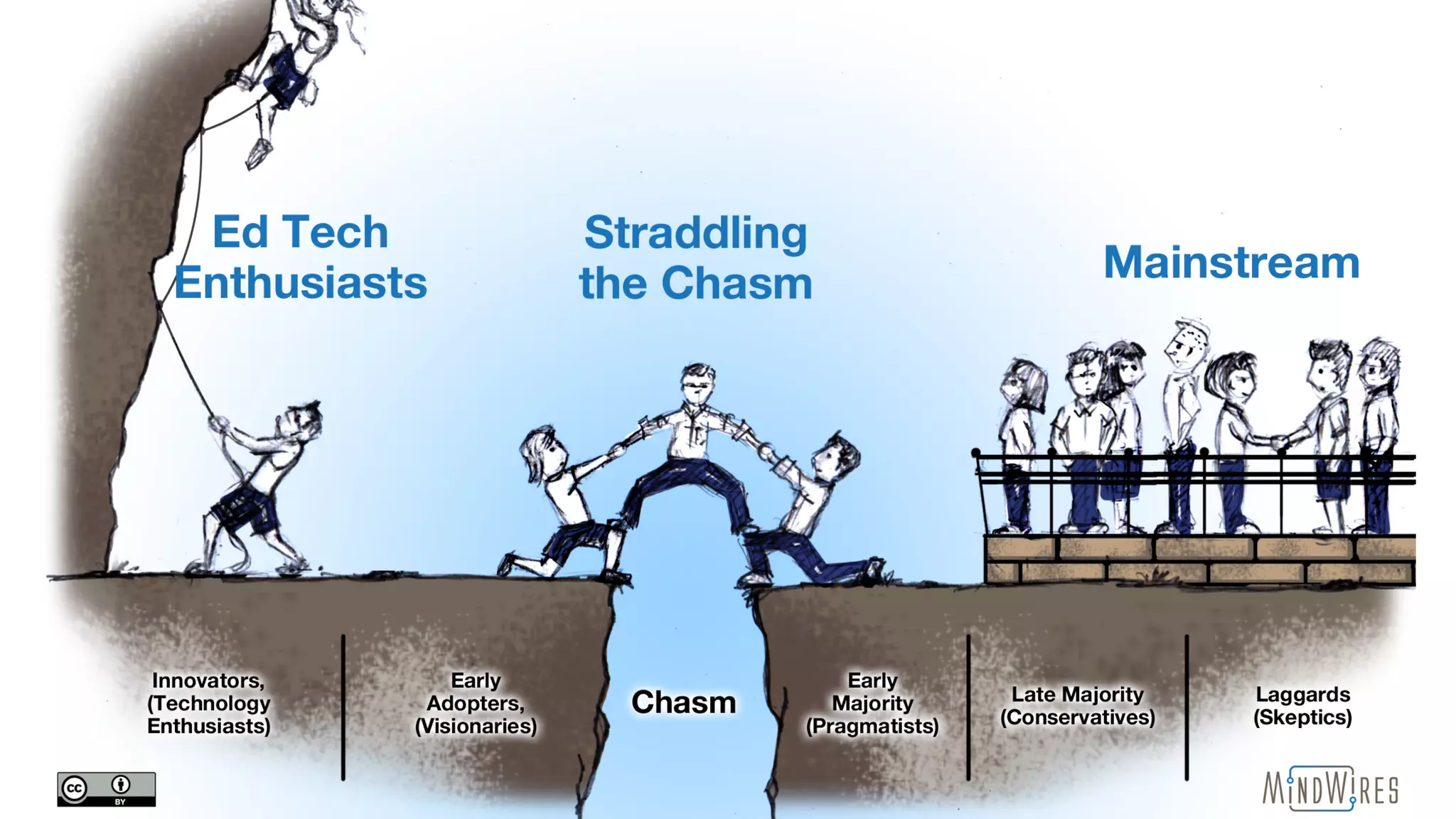
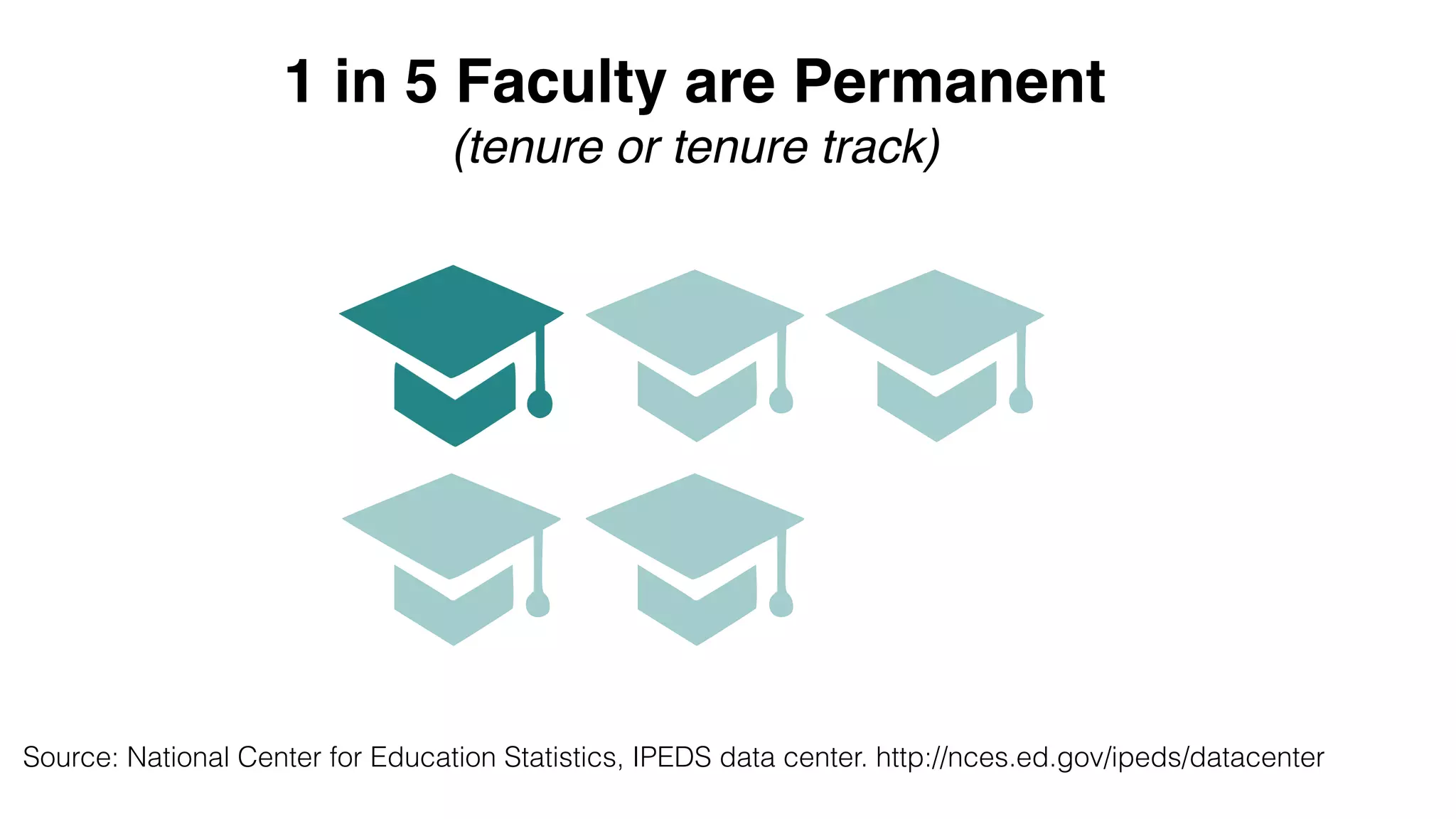
The document discusses the importance of professional development and support for faculty in higher education, particularly in the context of technological innovation and online teaching. It highlights the need for just-in-time resources, community engagement, and effective use of learning management systems to enhance faculty satisfaction and adapt to changing educational environments. Additionally, it emphasizes the role of technology in shaping professional identities and fostering collaborative learning among educators.






















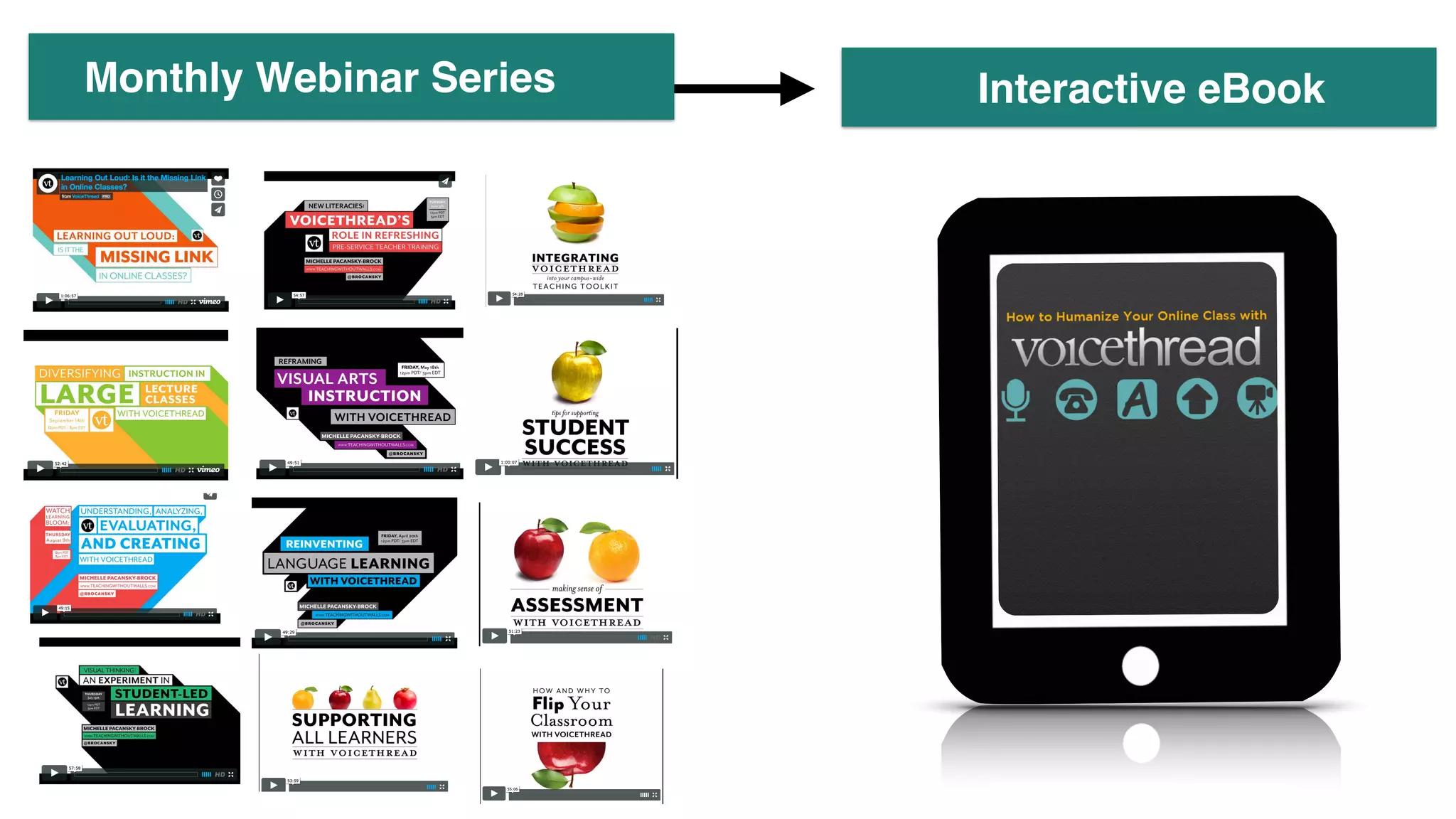



![JUST-IN-TIME
PROFESIONAL DEVELOPMENT
“I didn’t have to go anywhere. I had more freedom”
“I am at the center. In a workshop, I’m passive most of the time.”
“I could only attend a face-to-face event at one of the
three institutions [at which I teach].”
Pacansky-Brock, M. (2015). Examining the effects of an eBook to support faculty who teach with VoiceThread: An action research study. (Doctoral dissertation).](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/straddlingthechasm-150923020533-lva1-app6891/75/Straddling-The-Chasm-Rethinking-Faculty-Support-29-2048.jpg)