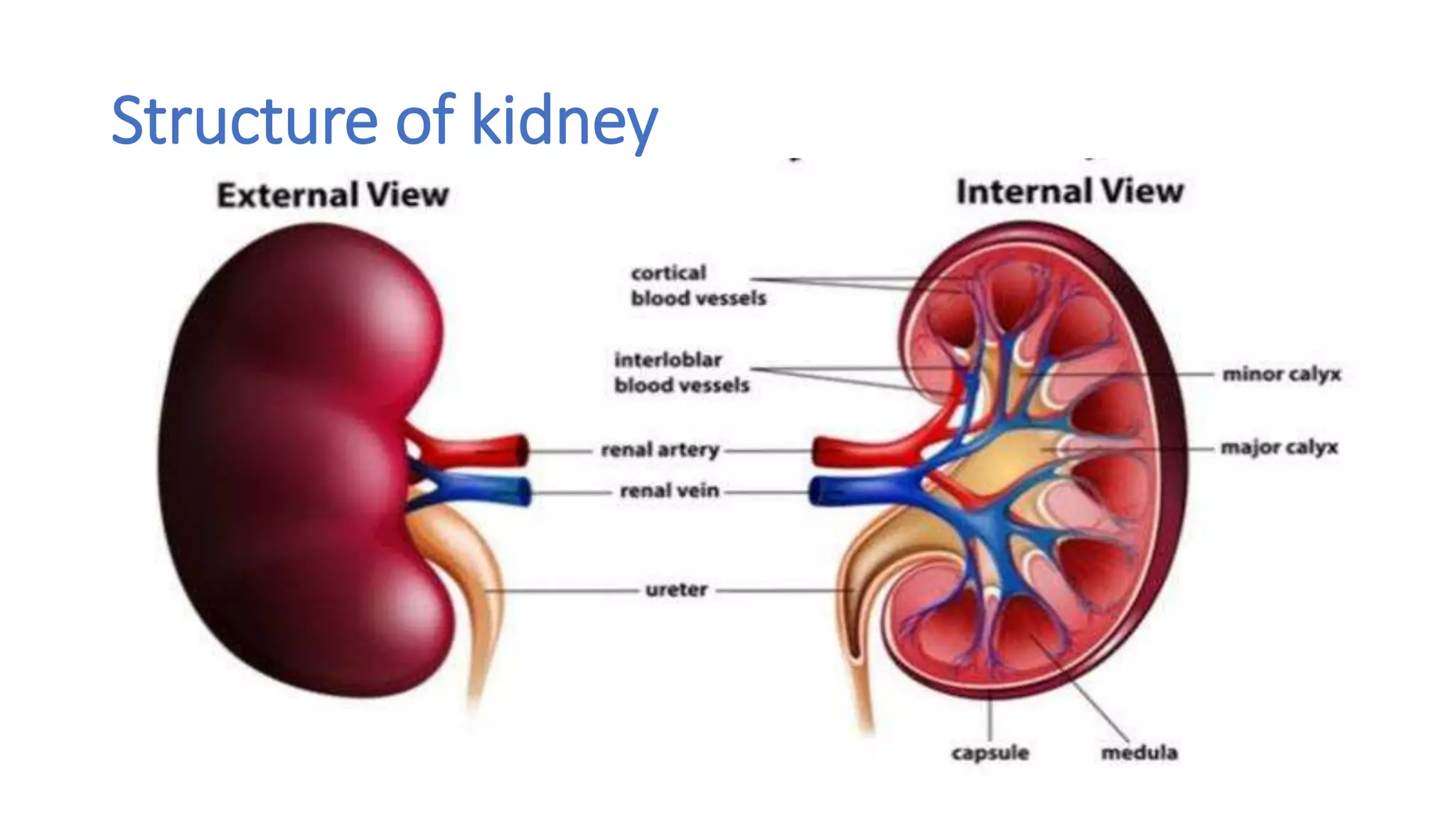
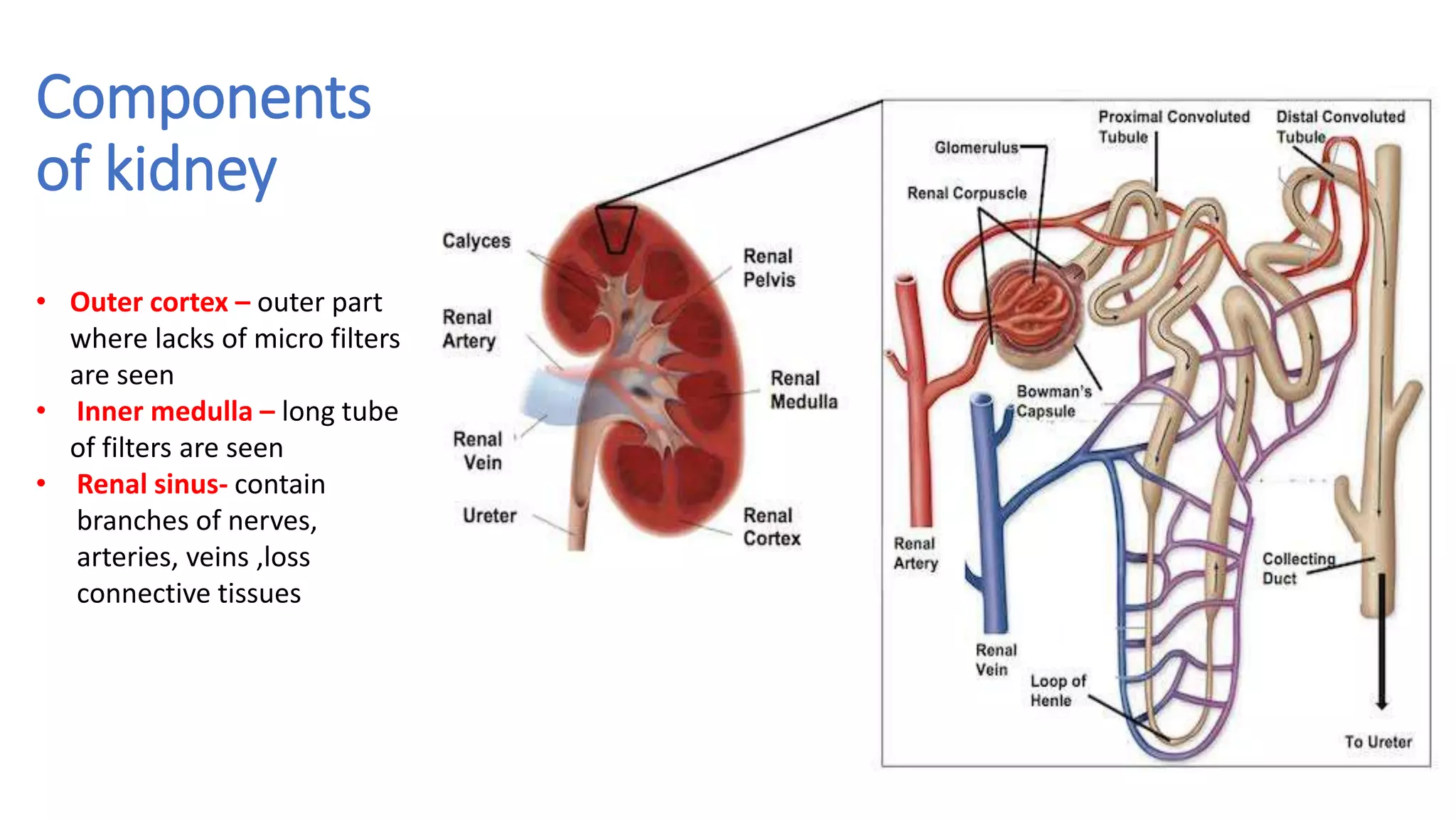
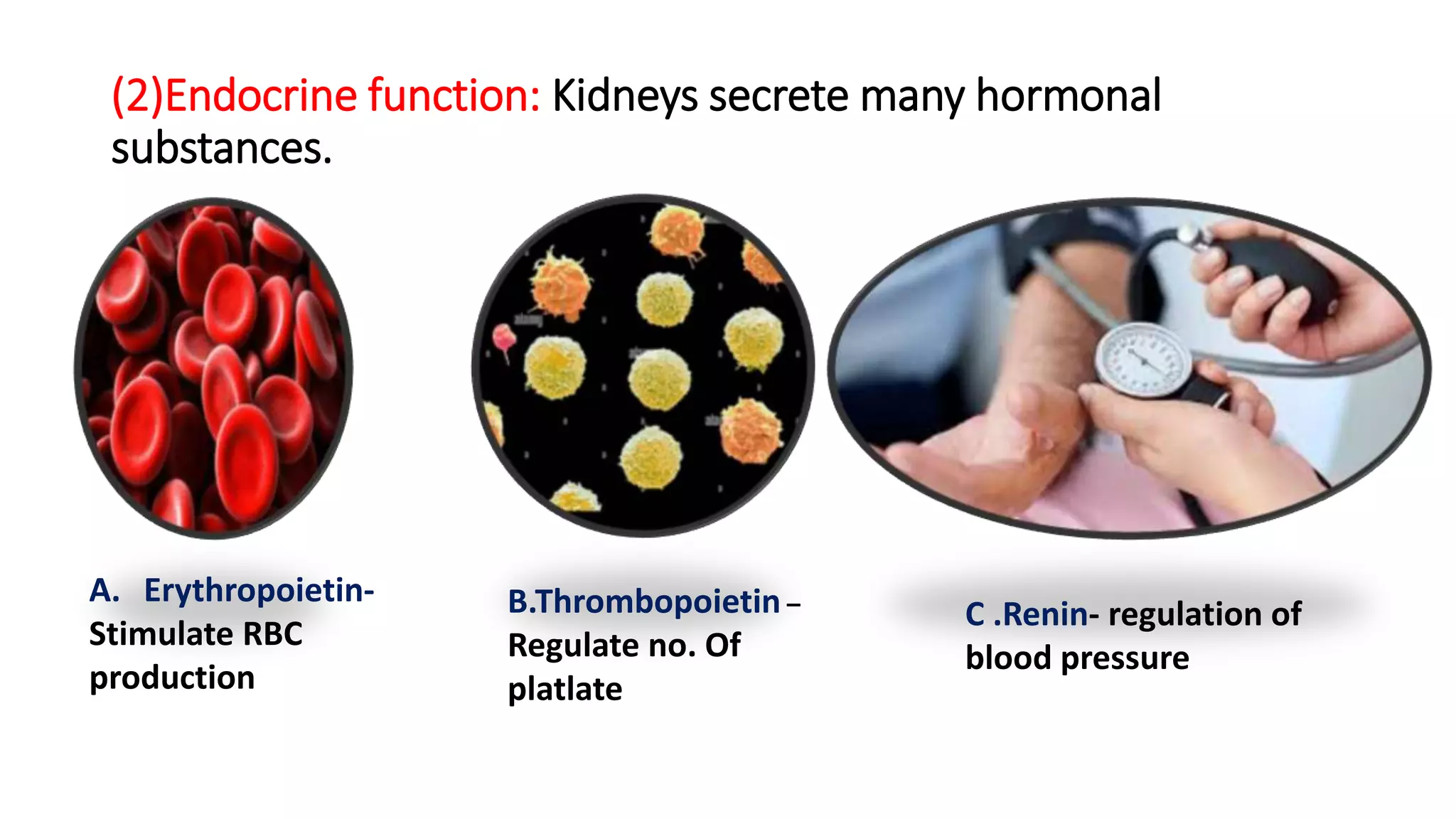
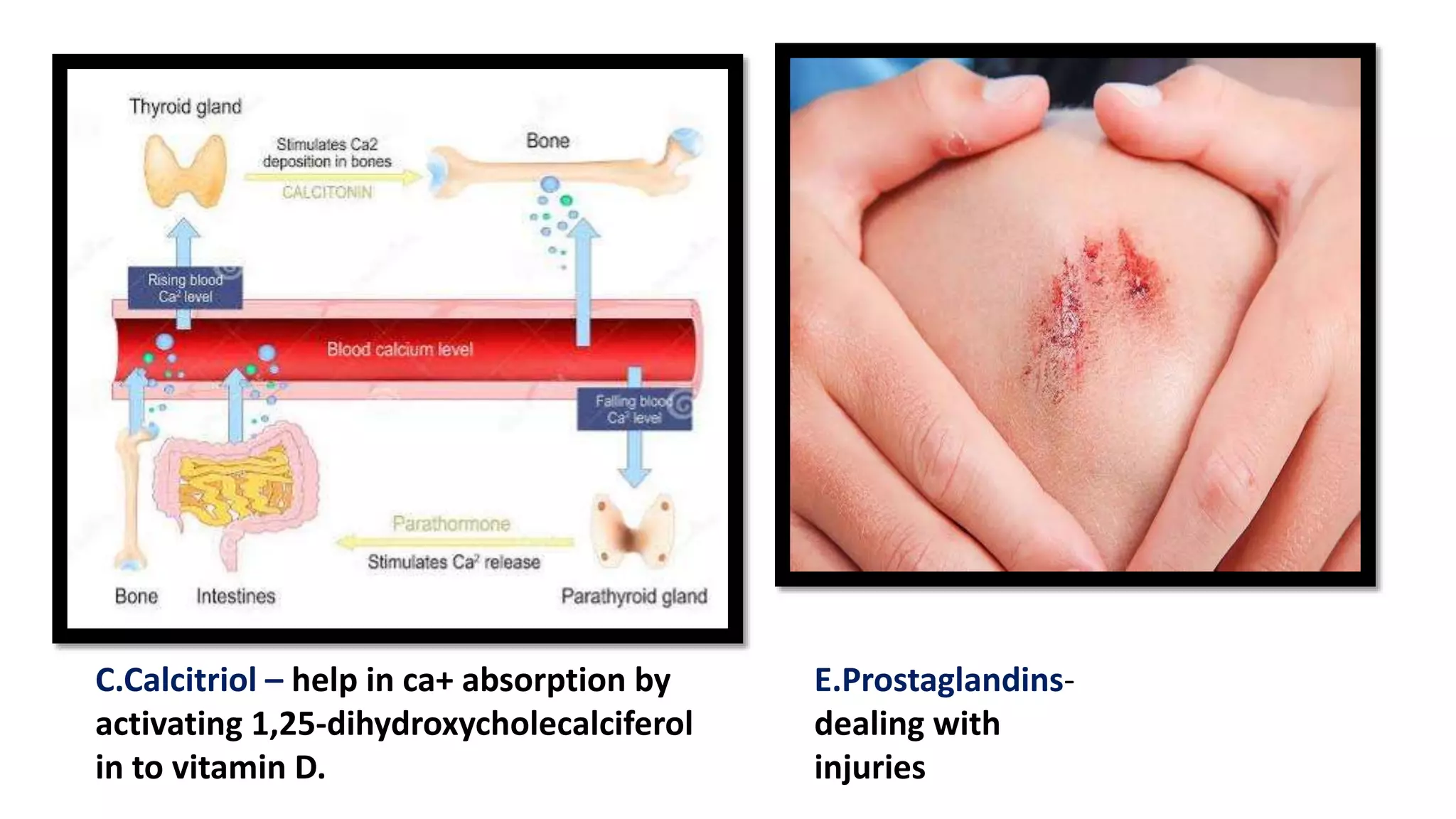
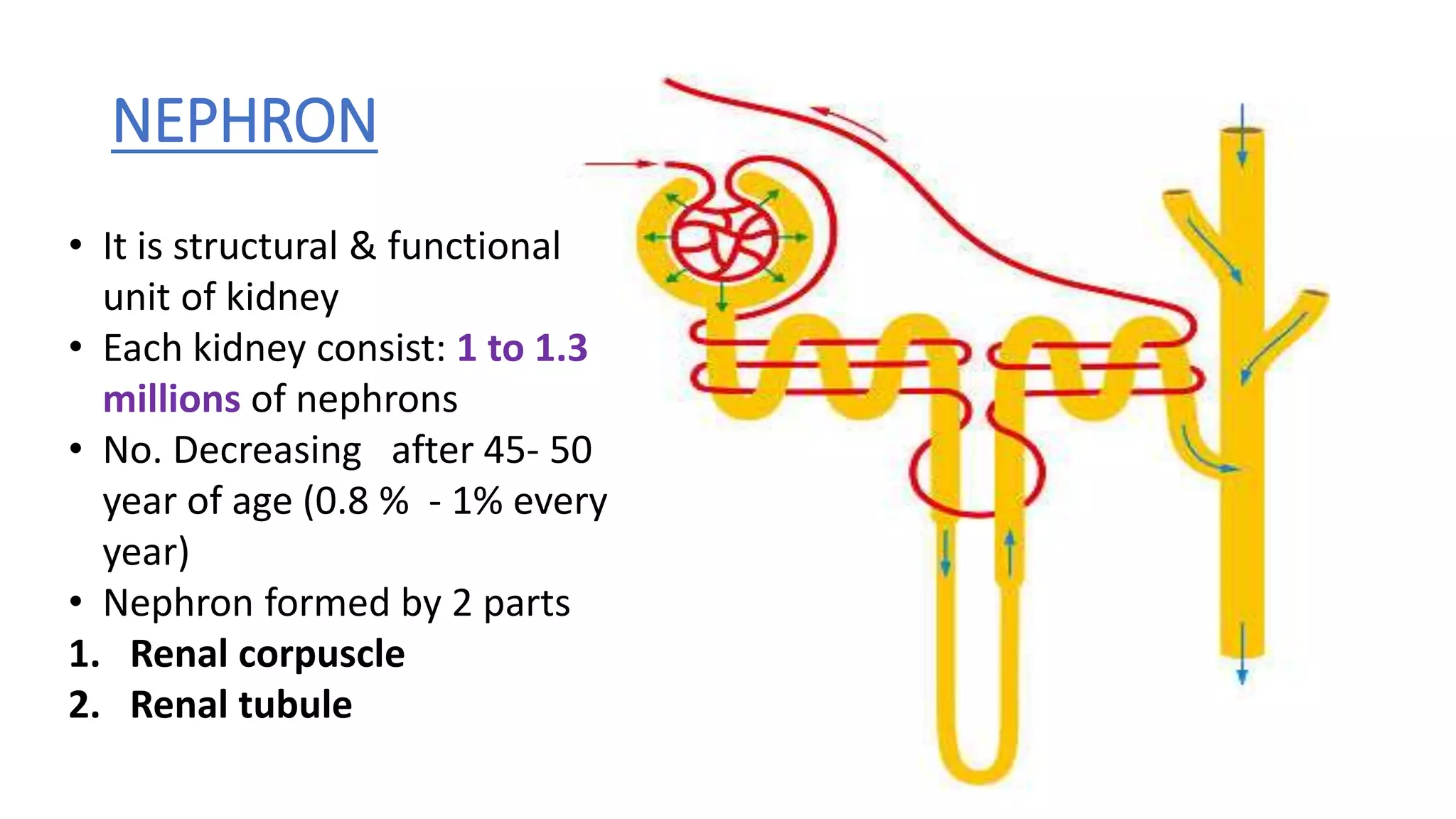
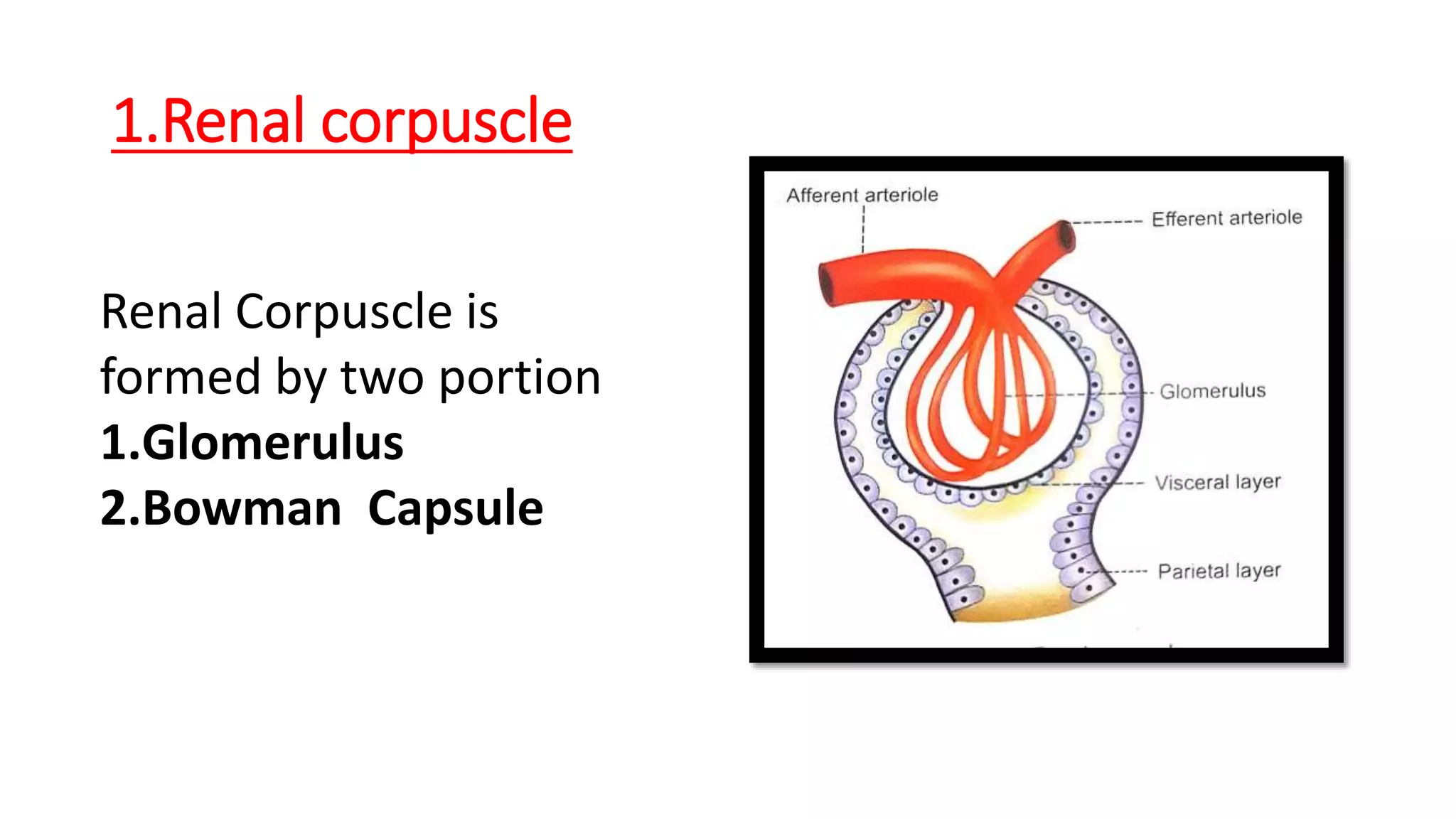
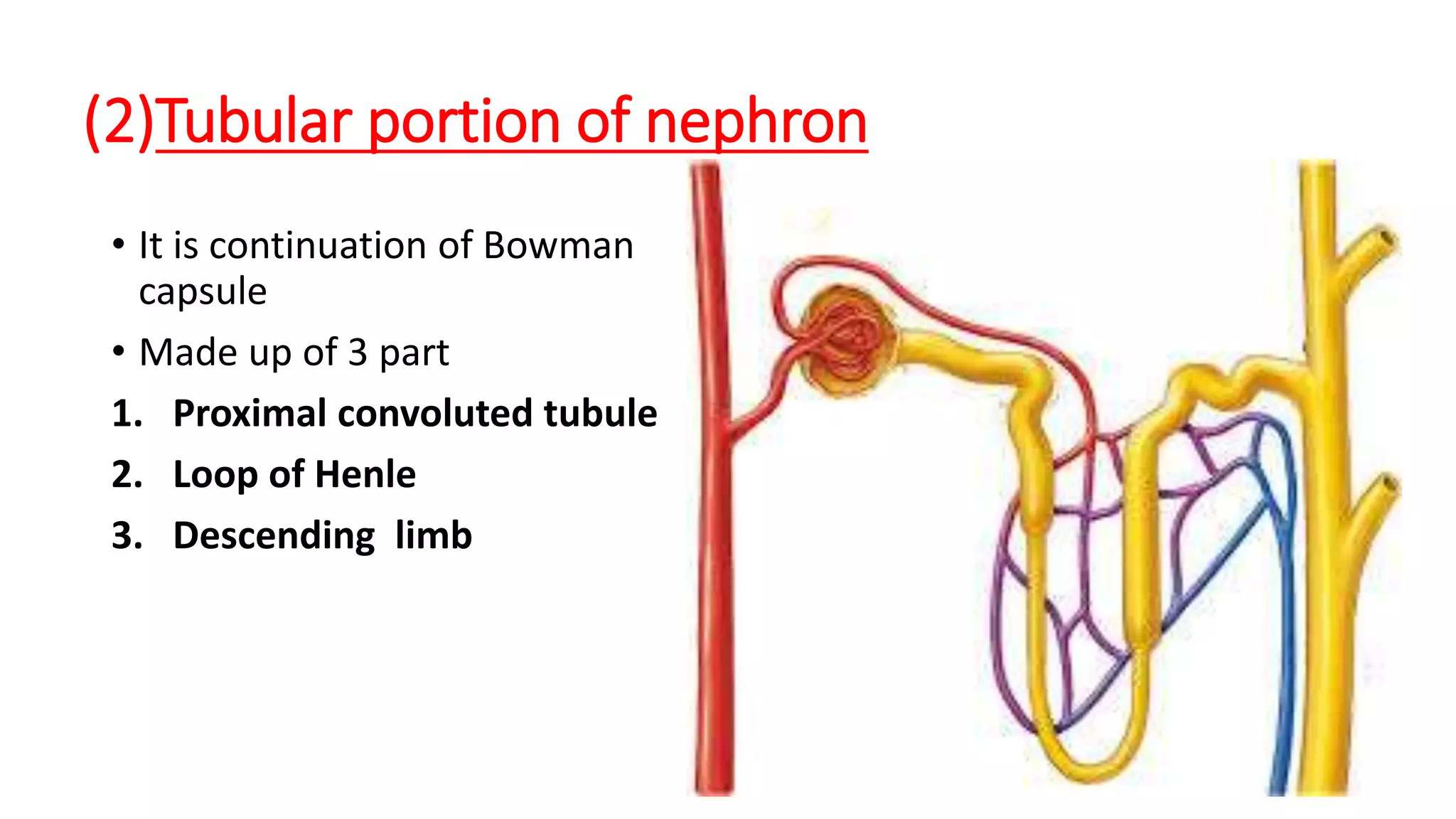
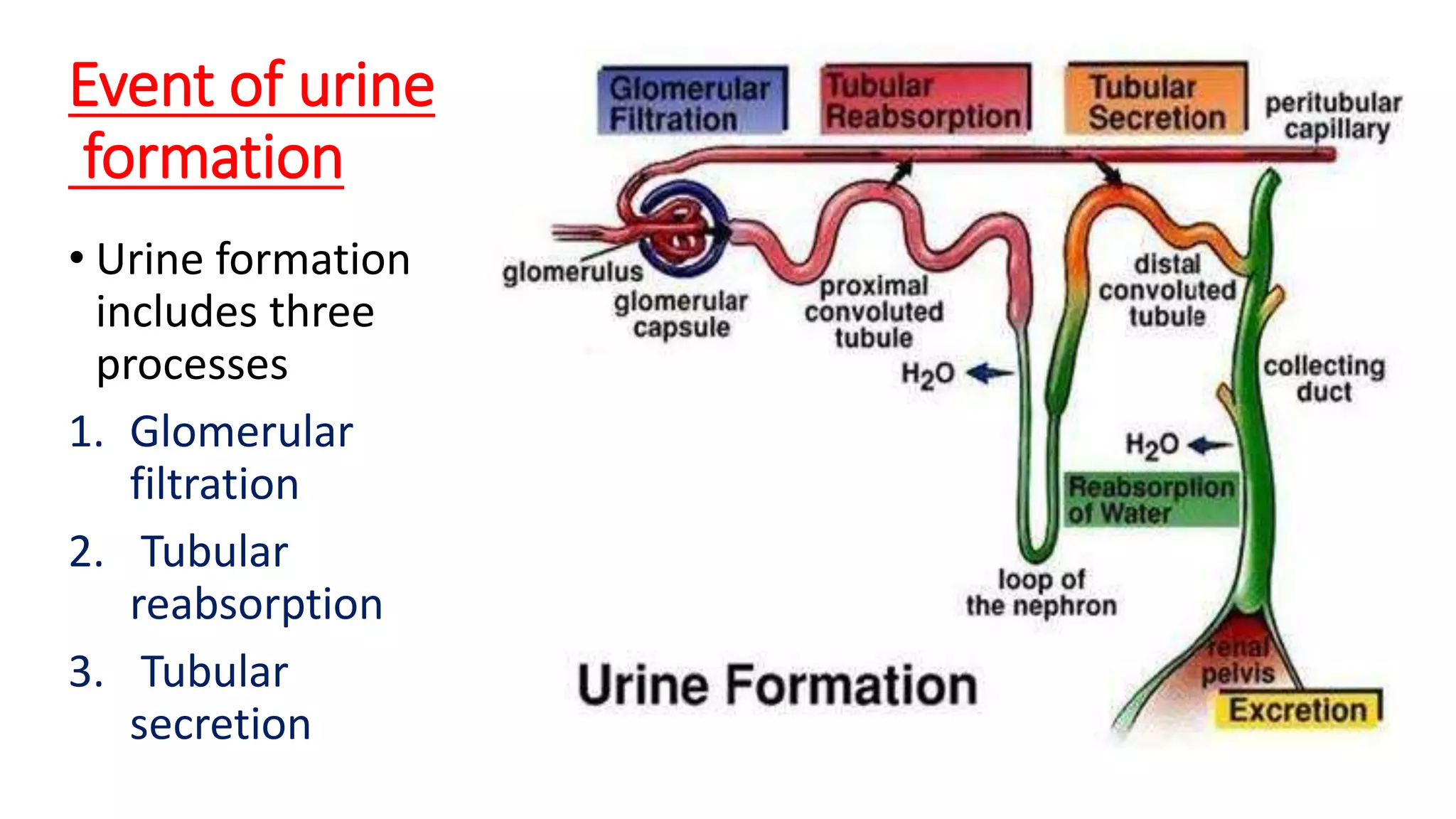
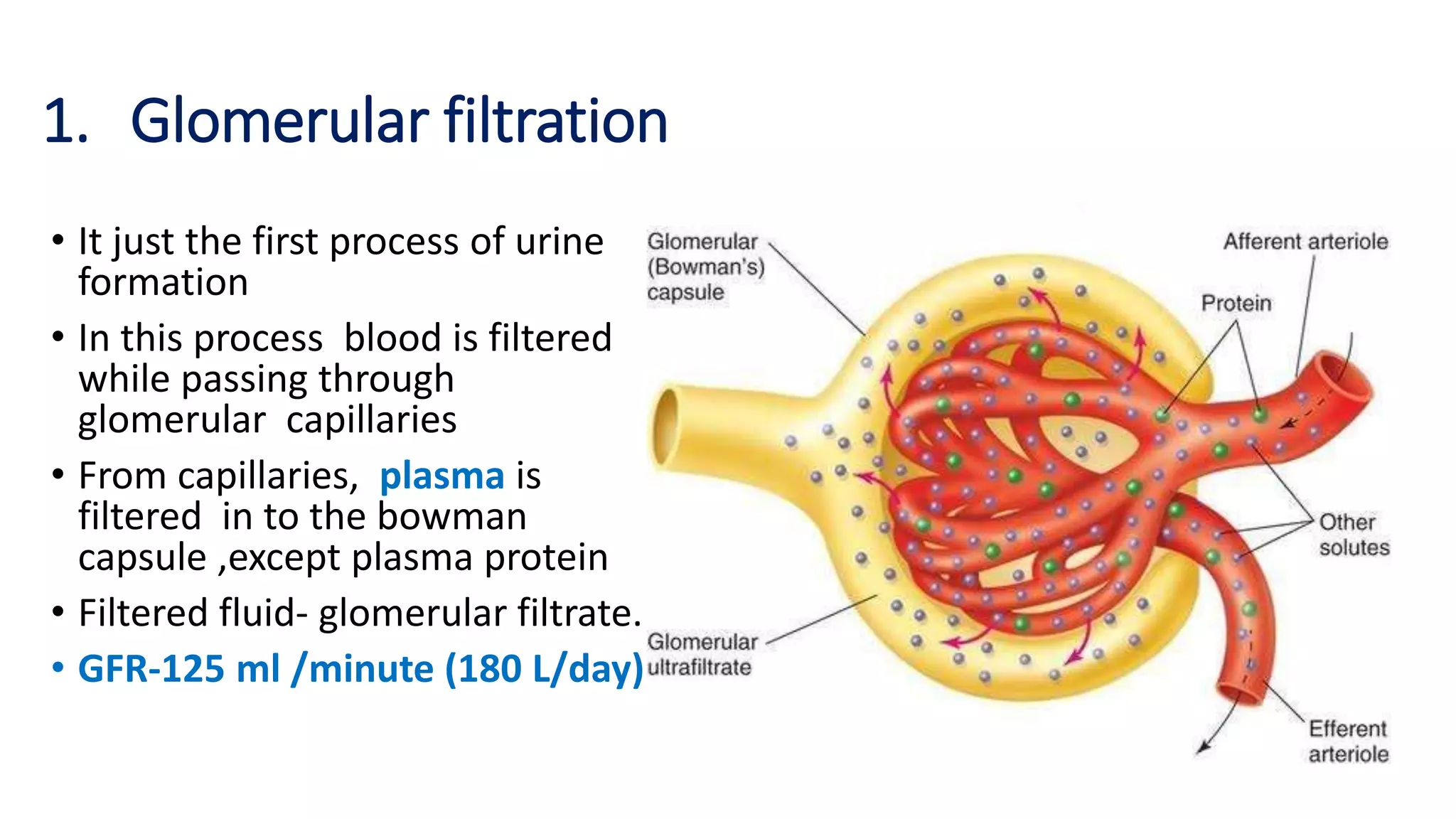
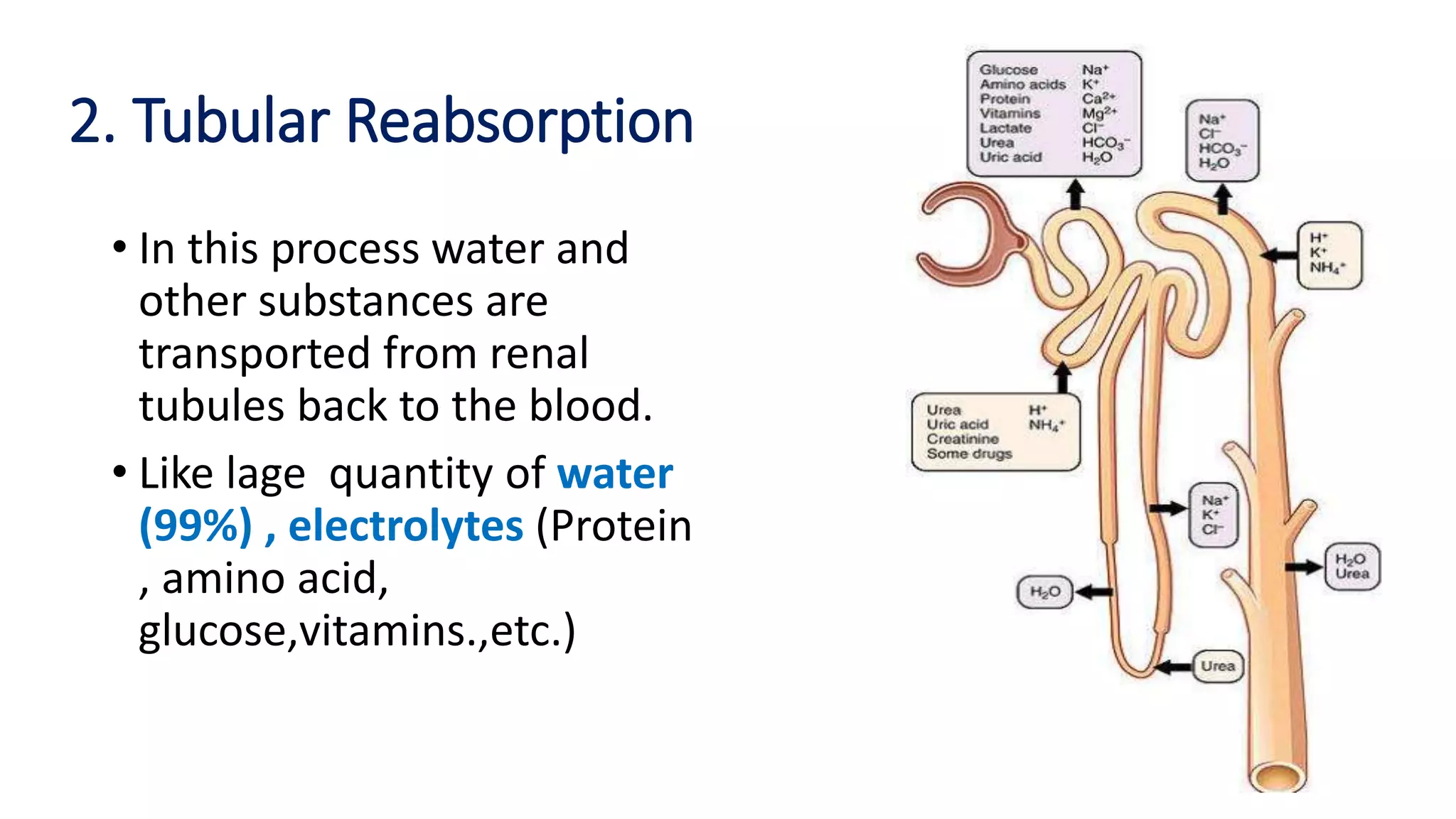
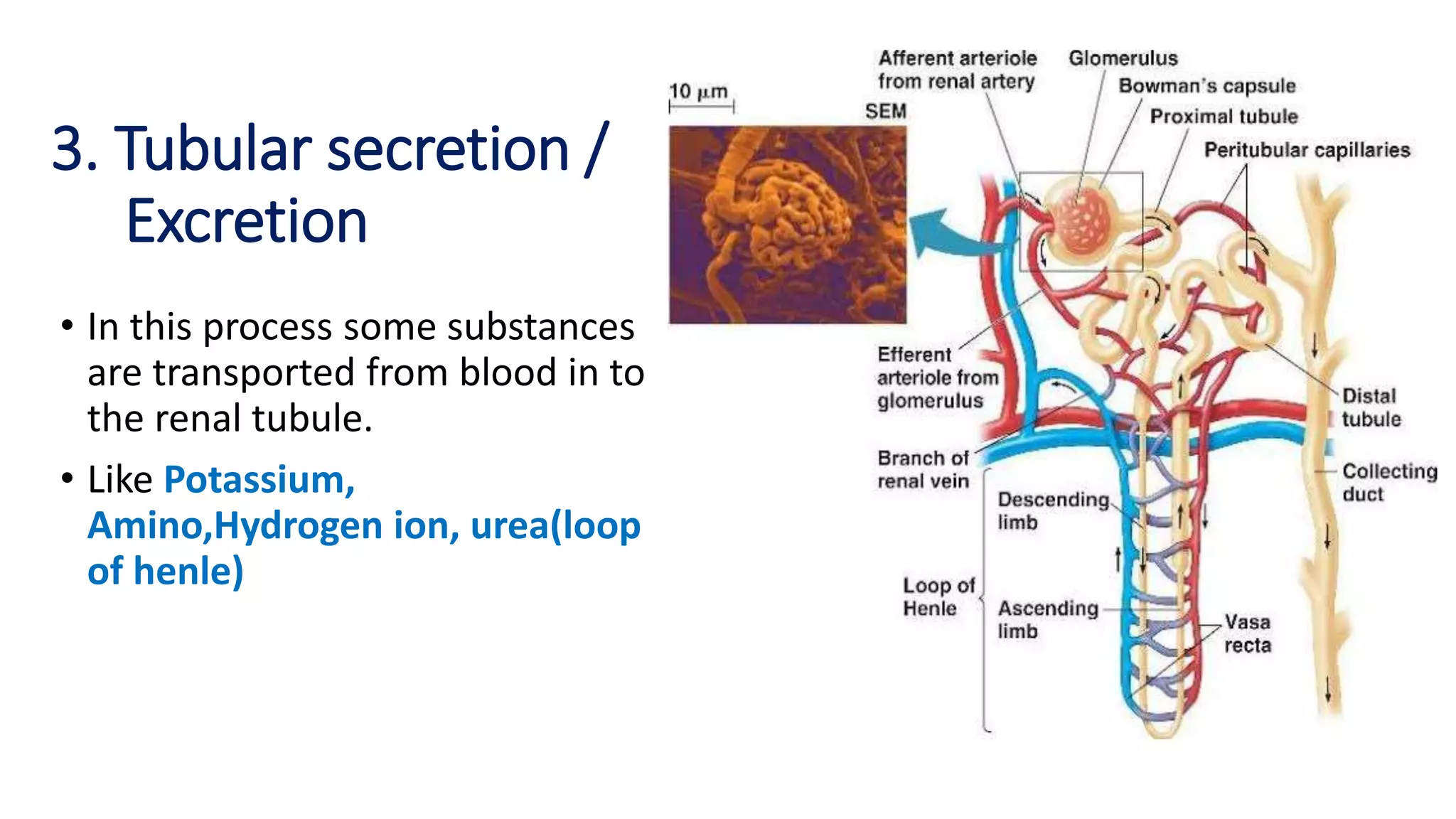
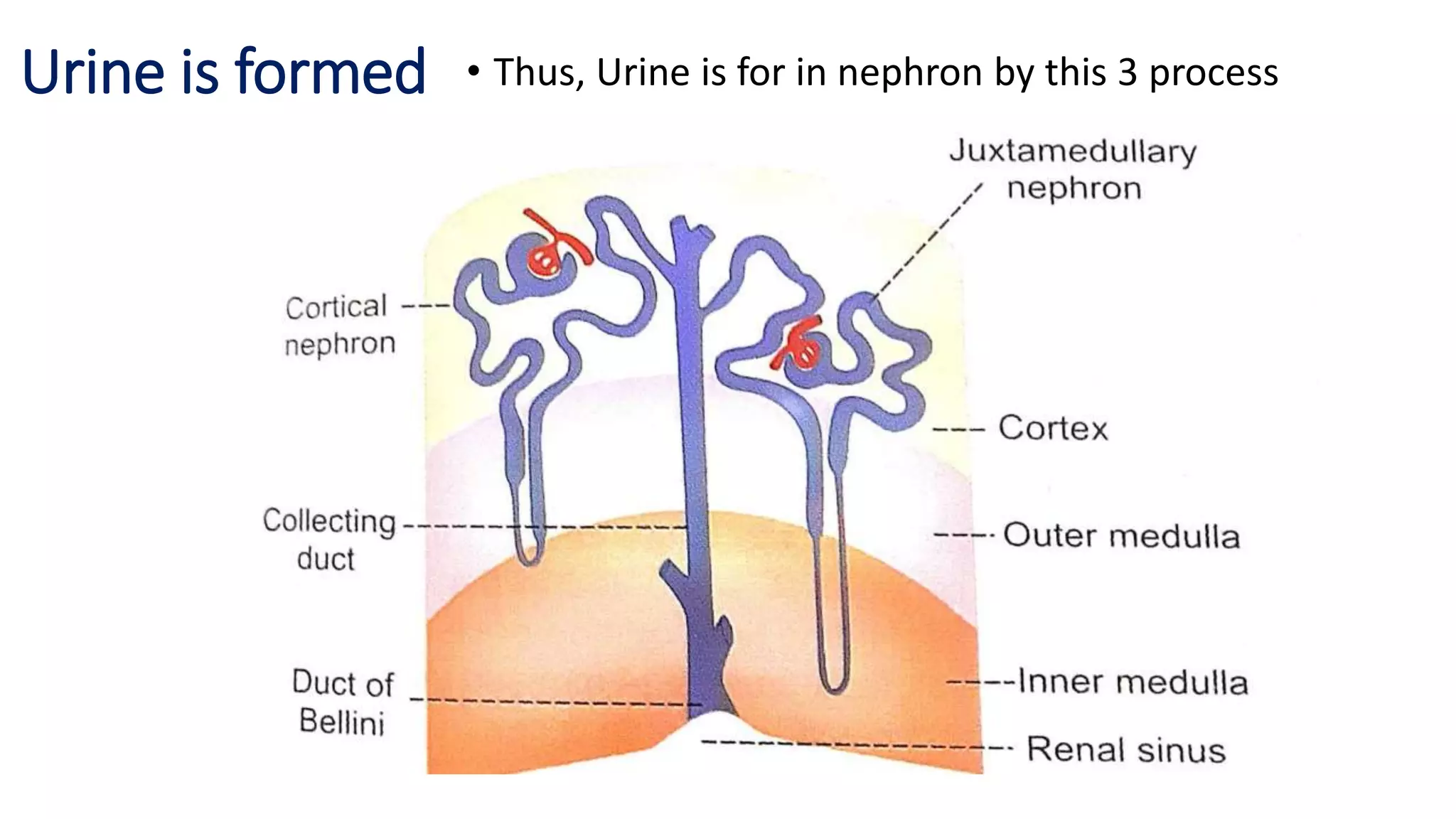
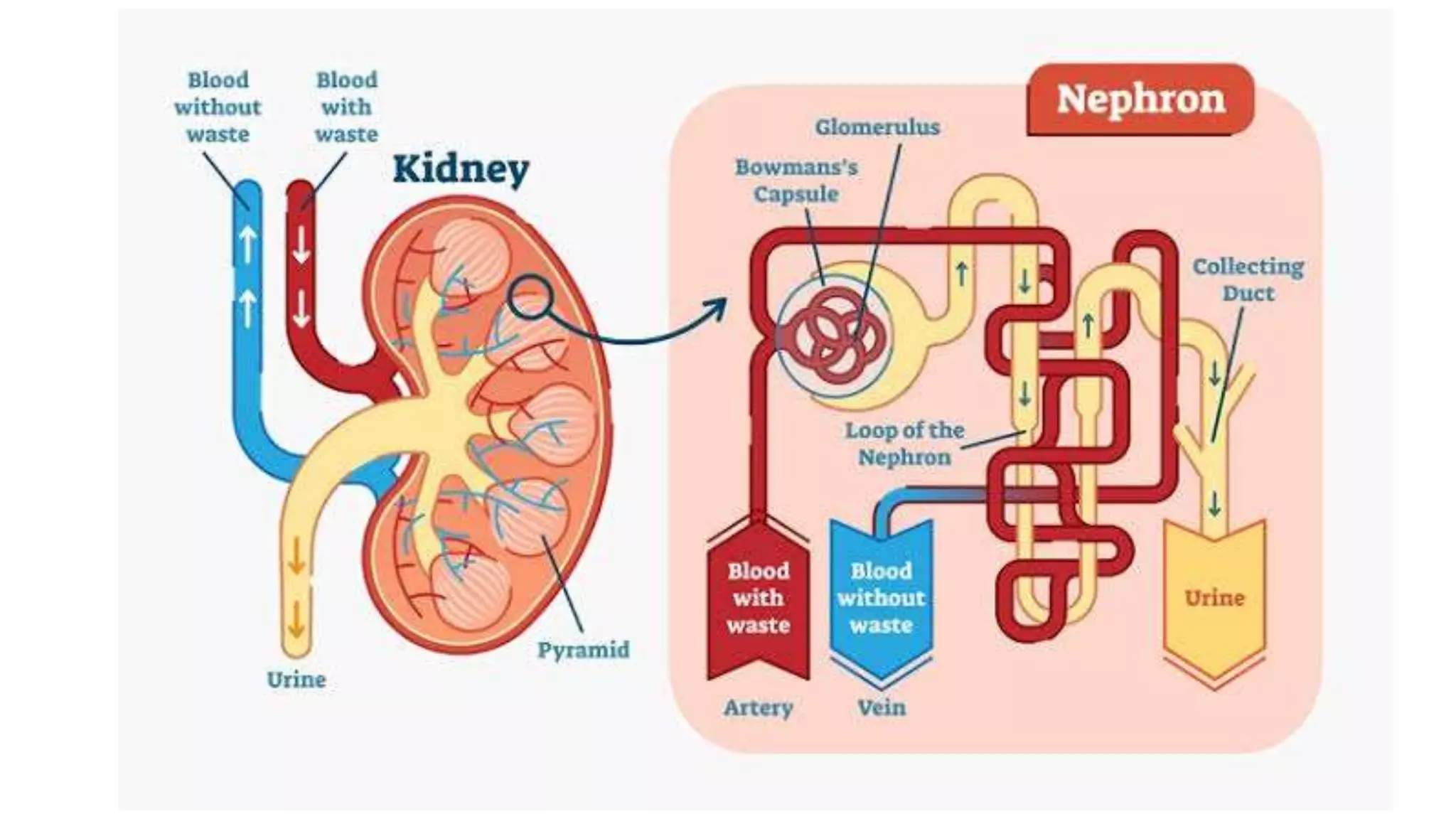
The document outlines the structure and functions of the kidneys, describing their role in homeostasis, waste excretion, and regulation of blood pressure and electrolytes. It details the nephron as the functional unit of the kidney, including the processes of urine formation: glomerular filtration, tubular reabsorption, and tubular secretion. Additionally, it highlights the kidneys' endocrine functions, including hormone secretion that impacts red blood cell production and calcium absorption.