The document discusses the eGranary Digital Library Project, which stores educational resources on hard drives and distributes them to institutions lacking adequate internet access. It is run by the Widernet Project and provides millions of internet resources through a fully searchable digital library. Some key points:
- The eGranary now has installations at over 350 institutions worldwide, delivering educational materials like videos, books and journals.
- Content is identified from websites and publishers are requested for permission to copy materials. It covers many subject areas.
- Users have provided positive feedback on accessing information otherwise not available due to limited bandwidth.
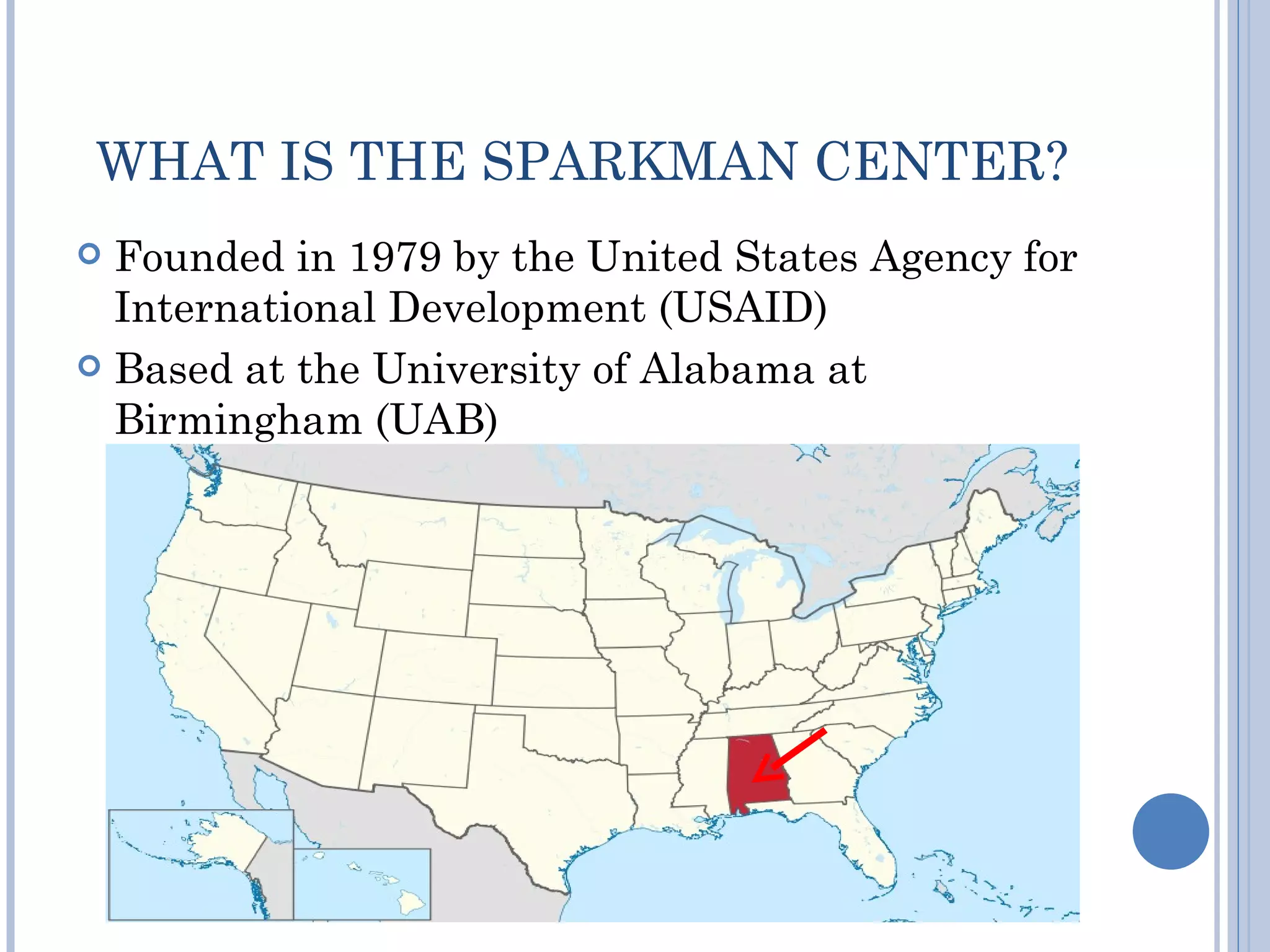
- The Sparkman Center has expanded health resources and supported installations across Zambia to increase access to materials.