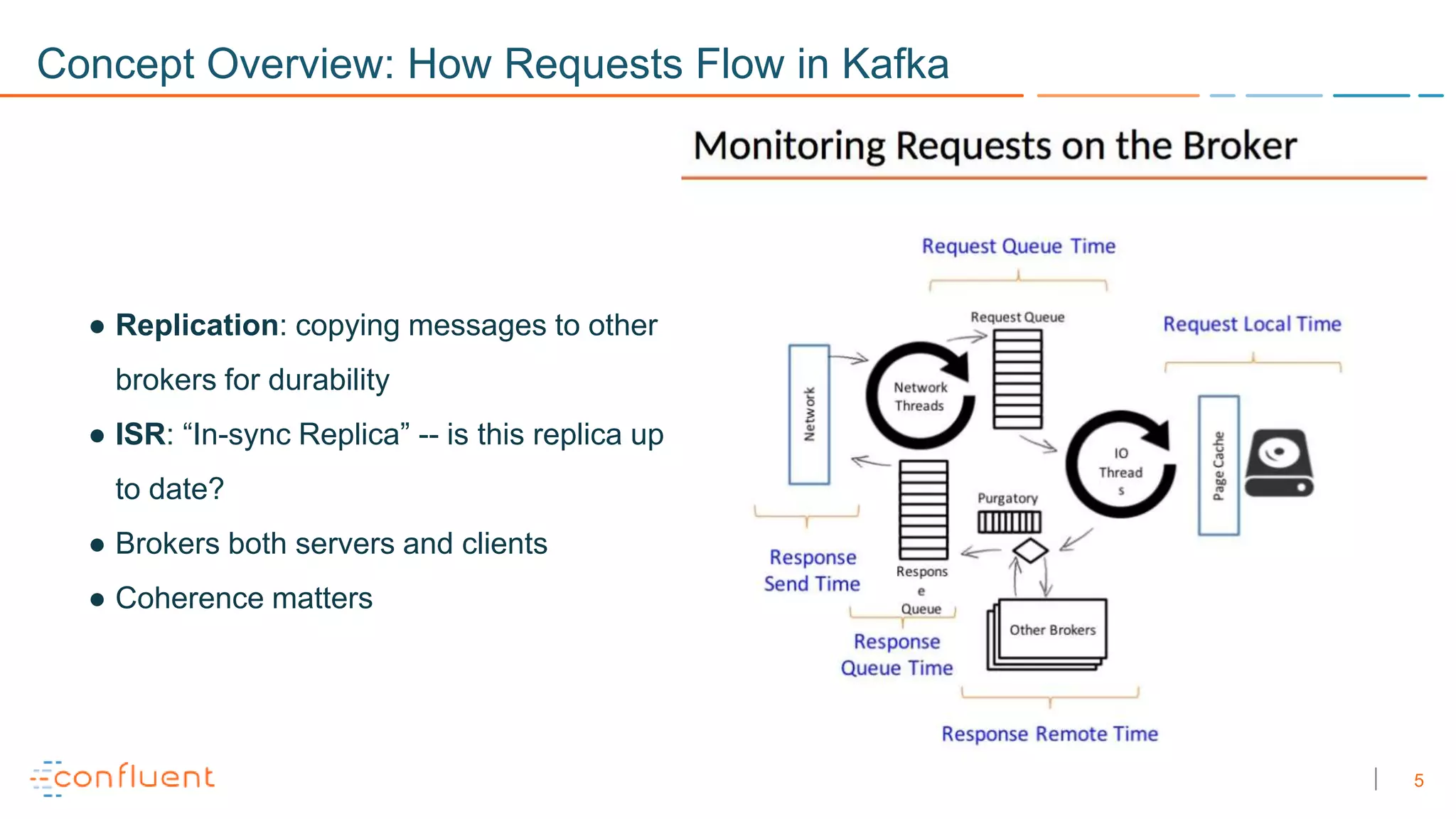
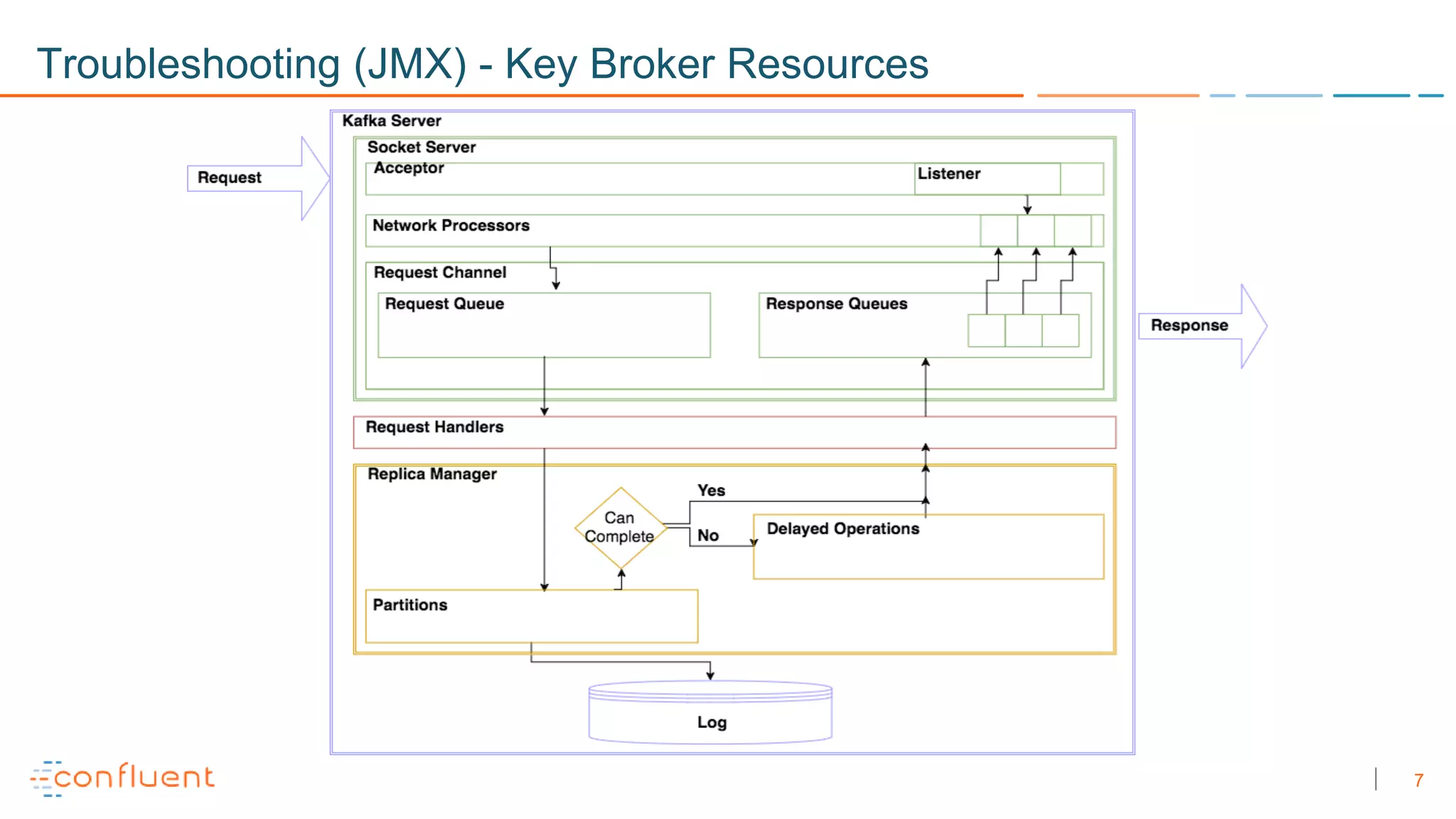
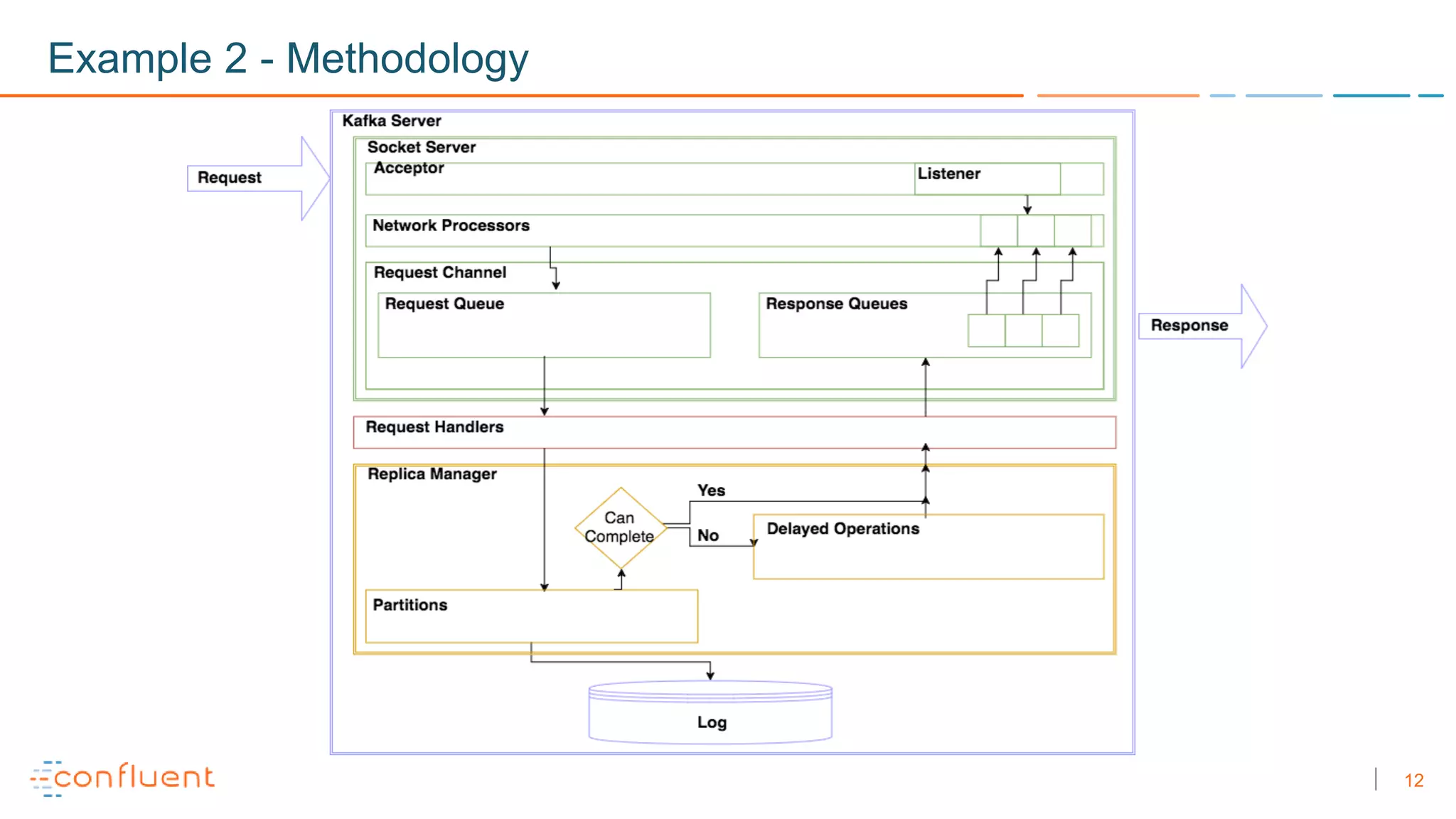
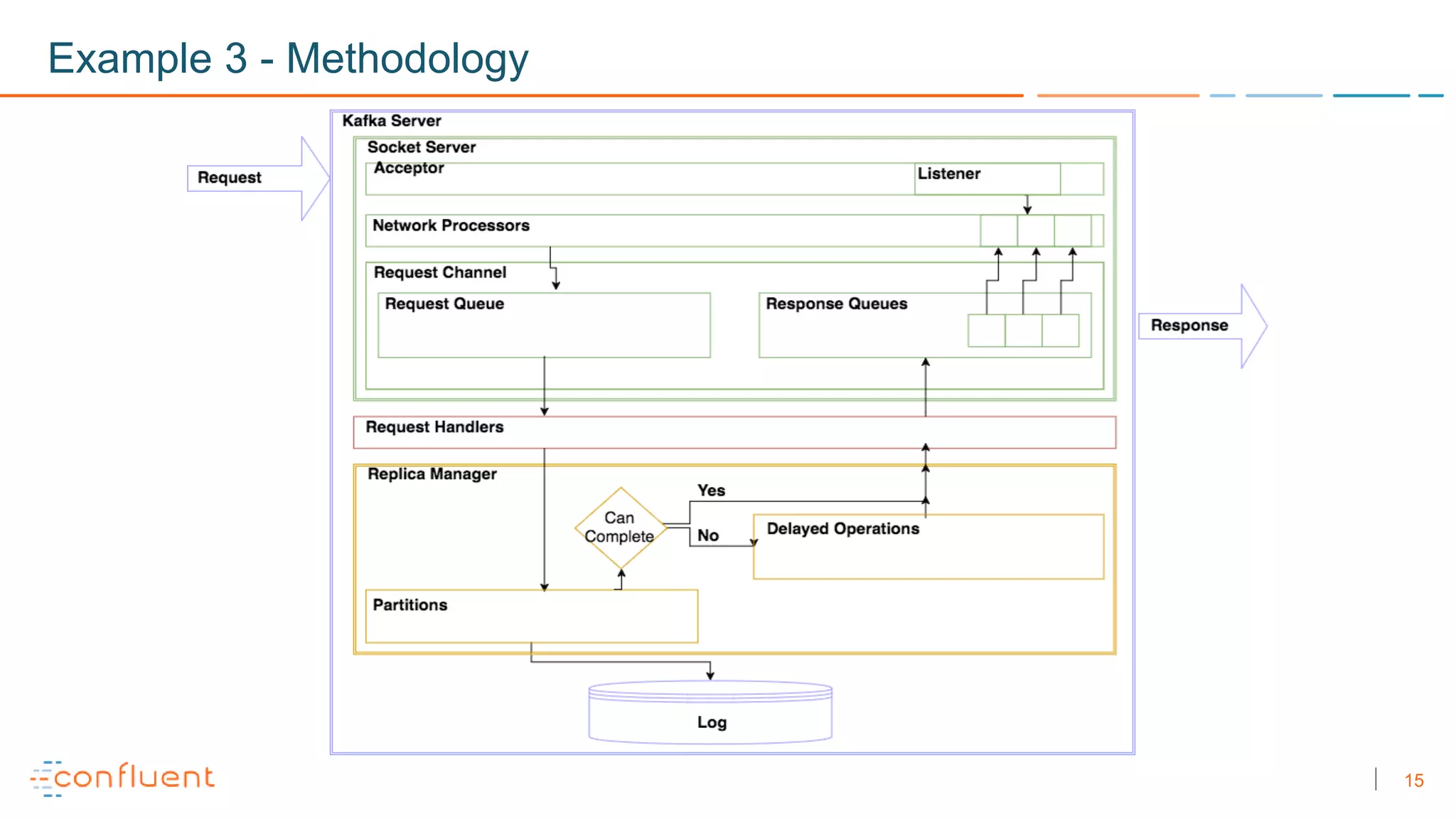
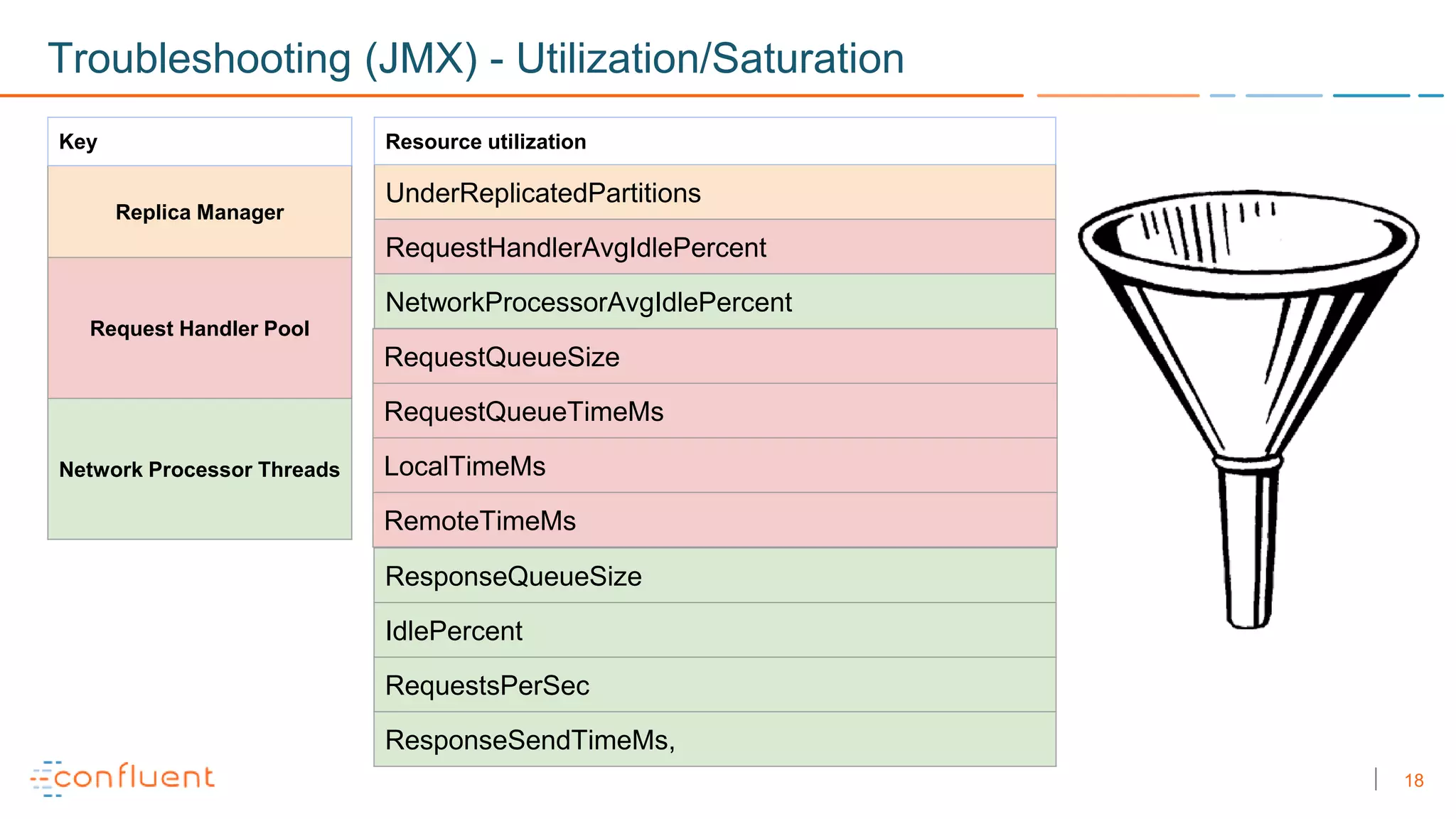
The document discusses troubleshooting techniques for Apache Kafka, emphasizing the importance of monitoring metrics via JMX to prevent and resolve common issues. It includes examples of problems encountered, their causes, and recommended solutions while highlighting the need for proper staging environments when implementing changes. Additionally, it offers resources for further learning about Kafka and its operations.