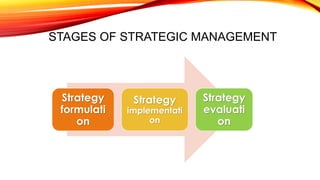
The document outlines the concept and features of strategic management, detailing its importance in achieving long-term goals through effective resource allocation and managerial decision-making. It discusses various levels of strategy, including corporate-level, business-level, and functional/operational-level strategies, along with the stages of strategic management, such as formulation, implementation, and evaluation. Additionally, it highlights common pitfalls in strategic planning and the benefits of strategic management for organizations.