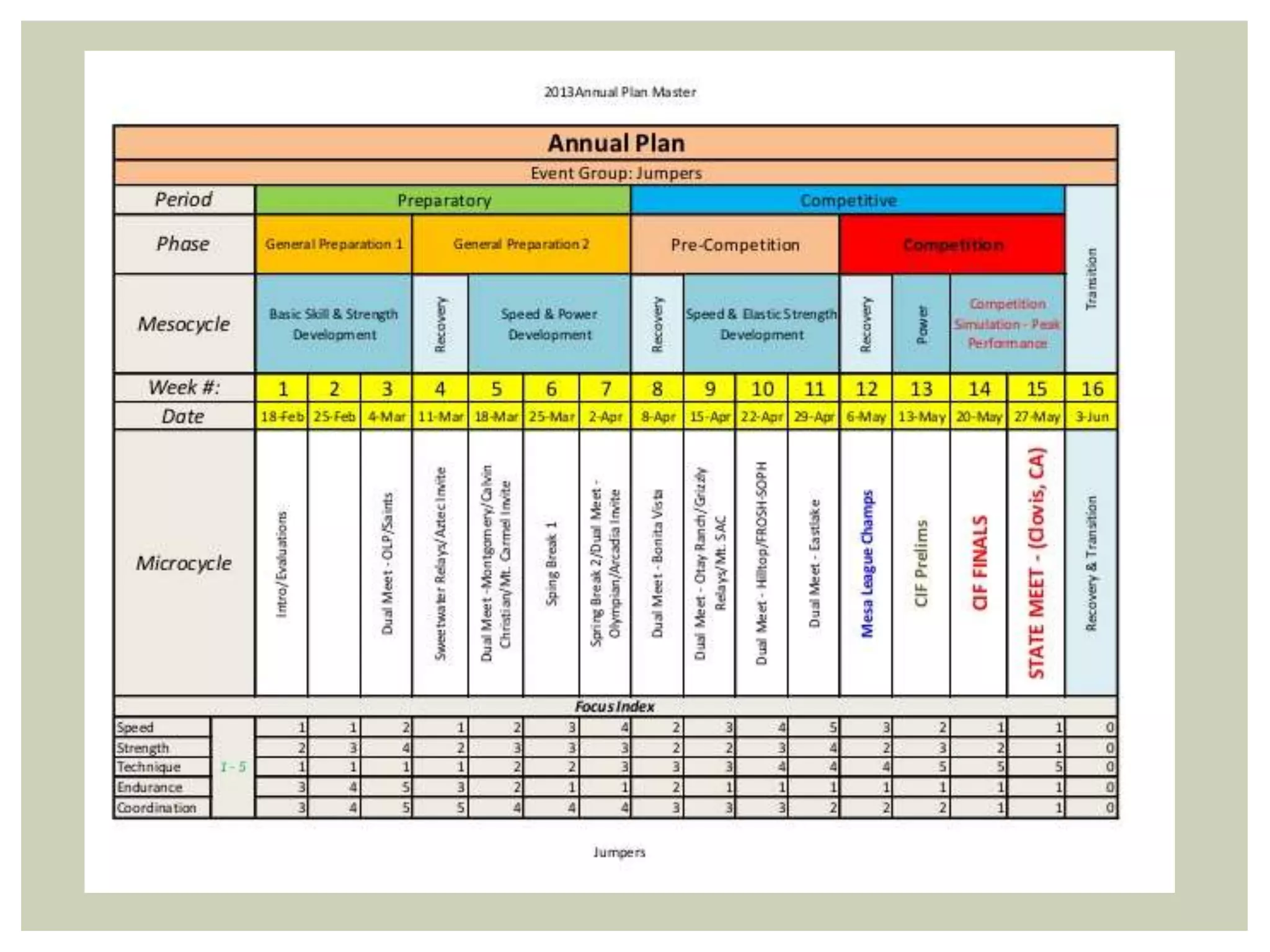
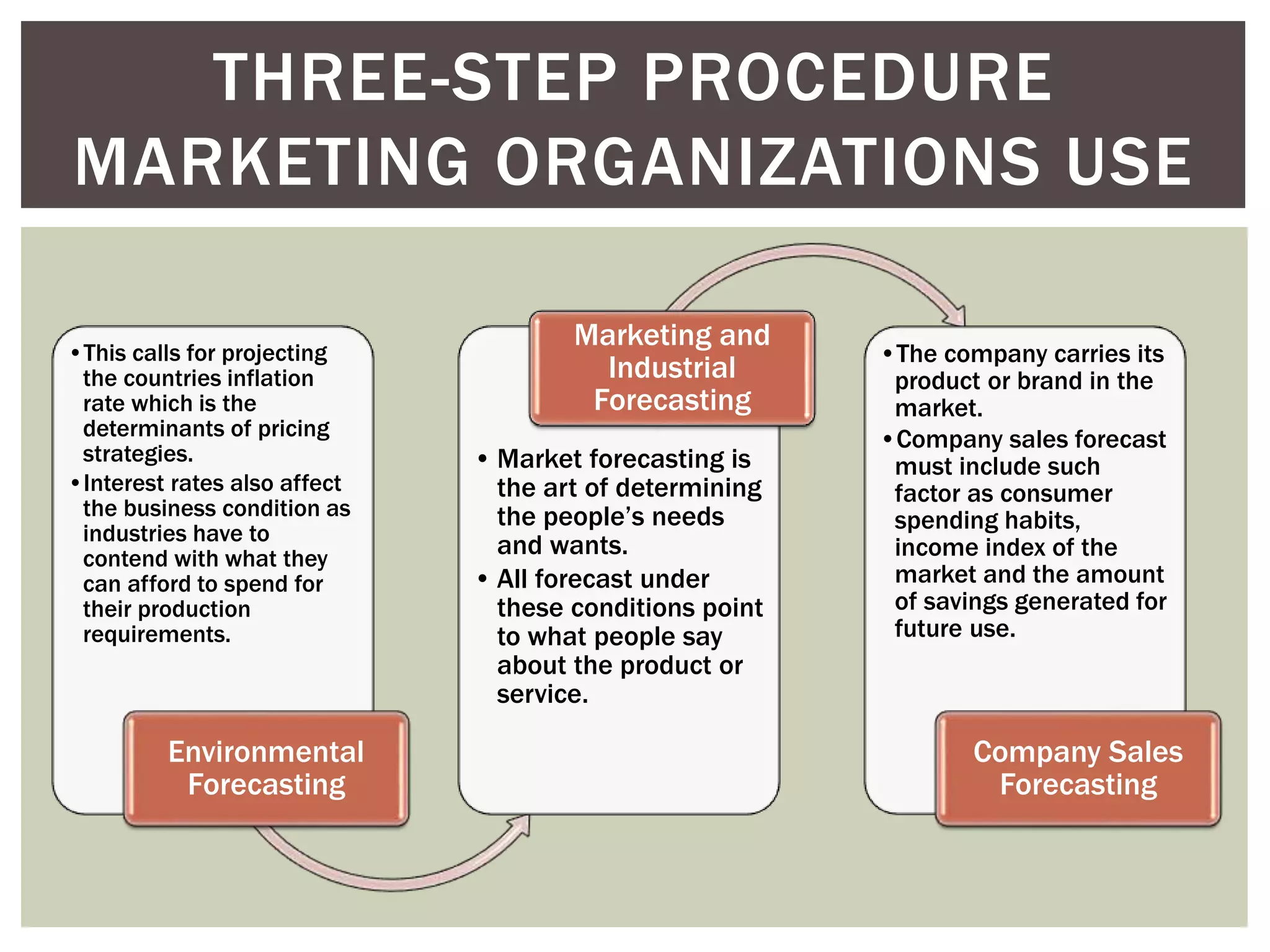
The document provides a comprehensive overview of strategic planning and forecasting in marketing, detailing essential processes like annual and long-range planning, situation analysis, and demand forecasting. It outlines the importance of setting clear objectives, analyzing past performance, and developing tailored marketing strategies and tactics to adapt to market conditions. Additionally, it emphasizes the need for thorough evaluation and ongoing adjustments to effectively meet customer needs and enhance organizational performance.