This document summarizes key points from a presentation on leveraging online tools for teacher learning. Some of the main ideas discussed include:
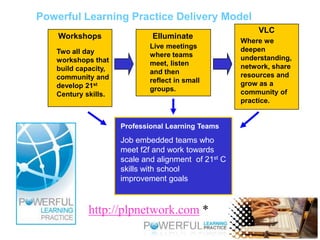
- Online professional development can enable sustained training over time, help teachers transfer learning to their classrooms, and facilitate strong content learning and discussions.
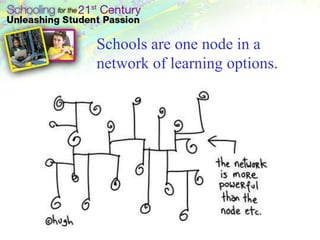
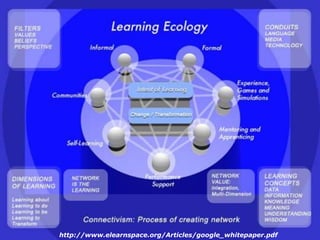
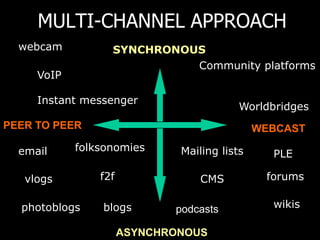
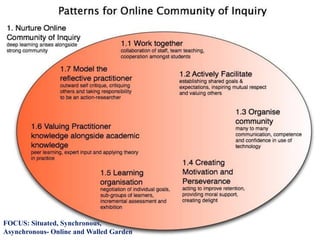
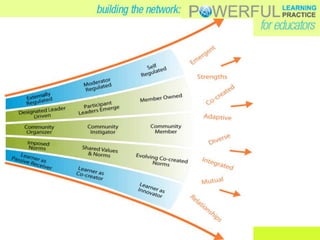
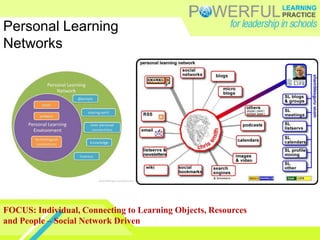
- Emerging online tools like course platforms, collaboration tools, and social networking sites provide new opportunities for online teacher learning and communities.
- Trend data shows an increasing number of teachers are using the internet for teaching ideas, online courses, and social networking to connect with other educators.
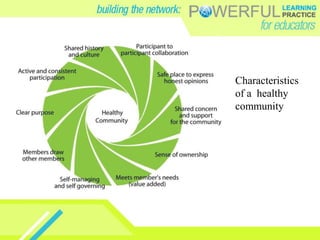
- Effective online professional learning models emphasize convenience for teachers, allow learning to emerge over time through relationships, and aim for fun rather than solely technology skills.












![Food for Thought Gerald Herbert/AP“I think that online professional development does have the promise to [overcome teachers’ frustrations with PD], but that promised is only realized if people use the tools well. … But I do think some online tools, if the training takes advantage of them, can help with some of the classic issues of professional development.” (Chris Dede, Interview, Teacher Professional Development Sourcebook, Fall 2009: http://www.edweek.org/go/tsb/dede)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nsdc-thisone-091208074047-phpapp02/85/Nsdc-This-One-13-320.jpg)