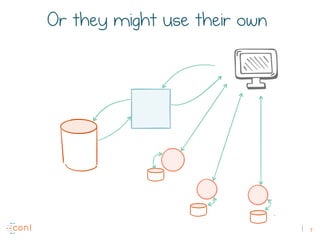
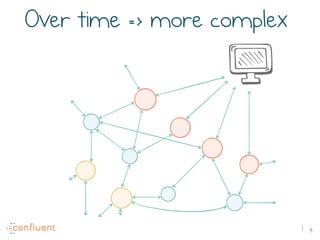
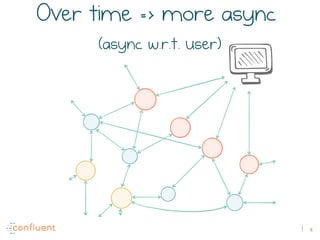
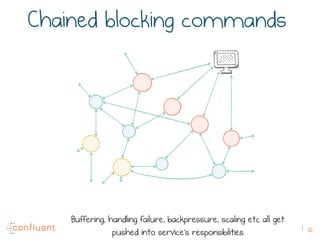
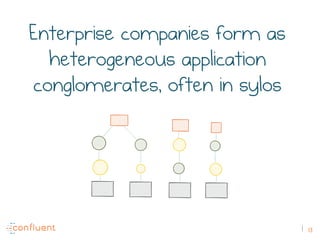
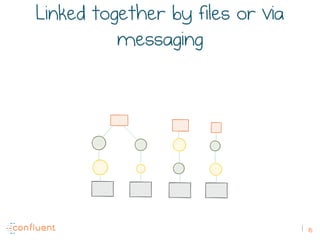
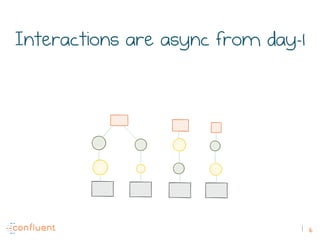
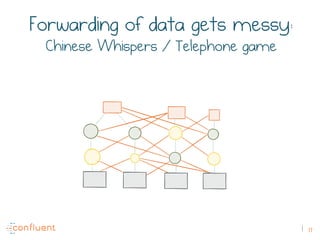
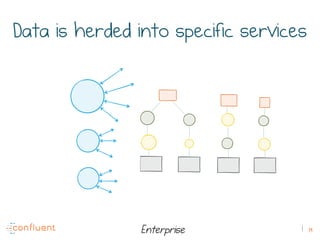
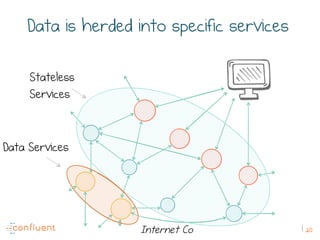
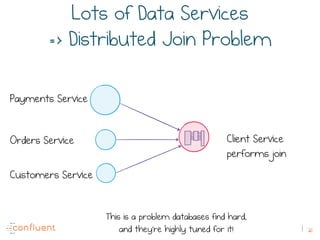
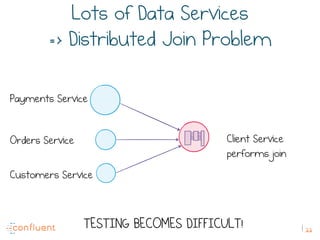
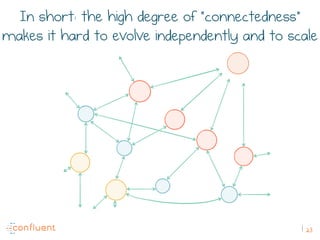
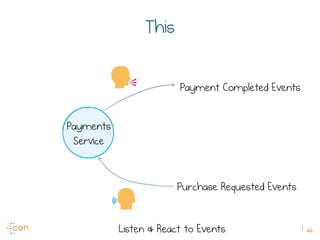
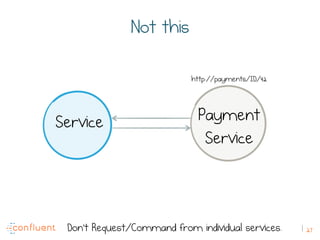
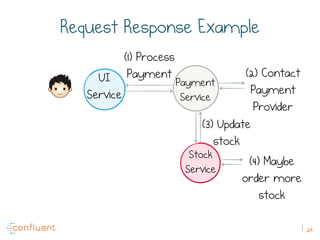
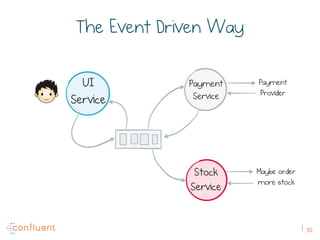
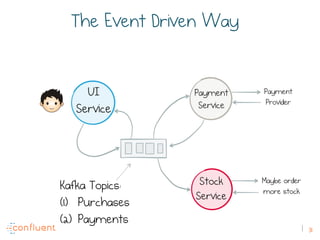
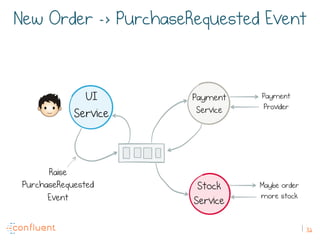
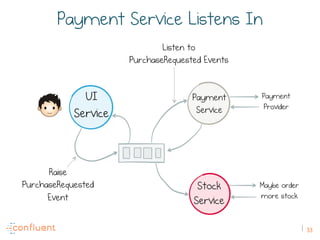
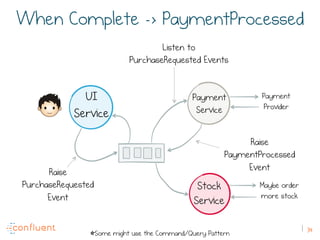
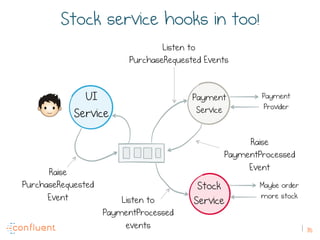
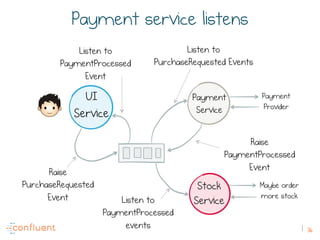
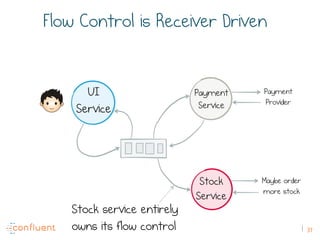
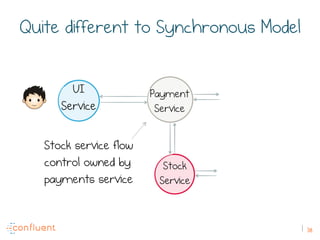
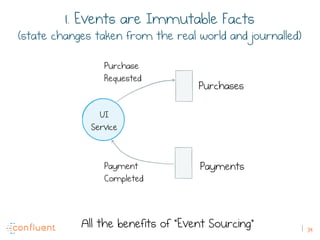
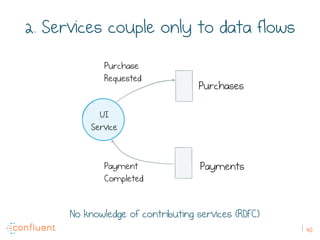
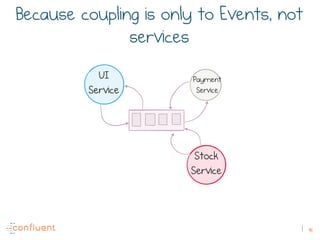
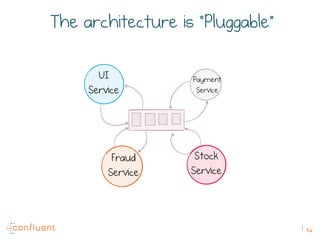
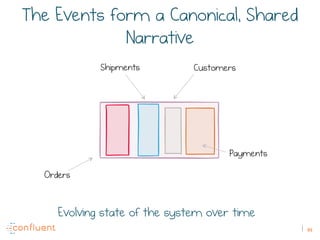
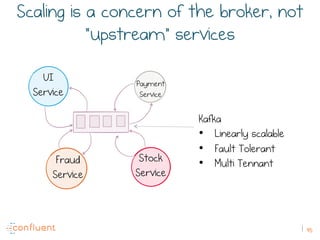
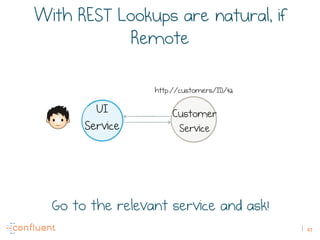
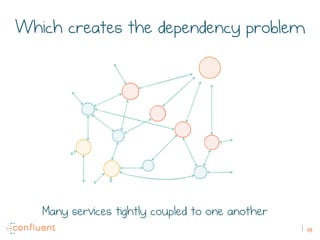
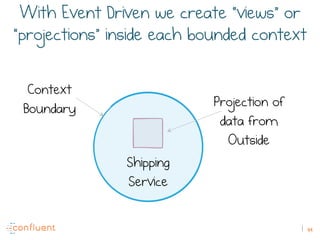
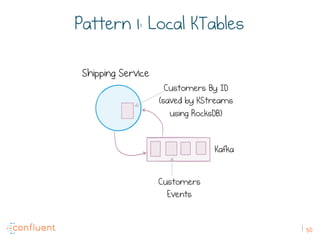
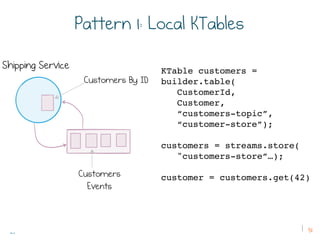
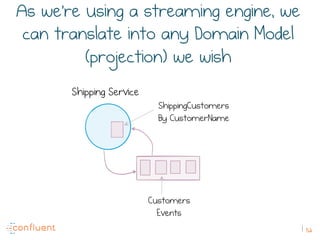
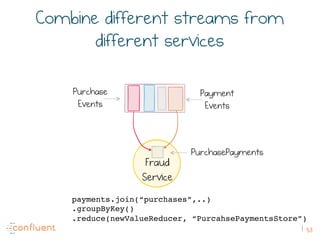
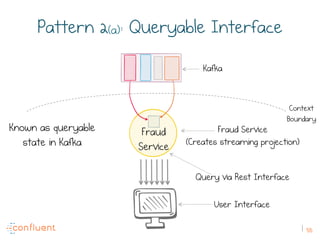
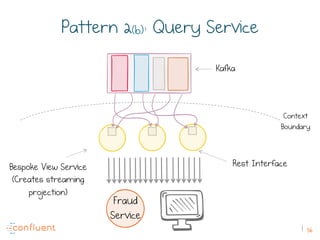
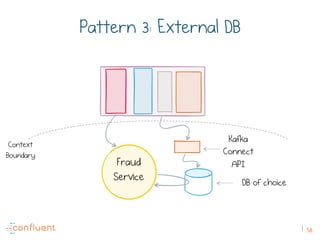
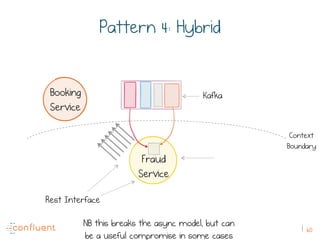
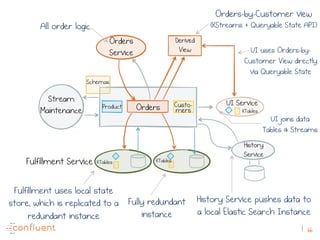
The document discusses the transition from traditional REST services to event-driven architectures using Apache Kafka, highlighting the challenges of data management in both internet and enterprise companies. It emphasizes the benefits of decoupling services through event interactions, utilizing immutability and shared narratives, and presents various patterns for querying data in event-driven systems. Ultimately, the talk promotes an architecture that allows for better scalability, flexibility, and fault tolerance in managing complex service interactions.